ESA - Functions
of Engine EC
U
STARTING IGNITION CONTRO
L
Starting ignition control is carried out once
immediately after input of the NE signal
following the
G(G1 or G2) signal
. This ignition
timing is called "initial ignition timing angle"
.
For further
details, see page 83
.
During sta
rt
ing, when the engine speed is still
below a specified rpm (usually around 500 rpm),
since the intake manifold pressure
(
PIM) signal
or the intake air volume (VS, KS or VG) signal is
unstable, the ignition timing is fixed at the initial ig-
nition timing (which differs depending on the
engine model)
. This initial ignition timing is set
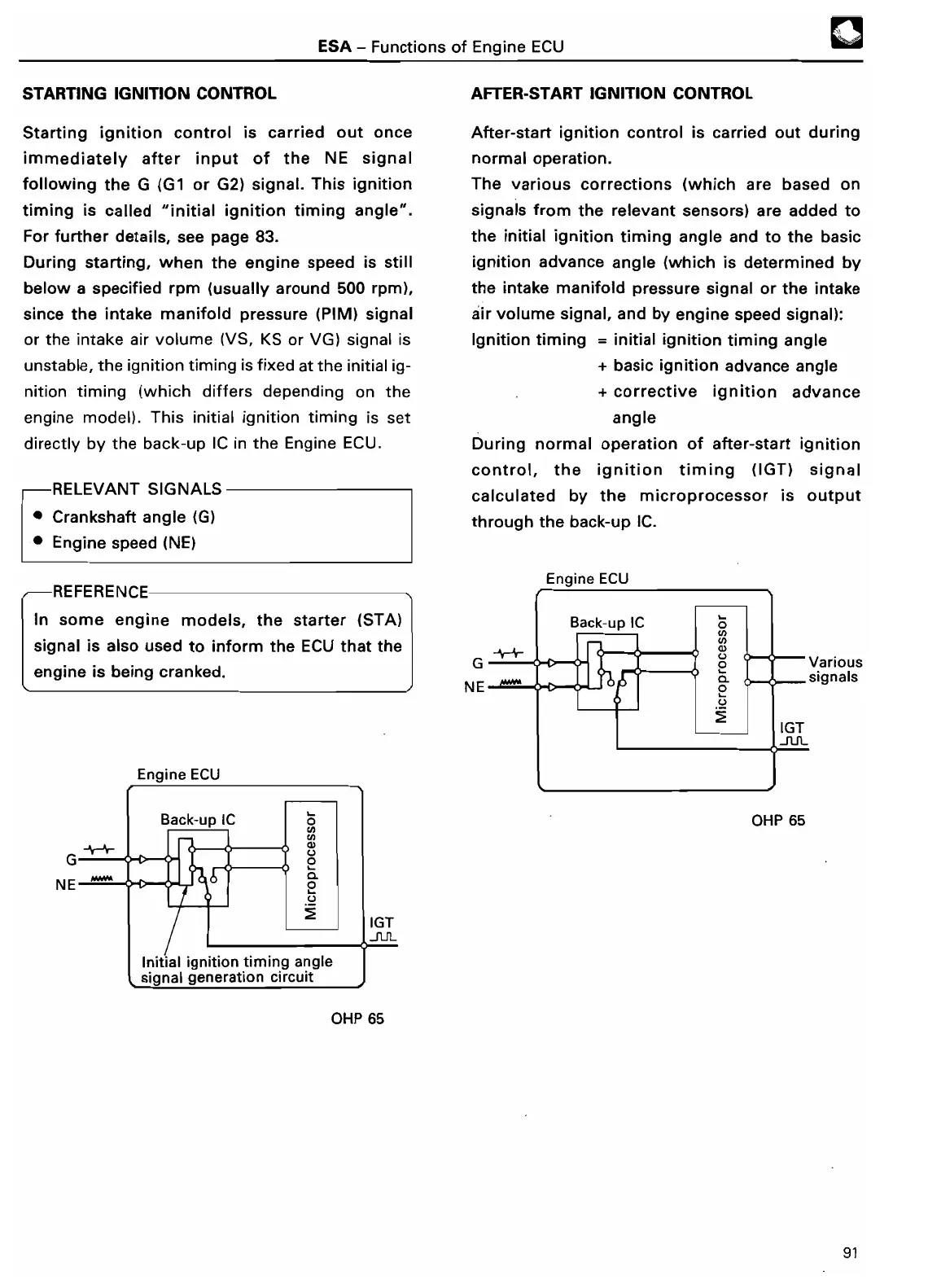
directly by the back-up IC in the Engine ECU
.
F
RELEVANT SIGNALS
Crankshaft angle (G)
Engine speed (NE
)
REFERENCE
In some engine models,
the starter (STA)
signal is also used
to inform the ECU that the
engine is being cranked
.
Engine EC
U
NE
'""""
Initial ignition timing angl
e
l signal generation
circuit
11
AFTER-START IGNITION CONTRO
L
After-start ignition control is carried out during
normal operation
.
The various corrections (which are based on
signals from the relevant sensors) are added to
the initial ignition timing angle and to the basic
ignition advance angle (which is determined by
the intake manifold pressure signal or the intake
air volume signal, and by engine speed signal)
:
Ignition timing = initial ignition timing angle
+ basic ignition advance angl
e
+ corrective ignition advance
angl
e
During normal operation of after-start ignition
control, the ignition timing (IGT) signal
calculated by the microprocessor is output
through the back-up IC
.
Engine ECU
OHP 65
IG
T
JU
L
OHP 65
91
 Loading...
Loading...