4
Chapter 3: Theory of Operation
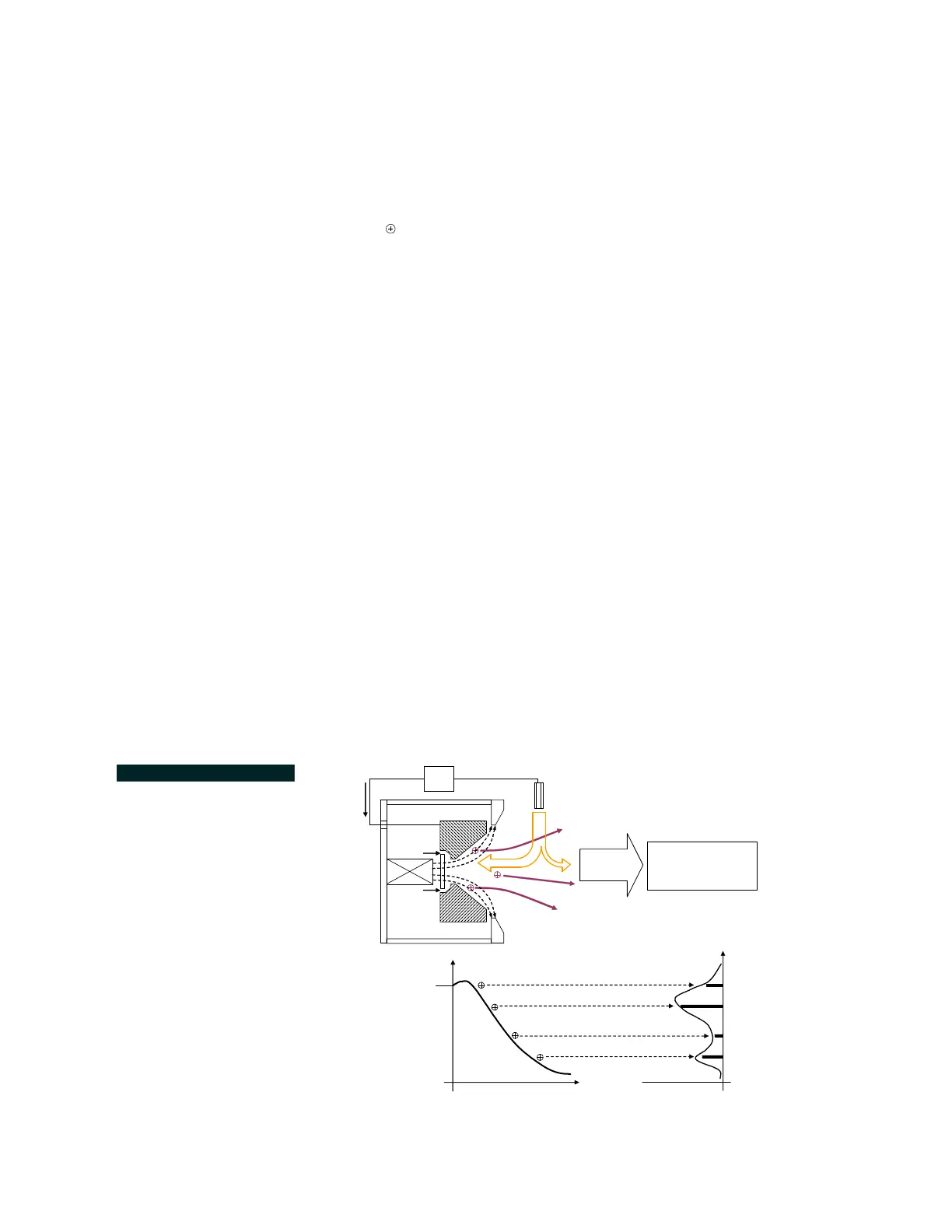
The Mark series gridless ion source operates by producing a low pres-
sure gas discharge or plasma (typically 0.13 to 1.33x10
-1
Pa/0.1 to 1.0
x10
-3
Torr) near a cusped magnetic field that lies between an electron
emitter (either a filament or a hollow cathode) and an angled anode. FIG-
URE 3.1 illustrates this ion source’s basic operating principles. A DC
magnetic field is formed by a permanent magnet and the source’s open-
ended magnetic stainless steel shell. Primary electrons, emitted from the
cathode, are drawn to the cone-shaped anode by means of an applied DC
potential, through which a working gas is injected. The accelerated elec-
trons strike and ionize the input gas’s neutral atoms or molecules to form
a gas discharge or plasma. As the electrons drift toward the anode, the
magnetic field impedes their mobility or flow. This resistance to electron
flow results in a space charge (or potential field) within the plasma near
the anode. It is this spatially varying potential field that ultimately acceler-
ates ions away from the source anode (both axially and radially), to form
the source's gridless ion beam. Since ions can be produced at various
locations along the plasma space-charge, the output beam current’s
energy distribution and angular spread is broadly distributed. The mean
ion beam current energy is typically 60 to 80% of the anode potential.
In
the absence of electrostatic grids to separate electrons from ions, a near
equal number of electrons in the plasma are electrostatically drawn along
with the ions, essentially neutralizing the ion beam. It is often necessary
for many applications to inject additional electrons from the cathode into
the ion beam; this further enhances neutralization and decreases positive
charging of electrically isolated surfaces or work-pieces.
FIGURE 3.1 Schematic Dia-
gram of Ion Source Opera-
tion.
I
A
e
-
V
A
Energy (eV)
Ion Current Energy
Distribution
Electron
Source
(Cathode)
Anode
Mean ion current
energy, <E
B
>, is about
60-80% of V
A
Neutralized
Ion Beam
Input
Gas
S
S
Relative Distance from Anode
Discharge
Space
Potential
Typical operating vacuum
pressure: 0.1-1 mTorr
NS
Ion Source Shell
V
A
+

 Loading...
Loading...