DSLC Digital Synchronizer and Load Control Manual 02007
64 Woodward
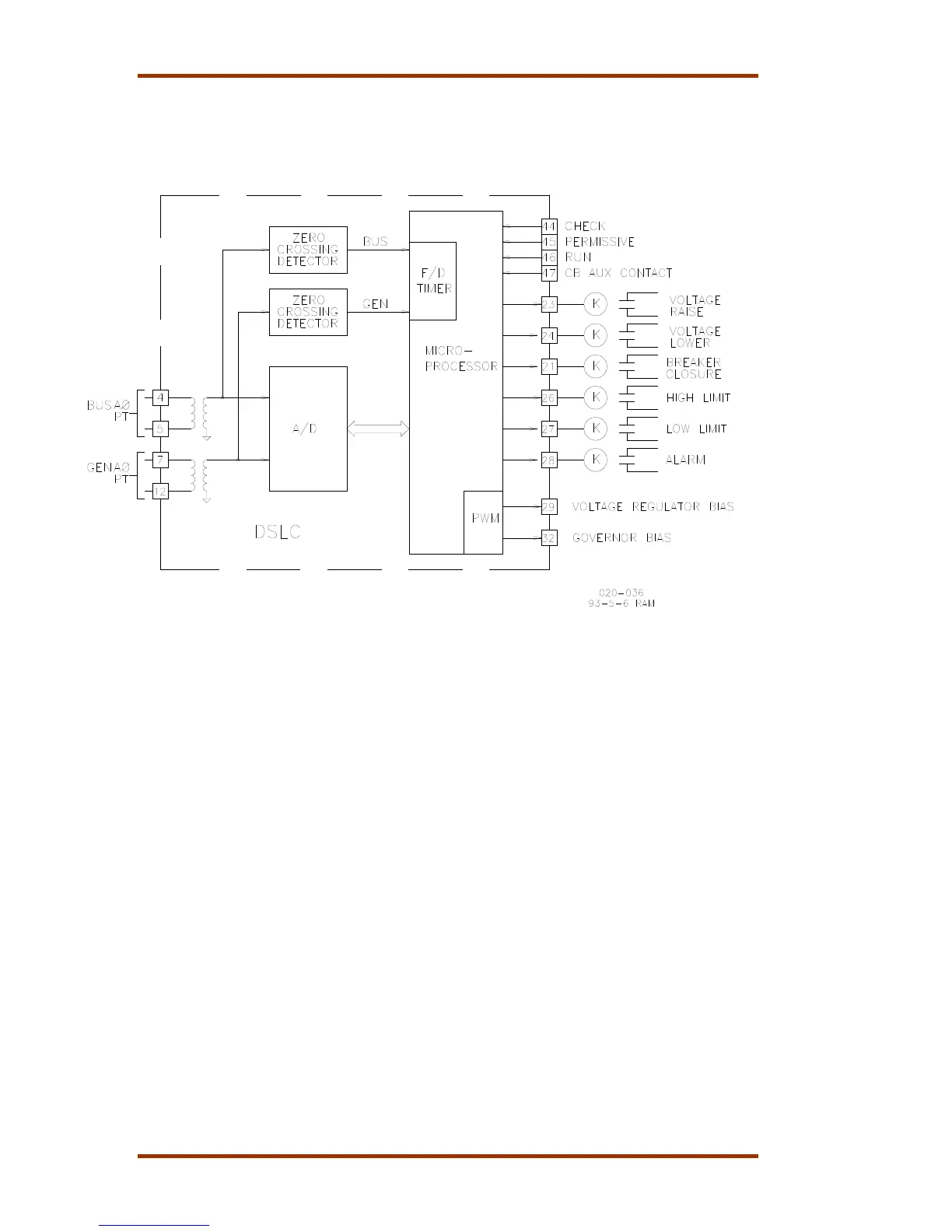
The voltage matching circuits of the synchronizer function in the DSLC control are
shown in Figure 4-3. The voltages proportional to the generator A phase and bus A
phase are input to the sample and hold circuits of the A/D (analog-to-digital)
converter where they held until actually read by the A/D converter. This process is
repeated for the desired number of samples and cycles of the ac input wave forms.
Figure 4-3. Synchronizer Block Schematic
The microprocessor then computes the RMS values of the voltages. The
processor issues appropriate raise or lower commands to the voltage regulator
MOP, or adjustment of the voltage bias signal if used, to the voltage regulator to
bring the generator voltage within the specified window above the bus voltage.
To guarantee that reactive power will be generated, window range is from equal
to bus voltage to the specified percentage above bus voltage.
The automatic voltage matching function may be enabled or disabled with a set
point. When enabled, voltage matching will occur in both the Check and Run
modes and is verified only by the sync-check function in Permissive mode.
Phase Matching Synchronizing
The phase matching synchronizing mode corrects the frequency and phase of
the generator to lock it to the bus frequency and phase. Phase matching
synchronizing is automatically selected when the slip frequency reference set
point is set to zero. The microprocessor uses signal processing techniques to
derive the difference in phase of the generator A and bus A phase voltage
signals. When there is a difference, the synchronizer sends a correction signal to
the speed control. The correction signal from the speed bias output increases or
decreases engine speed depending on whether the slip is faster or slower than
the bus. A PI (proportional, integral) controller provides the correction signal.
Gain and Stability adjustments to the PI controller are provided to allow stable
operation of the automatic synchronizer function over a wide range of system
dynamics.

 Loading...
Loading...











