Compact Stabilized Light Sources Chapter 3: Product Overview
Rev F, October 14, 2021 Page 3
Chapter 3 Product Overview
3.1. Planck's Law and Black Body Radiation
A black body is an object that absorbs all incident electromagnetic radiation (e.g.
light), no light passes through or is reflected. However, despite the name, a black
body will also emit electromagnetic radiation. The radiation of a black body in
thermal equilibrium is described by Planck’s Law
(, ) =
2
1
1
Where
I
is the radiated power per unit area of emitting surface per unit wavelength
at temperature
T
;
K
is the Boltzmann constant,
h
is the Planck constant, and
c
is
the speed of light.
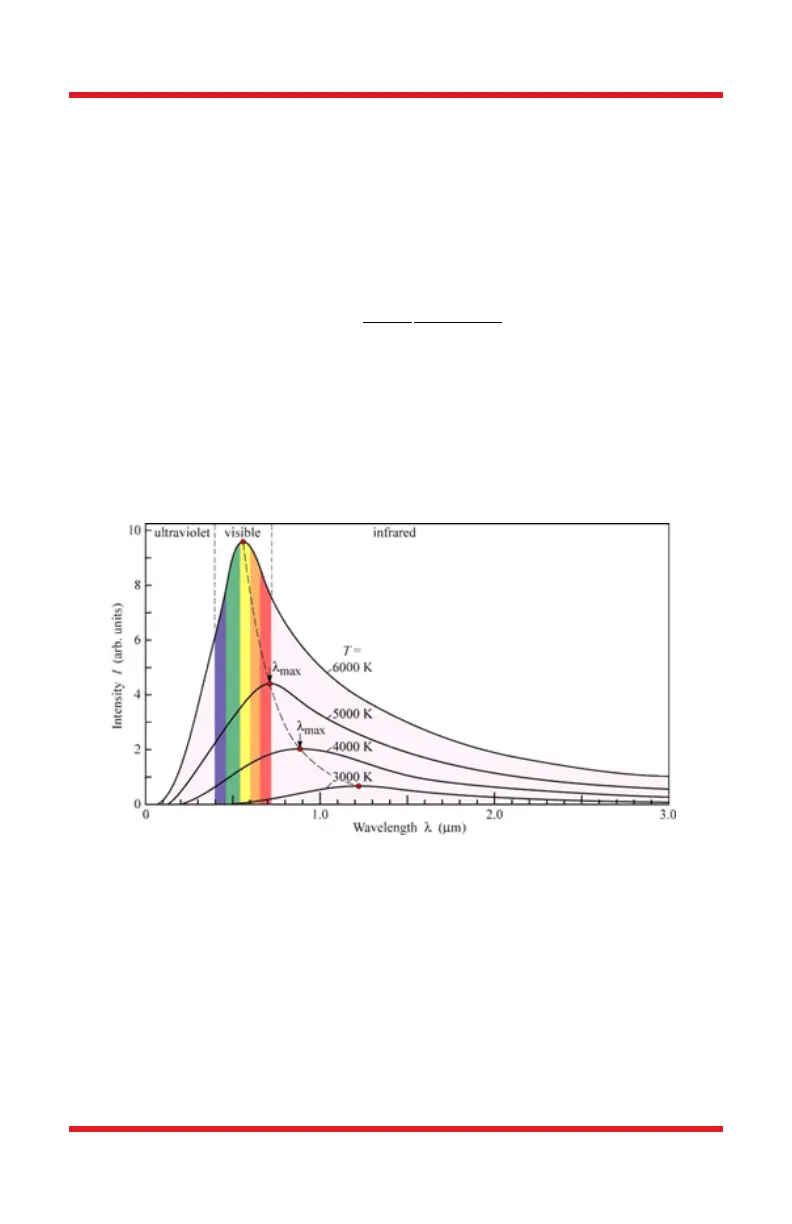
By measuring the spectrum of the black body radiation, we can calculate the
temperature of this black body. Figure.1 shows the radiated power per unit area I
as a function of wavelength at various temperature.
Figure 1 Black body radiation at different temperatures
In real life, broadband light sources may vary widely from the ideal black body in
terms of the frequency and intensity of the light emitted. By comparing the light
source to an ideal black body at a given temperature, one can characterize the
light source by the temperature of the black body radiator which has the same
chromaticity, which is known as the color temperature of the light source

 Loading...
Loading...