Chapter 4: Useful help | 27
B450MX / B450MX-S
4.5 RAID Functions
RAID Denions
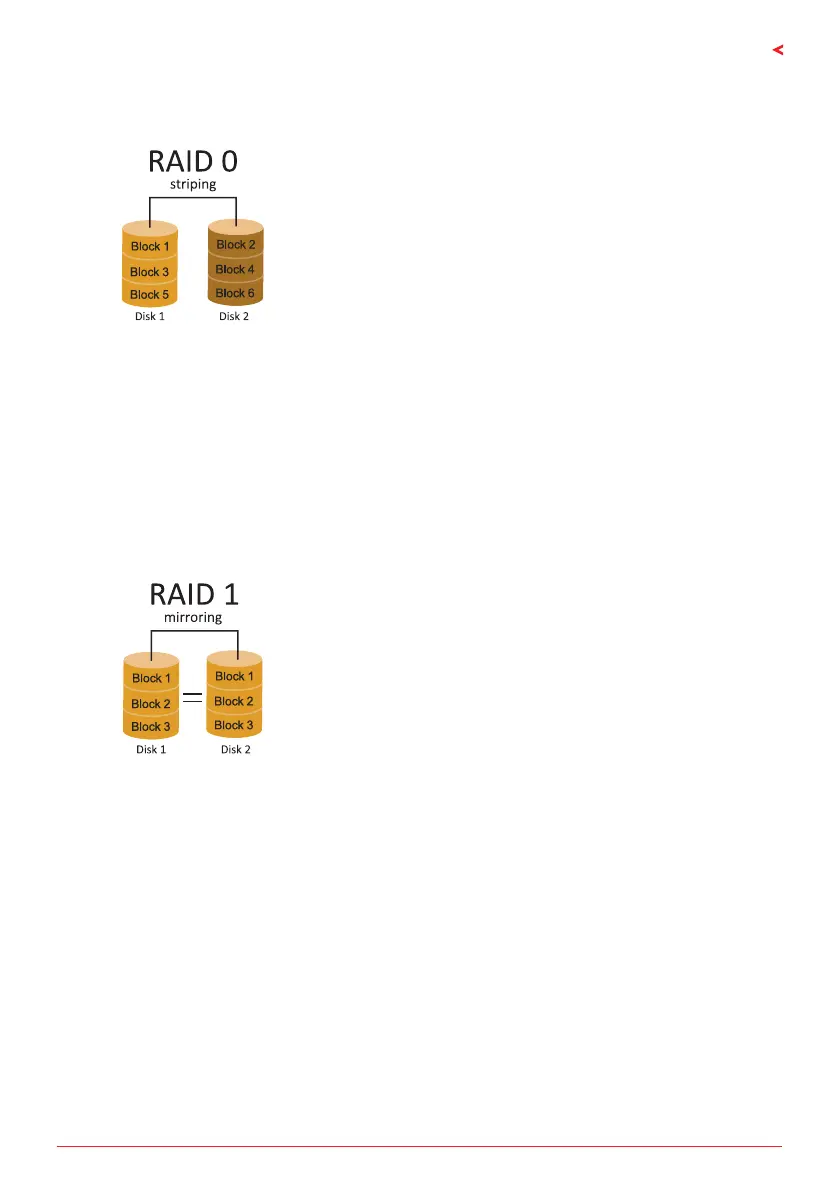
In a RAID 0 system data are split up in blocks that get
wrien across all the drives in the array. By using mulple
disks (at least 2) at the same me, this oers superior I/O
performance. This performance can be enhanced further by
using mulple controllers, ideally one controller per disk.
Features and Benets
• Drives: Minimum 2, and maximum is up to 6 or 8. Depending on the plaorm.
• Uses: Intended for non-crical data requiring high data throughput, or any environment
that does not require fault tolerance.
• Benets: provides increased data throughput, especially for large les. No capacity loss
penalty for parity.
• Drawbacks: Does not deliver any fault tolerance. If any drive in the array fails, all data is
lost.
• Fault Tolerance: No.
• Total Capacity: (Minimal. HDD Capacity) x (Connected HDDs Amount)
Data are stored twice by wring them to both the data disk
(or set of data disks) and a mirror disk (or set of disks) . If
a disk fails, the controller uses either the data drive or the
mirror drive for data recovery and connues operaon. You
need at least 2 disks for a RAID 1 array.
Features and Benets
• Drives: Minimum 2, and maximum is 2.
• Uses: RAID 1 is ideal for small databases or any other applicaon that requires fault
tolerance and minimal capacity.
• Benets: Provides 100% data redundancy. Should one drive fail, the controller switches
to the other drive.
• Drawbacks: Requires 2 drives for the storage space of one drive. Performance is impaired
during drive rebuilds.
• Fault Tolerance: Yes.
 Loading...
Loading...