38
12. Finding average dispersion value and Abbe number
2. Finding average dispersion
value
Dispersion value (nF-nC) can be found
according to the following equation.
nF 㸫 nC = A + BȘ
In the above equation, values A and B
can simply be found out of Table 1 on
page 40 by checking up values
corresponding to a measured Refractive
Index on the table after measuring the
sample.
To obtain a value Ș, achromatize
the boundary line by turning the color
compensator knob and read the scale
indication (Z) on the knob at the time.
A value Ș can simply be found out of
Ta ble 2 on page 41 by checking up a
value Ș corresponding to the value Z
on the table.
Abbe number can be obtained by
calculation with the following
equation.
3. Finding Abbe number
Ȥ=
nD㸫1
nF㸫nC
Ȥ= Abbe number
nD = Refractive Index
nF㸫nC = Dispersion
value
where,
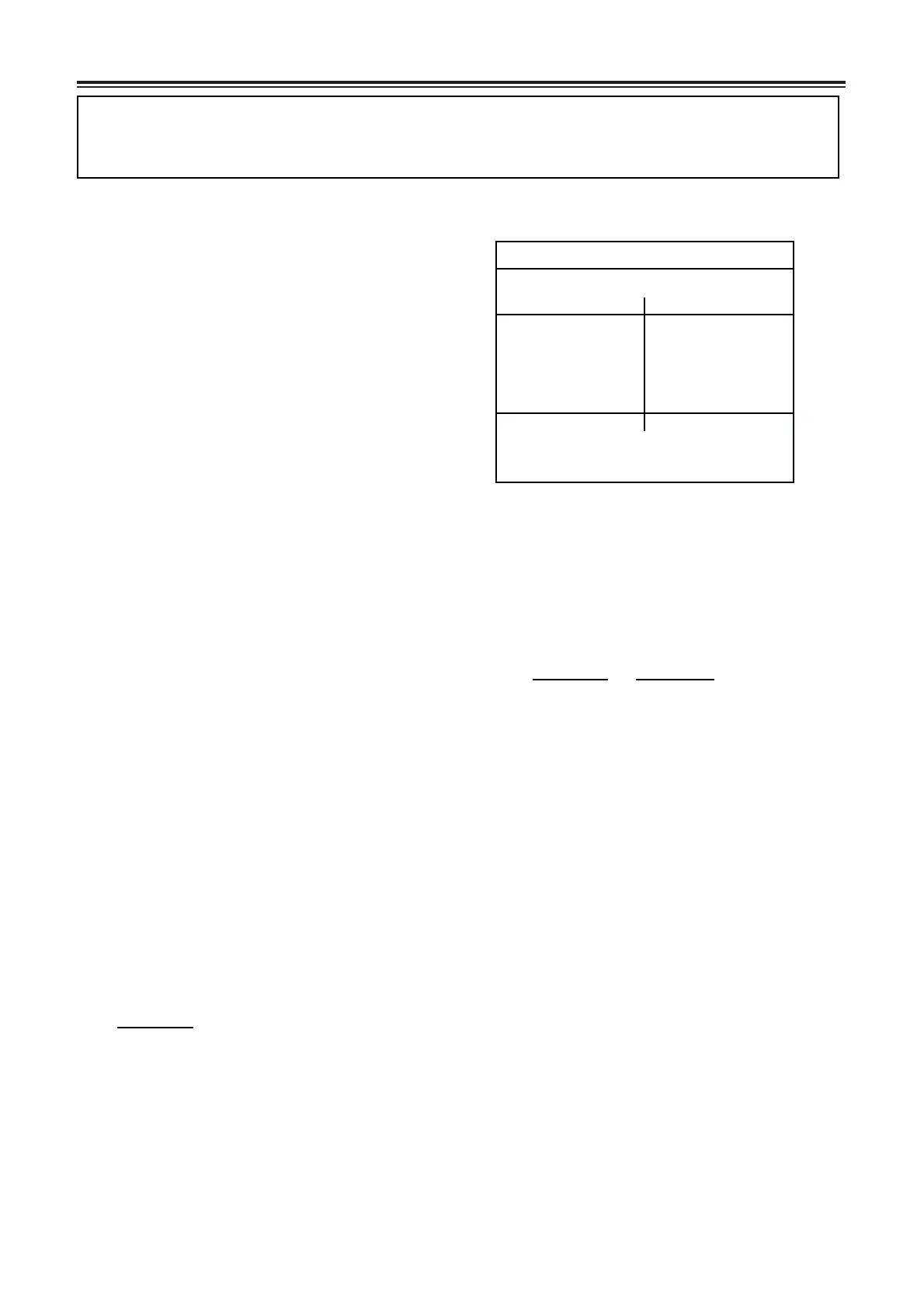
4. Example of measurement
Refractive Index (nD)=1.4827
Reading of dispersion scale
Left Right
42.3
42.2
42.2
42.2
42.2
42.1
42.3
42.2
42.2 42.2
Average reading for right and
left (Z)=42.2
A=0.02336
nF 㸫 nC=A+BȘ =0.00683
BȘ= 㸫 0.01653
Ș= 㸫 0.596
B=0.02774
Z=42.2
Ȥ=
nD 㸫 1
nF 㸫 nC
=
0.4827
0.00683
=70.7
5. Finding values A and B
more accurately
Assuming that nD (Refractive
Index) = 1.4827;
look up in the column A for a value
corresponding to 1.48 in the nD column
of Ta ble 1, and there is 0.02337 found as
the objective value.
0.02337...................................................(a)
In the same manner, 㸫 2 is found in the
Difference column.
When (a) and 㸫 2 are applied to the
following equation, calculation is carried
as:
27(㸫2)10
㸫7
= 㸫 0.0000054............(b)
Therefore,
A = a + b Ҹ 0.02336
Carry out the same calculation for a
value of B.
[Example]
When measuring a sample to calculate the Abbe value, be sure to use the natural light
(white light) instead of the accompanying illuminator lamp (orange light).
Note:

 Loading...
Loading...