Rhein-Nadel Automation GmbH 9
VT-BA-SCU1000-2000-EN_2019 / 27.06.2019 SJ
4. Notes on start-up
4.1. Modes of operation
RNA vibratory drive systems employ mechanical spring vibrators which are set to a vibrating frequency near the mains
frequency or near double mains frequency depending on weight and/or size.
This is why two modes of operation are possible:
Mode 1: Asymmetric half-wave mode:
The vibrating drive operates at mains frequency.
Mode 2: Symmetric full-wave mode:
The vibrating drive operates at double mains frequency.
To assist the operator the cable glands on the drive connector are colour-coded.
Mode 1: black
Mode 2: grey
In terms of the vibrating frequency this means:
Vibration frequency
50 Hz ≙ 3000 min
-1
Vibration frequency
60 Hz ≙ 3600 min
-1
Vibration frequency
100 Hz ≙ 6000 min
-1
Vibration frequency
120 Hz ≙ 7200 min
-1
4.2. Automatic mode change
Vibratory drive systems by RNA do not require the operator to take care of selecting the right operating mode. The op-
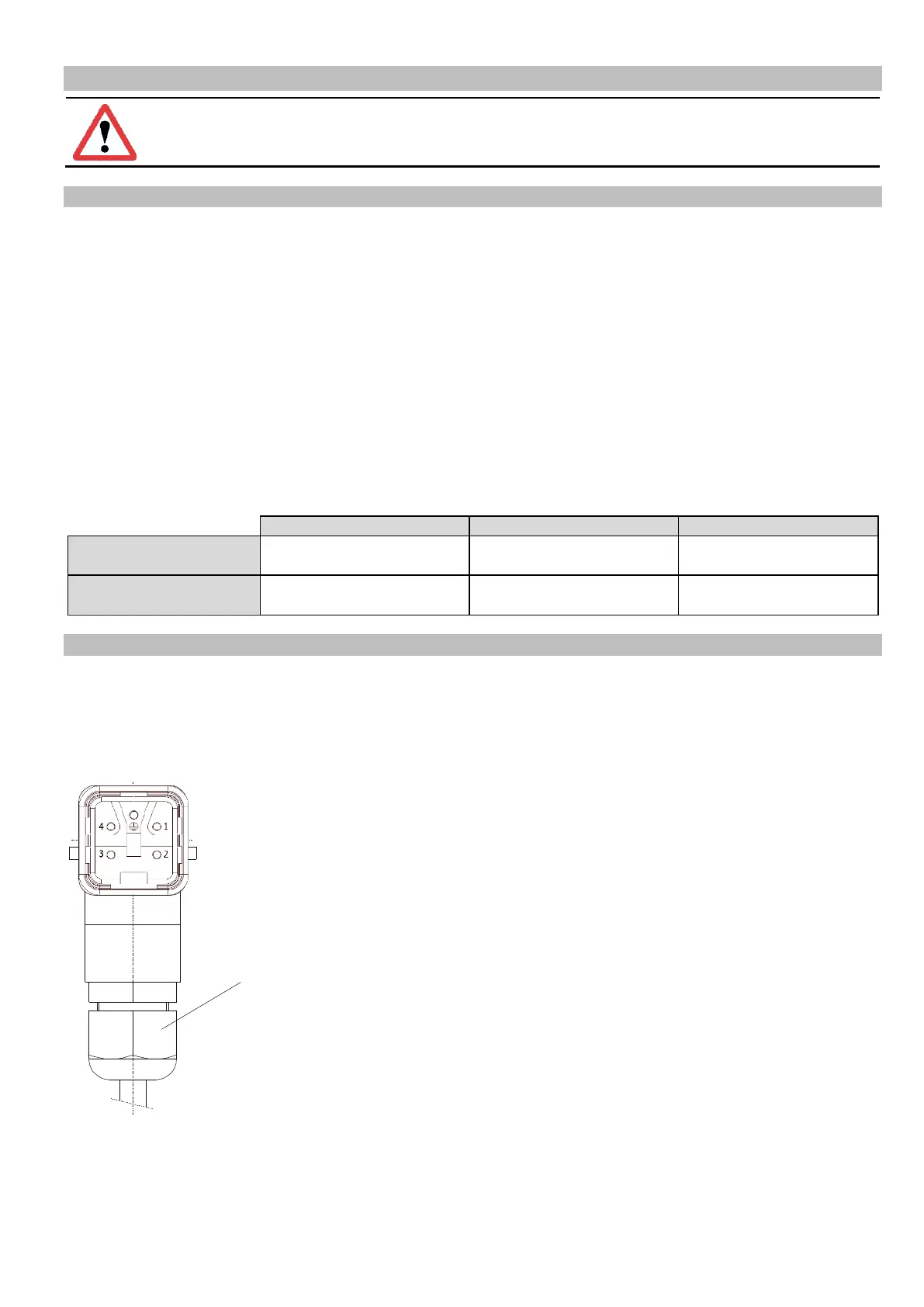
erating mode is determined by a code in the RNA vibrating drive connector. A wire jumper from pin 3 to 4 in the con-
nector switches the controller to mode 2: 100 or 120 Hz. In the absence of this wire jumper the controller operates in
mode 1: 50 or 60 Hz.
The RNA vibratory drive systems come with the right code in the connector.
Mode changes are made only and exclusively via the coding in the vibrating drive connector.
(Where frequency controllers with selectable output frequency are used, an EMC metal gland and a shielded cable are
provided.)
Attention!
Set the controller to minimum output before switching-on for commissioning or start-up after repairs or re-
placement of controllers/vibratory drives. Then watch proper operation while the output is increased.
M20 gland
Black: 50/60Hz vibrating frequency
Grey: 100/120Hz vibrating frequency
(EMC metal gland if frequency controllers are
used.)

 Loading...
Loading...