20
q accuracy is given as:
±[(180/p) x (A
e
/100)] (absolute degrees)
Note: 1. A
e
= (A
n
+ B)
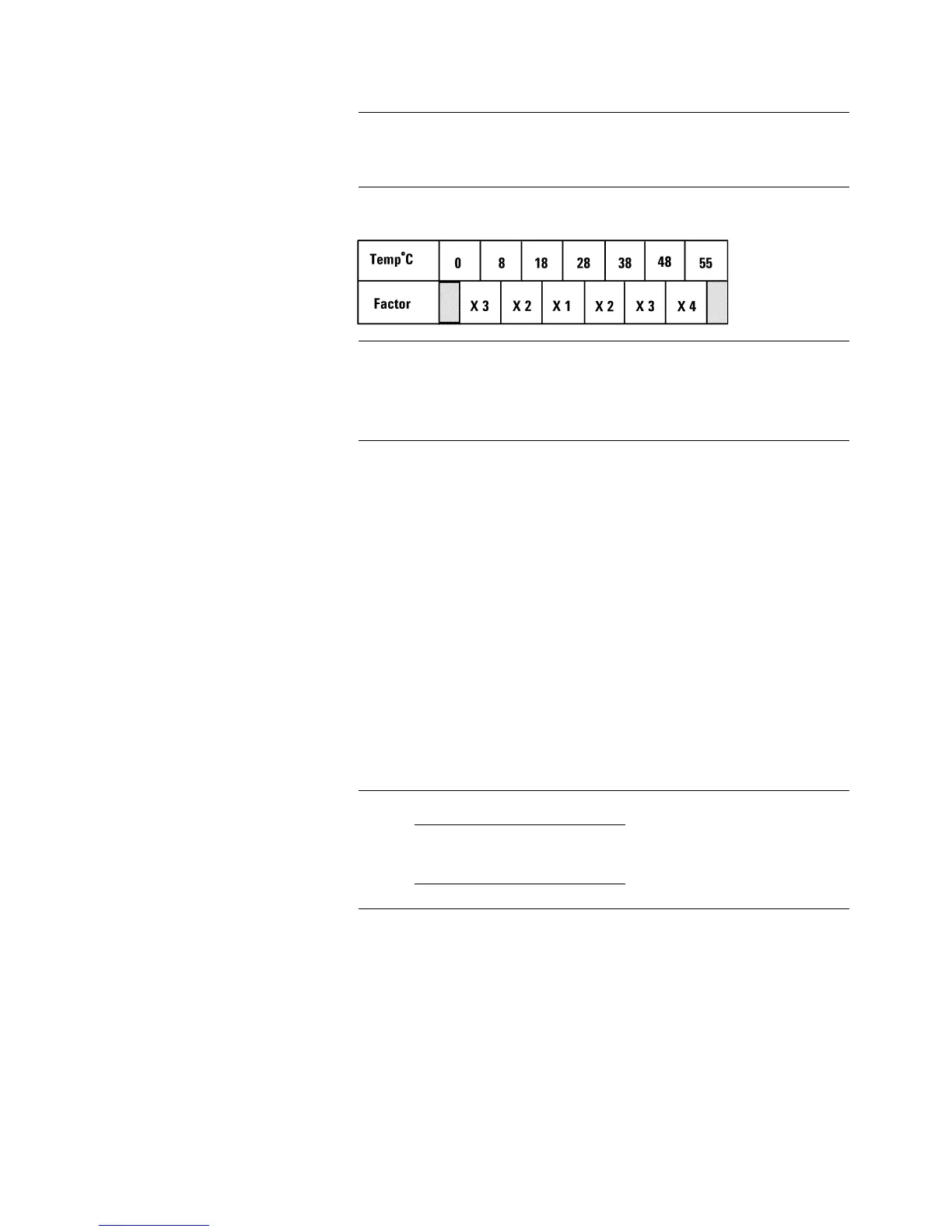
Additional error due to temperature:
Multiply the measurement accuracy by the following temperature factors.
Example L and Q accuracy calculation
Measurement conditions:
Frequency: 500 kHz L value measured: 2 mH
Test signal level: 1 Vrms Integration time: Long
Cable length: 0 meters Q value measured (Qx): 200
Calculation:
Step 1: Use Figure 2 to determine A
n
and Z
m
.
a. Find the frequency along the X-axis.
b. Find the inductance value along a diagonal.
c. Note the intersection of steps a and b.
In this case A
n
= A
5
. Refer to the equations in Table 3.
d. Note that in step c Z
m
is 6.3 kΩ.
Step 2: Use Tables 3 and 4 to determine A
n
and B.
a. A
n
is equation A
5
for long integration times:
0.18% + [(|Z
m
|/5 k) x 0.02%]
b. A
5
yields a value of 0.21%
c. Table 4 indicates that B has a value of 0.
(@ cable length = 0 m)
d. L accuracy is ±(A
n
+ B) = 0.21%
e. Determine D accuracy (D
e
): (A
n
+ B)/100 = 0.0021
f. Q accuracy: (∆Q)
±[(Q
x
2
x D
e
)/(1 ] (Q
x
x D
e
)]
g. ∆Q yields a value of –57 to 133, Actual Q: 143 to 333
N
1
, N
2
and N
3
are in Table 3.
Table 4. Cable length correction
Test cable length B (%)
0 meter 0
1 meter (16048A) f
m
/15
2 meter (16048D) f
m
/15
(f
m
: test frequency in MHz)
Specifications continued on page 21
Specifications
Continued from page 19
 Loading...
Loading...











