Product overview
EL34xx24 Version: 1.5
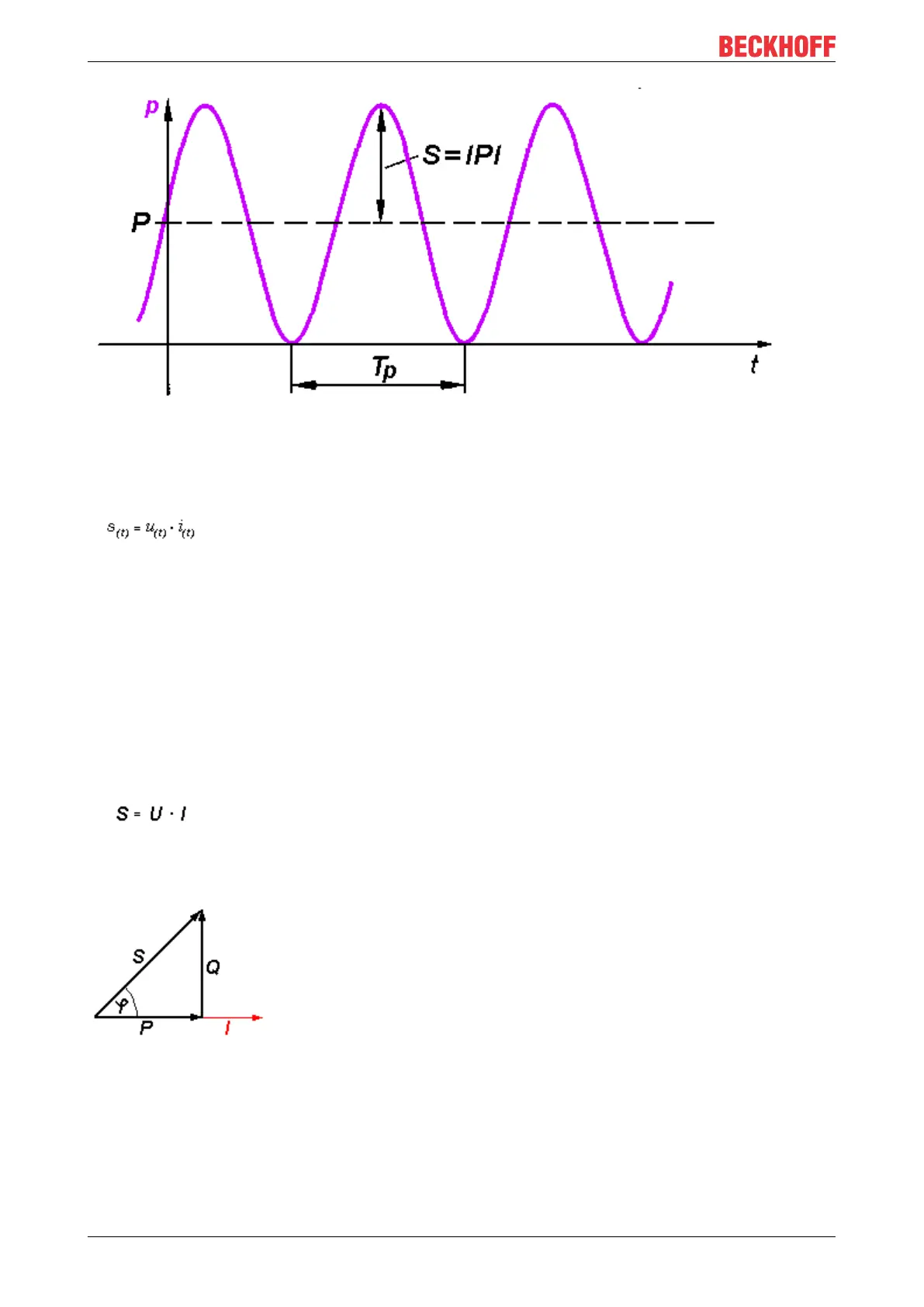
Fig.15: Power s
(t)
curve
In the first step, the power s
(t)
is calculated at each sampling instant:
The mean value is calculated over a period.
The power frequency is twice that of the corresponding voltages and currents.
Apparent power measurement
In real networks, not all consumers are purely ohmic. Phase shifts occur between current and voltage. This
does not affect the methodology for determining the RMS values of voltage and current as described above.
The situation for the active power is different: Here, the product of RMS voltage and RMS current is the
apparent power.
The active power is smaller than the apparent power.
S: apparent power
P: active power
Q: reactive power
φ: Phase shift angle
 Loading...
Loading...