InGaAs Amplified Detector Chapter 4: Operation
Rev F, July 15, 2017 Page 5
4.3. Dark Current
Dark current is leakage current which flows when a bias voltage is applied to a
photodiode. The PDA with Transimpedance Amplifier does control the dark
current flowing out. Looking at the figure above, it can be noted that Point B is
held at ground and the amplifier will try to hold point A to “Virtual Ground”. This
minimizes the effects of dark current present in the system.
The dark current present is also affected by the photodiode material and the size
of the active area. Silicon devices generally produce low dark current compared
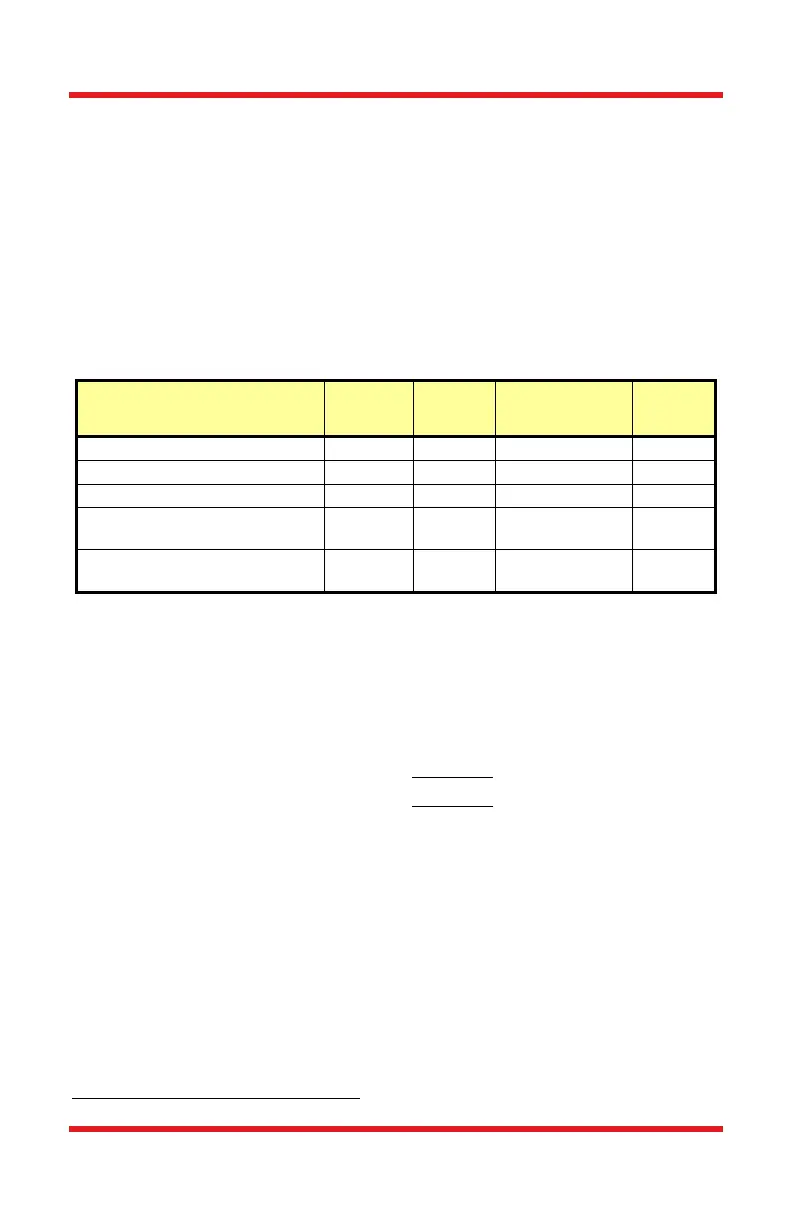
to germanium devices which have high dark currents. The table below lists
several photodiode materials and their relative dark currents, speeds, sensitivity,
and costs.
Material
Dark
Current
Speed
Sensitivity
1
(nm)
Cost
Silicon (Si) Low High 400 – 1000 Low
Germanium (Ge) High Low 900 – 1600 Low
Gallium Phosphide (GaP) Low High 150 – 550 Med
Indium Gallium Arsenide
(InGaAs)
Low High 800 – 1800 Med
Extended Range: Indium
Gallium Arsenide (InGaAs)
High High 1200 – 2600 High
4.4. Bandwidth and Response
A load resistor will react with the photodetector junction capacitance to limit the
bandwidth. For best frequency response, a 50 terminator should be used in
conjunction with a 50 coaxial cable. The gain of the detector is dependent on
the feedback element (R
F
). The bandwidth of the detector can be calculated
using the following:
3
4
Where GBP is the amplifier gain bandwidth product and C
D
is the sum of the
photodiode junction capacitance and the amplifier capacitance.
1
Approximate values, actual wavelength values will vary from unit to unit
 Loading...
Loading...