3 - Installation
24
Voltage Drops
The load wires must also be large enough to avoid excessive voltage drops due to the impedance of the
wires. In general, if the wires are heavy enough to carry the maximum short circuit current without
overheating, excessive voltage drops will not be a problem. The voltage drops across the load wires
should be limited to less than two volts. Refer to Table 3-2 to calculate the voltage drop for some
commonly used AWG copper wire.
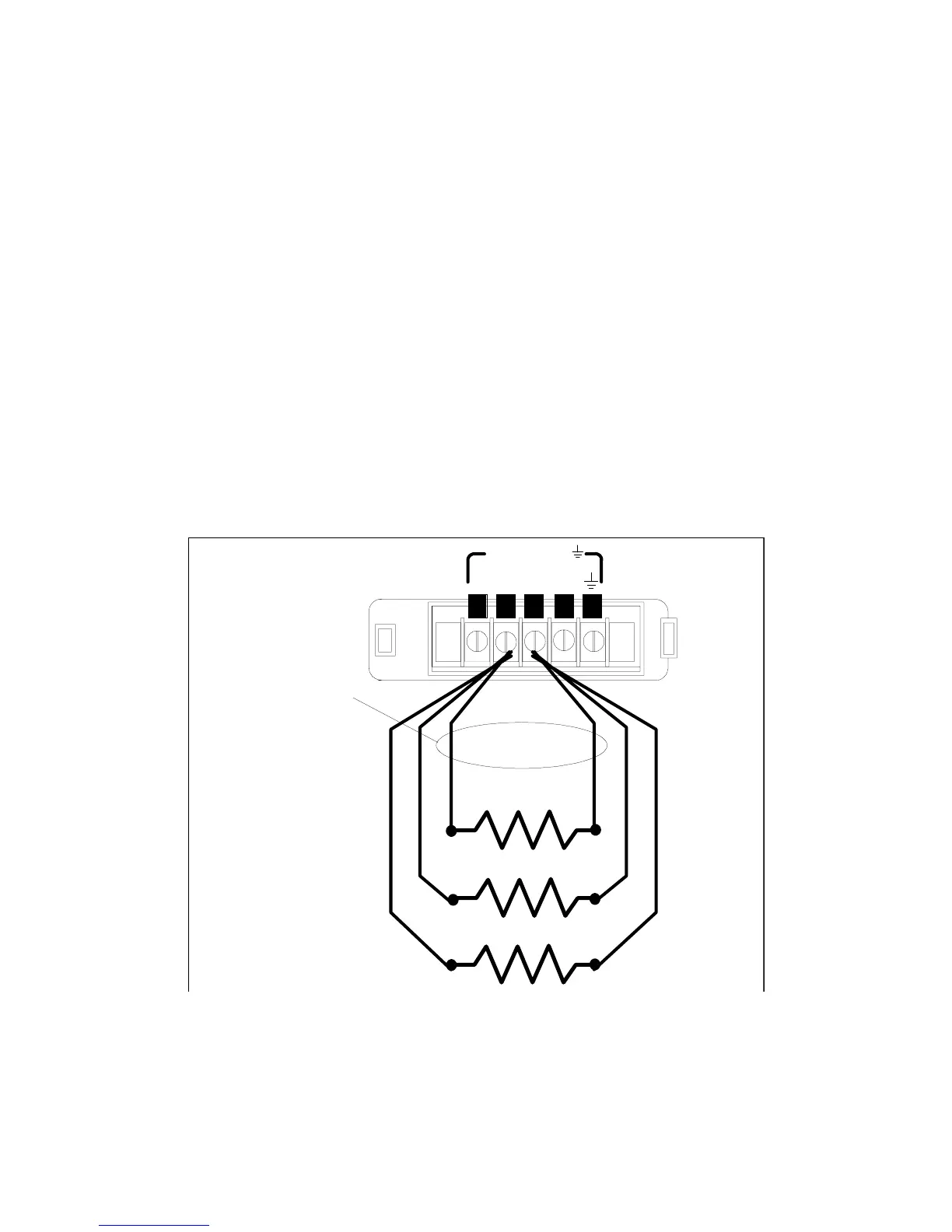
Multiple Load Connections
When the unit is in local sensing mode and you are connecting multiple loads to the output, connect each
load to the output terminals using separate load leads. This minimizes mutual coupling effects and takes
full advantage of the dc source’s low output impedance. Each pair of wires should be as short as possible
and twisted or bundled to reduce lead inductance and noise pickup.
If cabling considerations require the use of distribution terminals that are located remotely from the dc
source, connect the dc source’s output terminals to the remote distribution terminals by a pair of twisted
or bundled wires. Connect each load to the distribution terminals separately. Remote voltage sensing is
recommended under these circumstances. Sense either at the remote distribution terminals, or if one load
is more sensitive than the others, sense directly at the critical load.
+S
+
-
-S
+ 240 VDC MAX TO
-
LOAD 3
LOAD 2
LOAD 1
twist or bundle
each pair
Figure 3-2. Multiple Load Connections

 Loading...
Loading...











