2-46
Testing Sensors
Section
2
What is It
and
How is It
Used?
— The computer needs to know rotational speed (or
position) of the engine crankshaft/camshaft for controlling
ignition and fuel injector systems. If the computer is
handling a Distributorless (or Direct) ignition system or
controlling the operation of individual fuel injectors, it also
needs to know when cylinder #1 is active. The sensors have
various names such as:
Crankshaft Position, Crank Angle,
Flywheel, Distributor Pick-Up, Camshaft Position, Cylinder,
TDC and RPM.
— Similar sensors are used in anti-lock brake and electroni-
cally shifted transmission systems. These sensors have
names such as:
Wheel Speed, Vehicle Speed and
Driveshaft.
— The sensors come many styles using different connectors.
Sometimes an assembly contains more than one sensor.
Other versions combine two functions into a single sensor
(usually camshaft position and cylinder #1 identification).
— The most common sensor types are
Magnetic Reluc-
tance
and
Hall Effect.
These are described below along with
Optical
types which are in limited use.
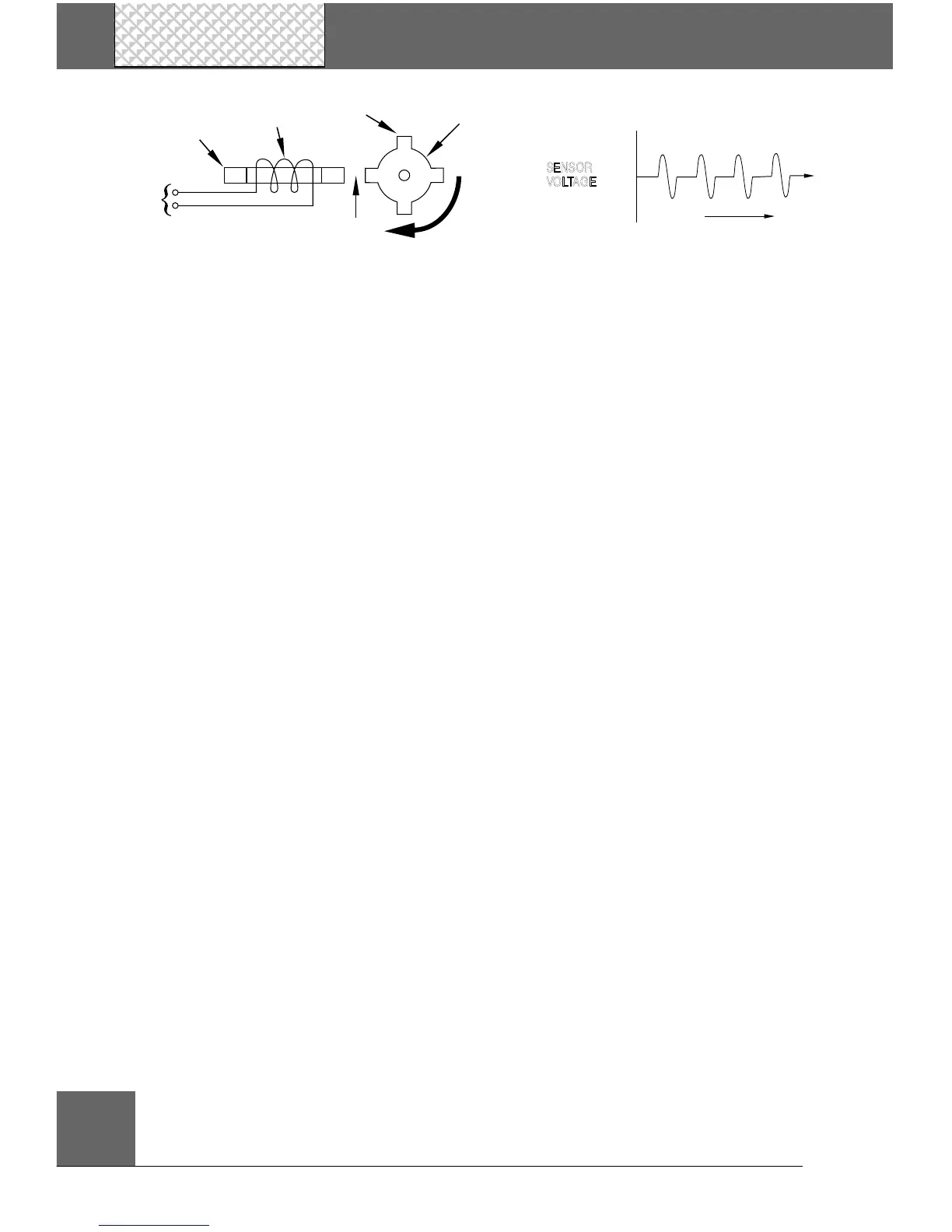
The basic reluctance sensor consists of a permanent
magnet with a coil of wire wrapped around it. Nearby the
sensor is a toothed ring made of iron or steel (sometimes
called a “reluctor”). The ring is attached to a rotating
component such as the crankshaft or camshaft. Whenever
a tooth from the ring passes by the sensor, it attracts the
magnetic field lines surrounding the magnet. As the field
lines move, they pass through the wire coil and generate a
small voltage pulse (magnetic induction principle). Thus a
voltage pulse is generated every time a tooth passes by
the sensor coil.
• Magnetic
Reluctance
Rotation
Reluctor Ring
Tooth
Wire Coil
Magnet
To
Computer
Air Gap
NS
Crankshaft/Camshaft Position sensors
Reluctance Sensor Operation
Typical Sensor Signal Voltage
ROTATION
Positive
Negative
Zero
SENSOR
VOLTAGE
 Loading...
Loading...