EFI - Functions
of Engine EC
U
AIR-FUEL RATIO FEEDBACK CORRECTIO
N
a
. Oxygen Senso
r
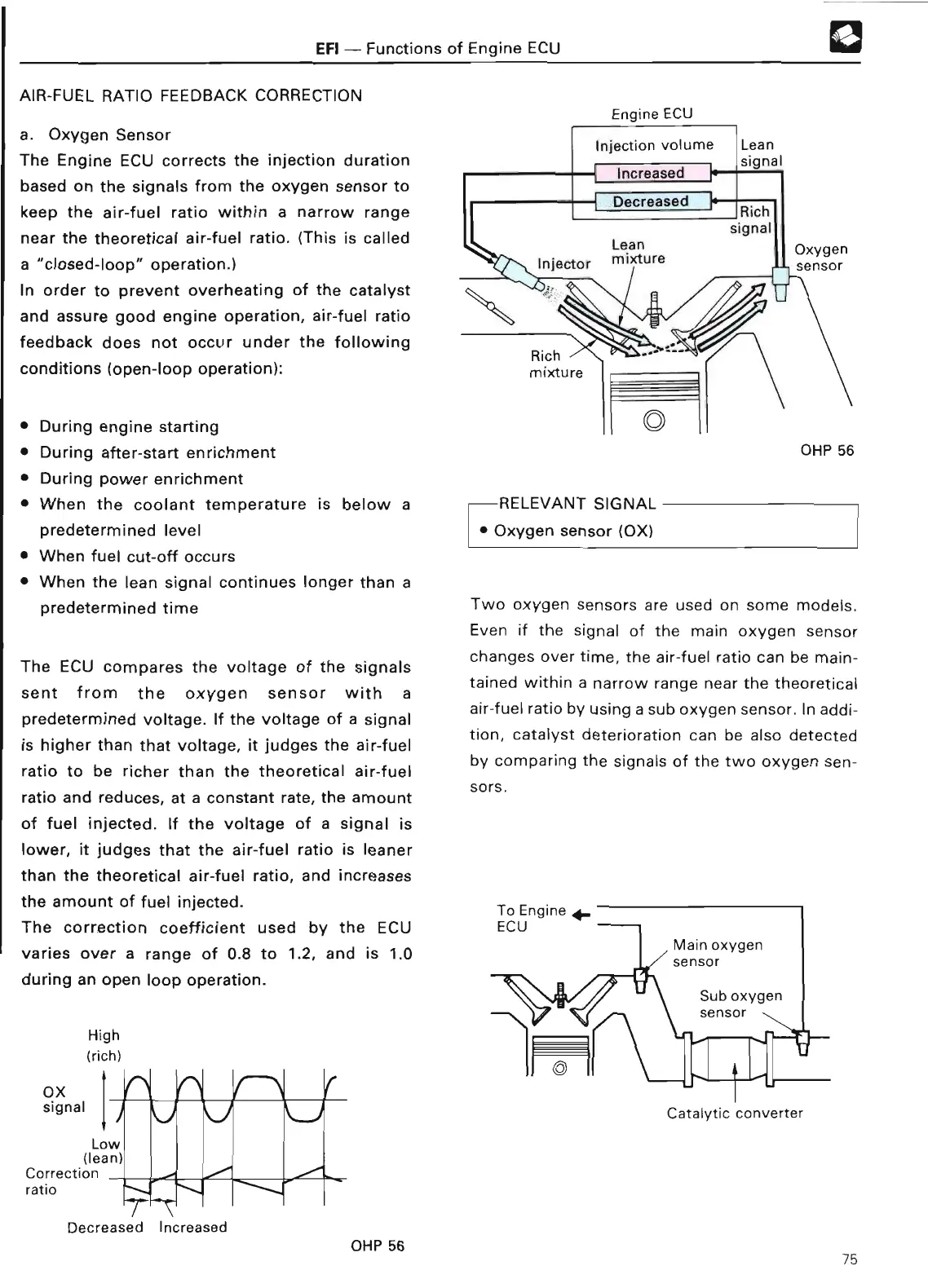
The Engine ECU corrects the injection duration
based on the signals from the oxygen sensor to
keep the air-fuel ratio within a narrow range
near the theoretical air-fuel ratio
. (This is called
a "closed-loop" operation
.
)
In order to prevent overheating of the catalyst
and assure good engine operation, air-fuel ratio
feedback does not occur under the following
conditions (open-loop operation)
:
• During engine sta
rt
in
g
• During after-start enrichment
• During power enrichmen
t
• When the coolant temperature is below a
predetermined leve
l
• When fuel cut-off occur
s
• When the lean signal continues longer than a
predetermined tim
e
The ECU compares the voltage of the signals
sent from the oxygen sensor with a
predetermined voltage
. If the voltage of a signal
is higher than that voltage, it judges the air-fuel
ratio to be richer than the theoretical air-fuel
ratio and reduces, at a constant rate, the amount
of fuel injected
. If the voltage of a signal is
lower, it judges that the air-fuel ratio is leaner
than the theoretical air-fuel ratio, and increases
the amount of fuel injected
.
The correction coefficient used by the ECU
varies over a range of 0
.8 to 1
.2, and is 1
.0
during an open loop operation
.
High
(rich)
RELEVANT SIGNAL
~Oxygen
sensor (OX)
OHP 5
6
Two oxygen sensors are used on some models
.
Even if the signal of the main oxygen sensor
changes over time, the air-fuel ratio can be main-
tained within a narrow range near the theoretical
air-fuel ratio by using a sub oxygen sensor
. In addi-
tion, catalyst deterioration can be also detected
by comparing the signals of the two oxygen sen-
sors
.
Catalytic converte
r
Decreased Increased
OHP 56
Engine ECU
75
 Loading...
Loading...