MAIN REG
SET
ALTERNATE
REG
SET
--
ACCUMULATOR
A
B
D
H
I
FLAGS
ACCUMULATOR
F
A'
c
B'
E
D'
L
H
INTERRUPT
I
MEMORY
VECTOR
REFRESH
I
R
INDEX REGISTER IX
INDEX REGISTER IY
STACK
POINTER SP
PROGRAM COUNTER PC
FLAGS
F'
c·
E'
L'
SPECIAL
PURPOSE
REGISTERS
Z-80A
CPU
REGISTER
CONFIGURATION
FIGURE
1.0-2
GENERAL
PURPOSE
REGISTERS
71
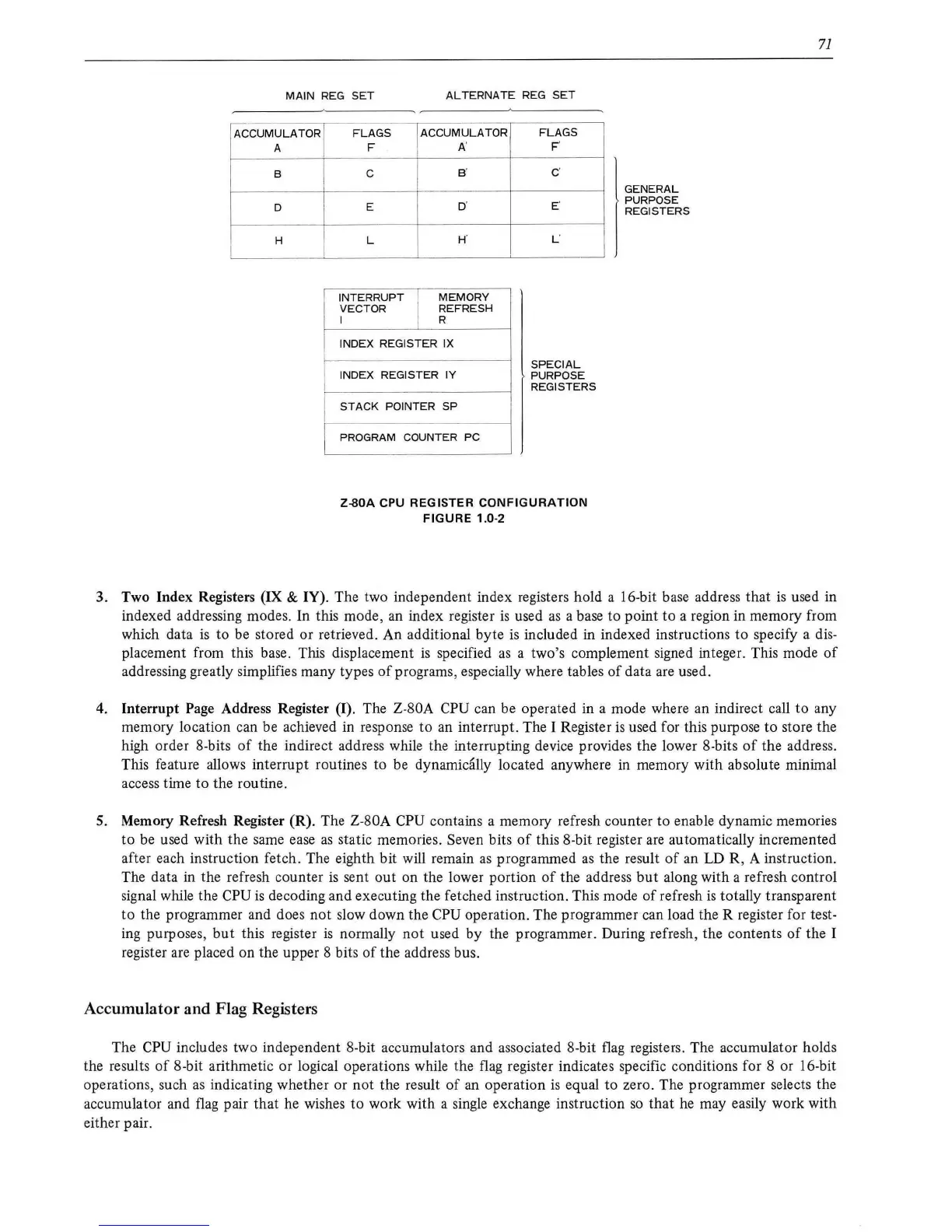
3. Two Index Registers
{IX
& IY). The two independent index registers hold a 16-bit base address that
is
used in
indexed addressing modes. In this mode, an index register
is
used
as
a base to point
to
a region in memory from
which data
is
to be stored or retrieved. An additional byte
is
included in indexed instructions
to
specify a
dis-
placement from this base. This displacement
is
specified
as
a two's complement signed integer. This mode
of
addressing greatly simplifies many types
of
programs, especially where tables
of
data are used.
4. Interrupt
Page Address Register {I). The Z-80A CPU can be operated in a mode where an indirect call
to
any
memory location can be achieved
in
response to an interrupt. The I Register
is
used for this purpose
to
store the
high order 8-bits
of
the indirect address while the interrupting device provides the lower 8-bits
of
the address.
This feature allows interrupt routines to be
dynamically located anywhere in memory with absolute minimal
access time
to
the routine.
5. Memory Refresh Register {R). The Z-80A
CPU
contains a memory refresh counter
to
enable dynamic memories
to be used with the same ease
as
static memories. Seven bits
of
this 8-bit register
are
automatically incremented
after each instruction fetch. The eighth bit will remain
as
programmed
as
the result
of
an LD R, A instruction.
The data in the refresh counter
is
sent
out
on the lower portion
of
the address
but
along with a refresh control
signal while the
CPU
is
decoding and executing the fetched instruction. This mode
of
refresh
is
totally transparent
to
the programmer and does
not
slow down the CPU operation. The programmer can load the R register for test-
ing purposes,
but
this register
is
normally
not
used by the programmer. During refresh, the contents
of
the I
register are placed on the upper 8 bits
of
the address bus.
Accumulator and Flag Registers
The CPU includes two independent 8-bit accumulators and associated 8-bit
flag
registers. The accumulator holds
the results
of
8-bit arithmetic or logical operations while the
flag
register indicates specific conditions for 8 or 16-bit
operations, such
as
indicating whether or not the result
of
an
operation
is
equal
to
zero. The programmer selects the
accumulator and
flag
pair that he wishes
to
work with a single exchange instruction
so
that he may easily work with
either pair.
 Loading...
Loading...