2.2 Real-time averaging mode (AVG option)
Acqiris SA240P User's Manual 23
Single accumulation of N records
Multi-record mode: possibility to perform successive accumulations of N record each. The trig-
ger re-arm time between sequences is ~ 100 ns.
Streaming: combined with the averaging mode (AVG), the CSToption allows to readout pre-
viously averaged record while performing a new accumulation. This mode enables multiples
and successive averaging sequences without missing any trigger. See Averager with sim-
ultaneous acquisition and readout (AVG & CST) (page 41).
User can define a post-trigger delay. The pre-trigger delay is not supported in averager mode.
The number of potential trigger lost between two acquisitions (single or multi-records) depends on
several factors:
The read time of the previous averaging sequence, depending on the number of samples to
transfer and mainly on the PCIe connection and CPU multitasking activity.
The time to initiate the next acquisition.
The function simultaneous acquisition and readout (CST) can be combined with the averager mode,
removing the above limitation and reducing the time between averaging sequences. See Averager
with simultaneous acquisition and readout (AVG & CST) (page 41).
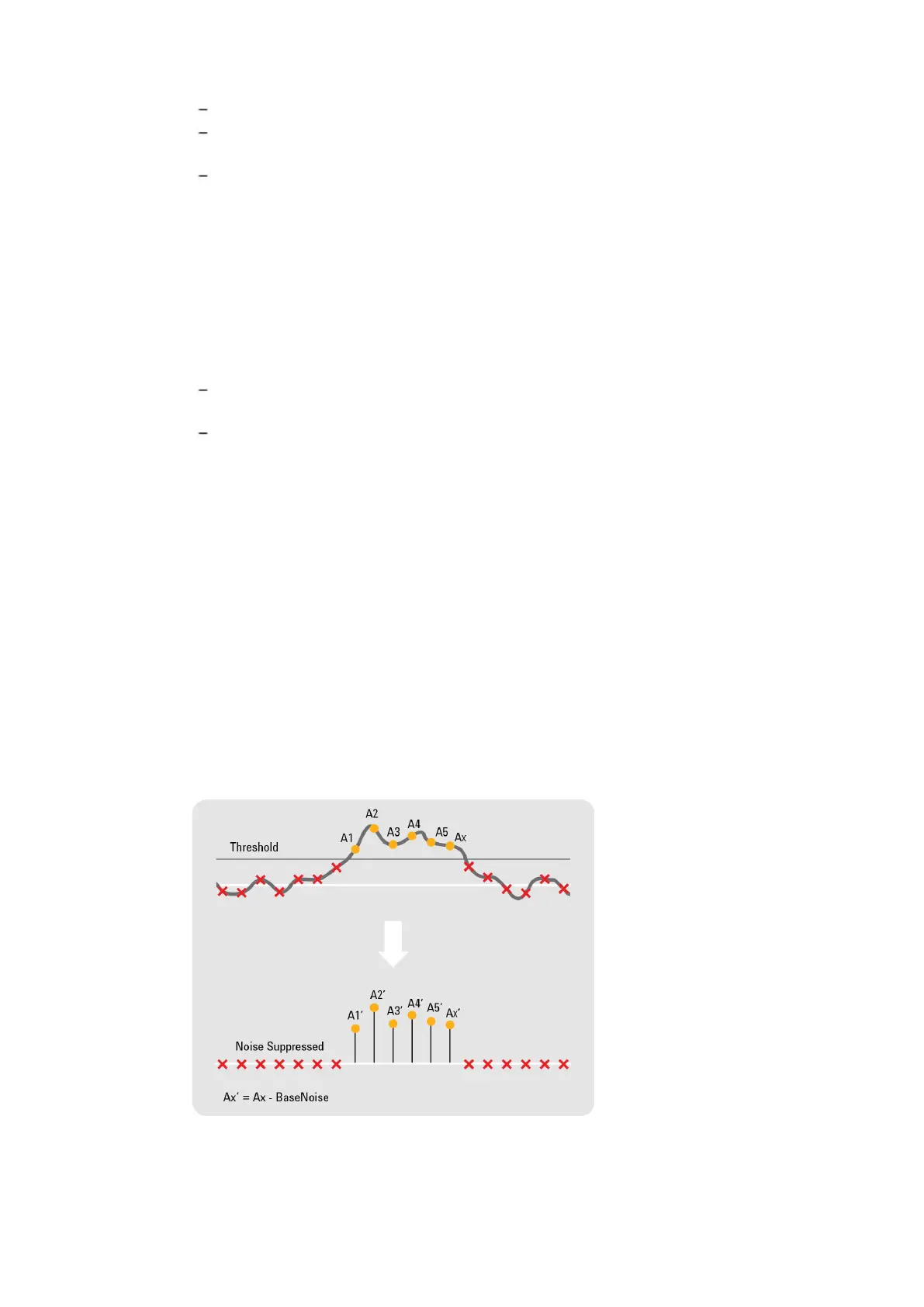
Noise suppressed accumulation (NSA)
In some applications, such as time-of-flight spectrometry, the signal is a rare event sitting on top of a
noisy baseline and the averaging process reduces the random noise.
As a consequence, to enhance the acquisition card ability to detect such signals in the presence of
synchronous noise, the averaging firmware allows the user to set a Threshold that must be
exceeded for each data value to be entered into the sum. Furthermore, the noise base can be
subtracted from each data value above threshold before the accumulation is done (See Figure
below). The noise base should always be equal or smaller than the threshold.
Figure 2.5 - Signal detection using noise suppressed accumulation.
 Loading...
Loading...