6 Using the product
28
that the surface temperature can be easily measured using
infrared.
Because of their low or non-uniform emissivity, bright metals
and metal oxides are only somewhat suited for infrared
measurement. You must anticipate highly inaccurate
measurements. A remedy for this is coatings that increase the
emissivity, e.g. paint or emission adhesive (art. no. 0554 0051)
which must be applied to the object being measured.
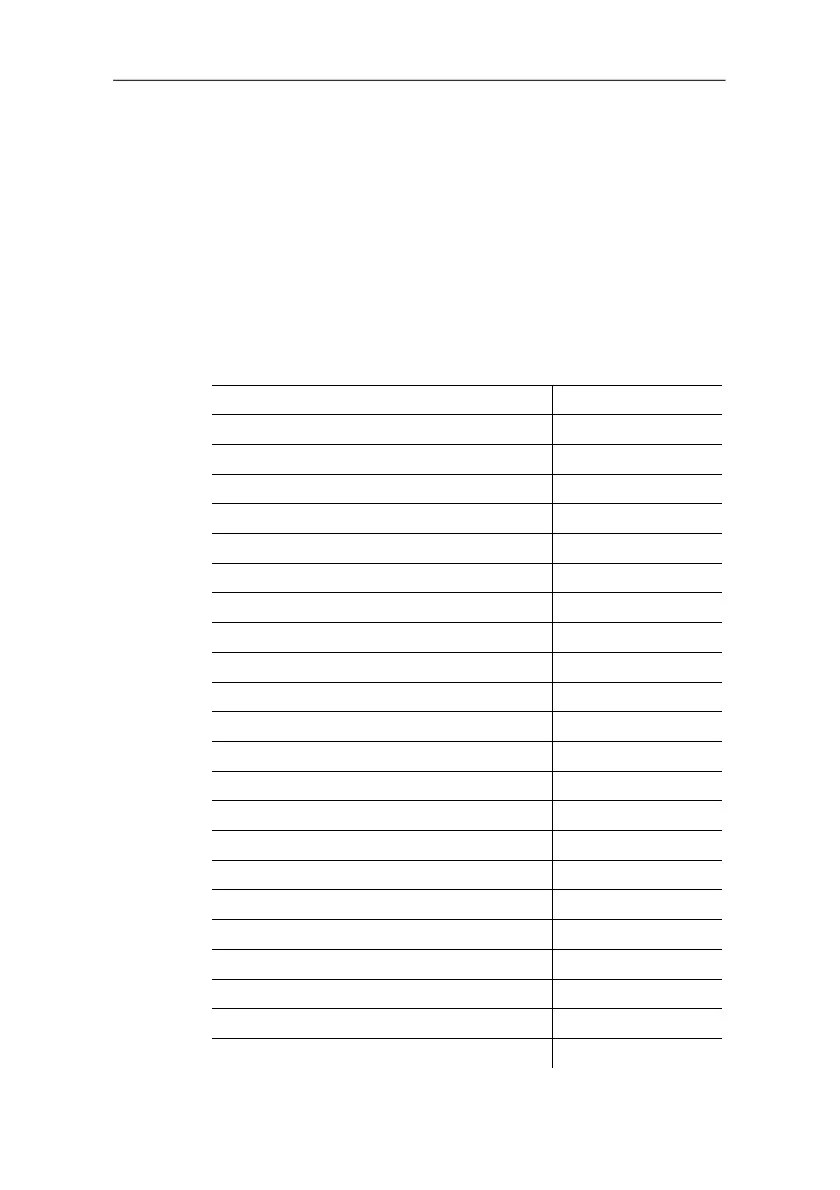
The following table gives typical emissivities of important
materials. These values can be used as orientation with the
user-defined settings.
Material (material temperature) Emissivity
Aluminium, bright rolled (170 °C) 0.04
Cotton (20 °C) 0.77
Concrete (25 °C) 0.93
Ice, smooth (0 °C) 0.97
Iron, emery ground (20 °C) 0.24
Iron with casting skin (100 °C) 0.80
Iron with rolling skin (20 °C) 0.77
Gypsum (20 °C) 0.90
Glass (90 °C) 0.94
Rubber, hard (23 °C) 0.94
Rubber, soft grey (23 °C) 0.89
Wood (70 °C) 0.94
Cork (20 °C) 0.70
Radiator, black anodised (50 °C) 0.98
Copper, slightly tarnished (20 °C) 0.04
Copper, oxidised (130 °C) 0.76
Plastics: PE, PP, PVC (20 °C) 0.94
Brass, oxidised (200 °C) 0.61
Paper (20 °C) 0.97
Porcelain (20 °C) 0.92
Black paint, matt (80 °C) 0.97
Steel, heat-treated surface (200 °C) 0.52
 Loading...
Loading...