4.5.
HUMIDITY MEASUREMENTS
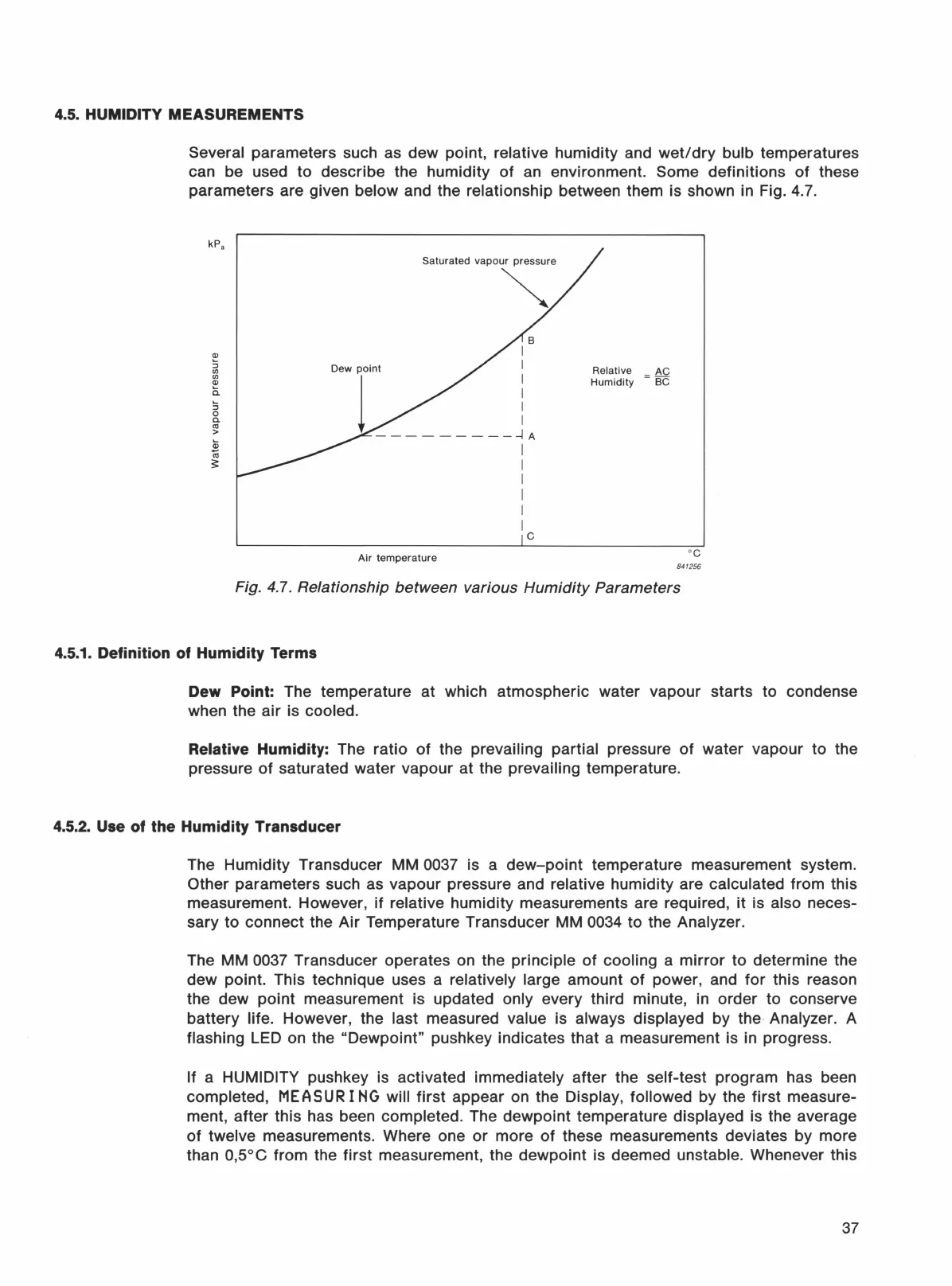
Several parameters such as dew point, relative humidity and
wet/dry
bulb temperatures
can be used
to
describe the humidity
of
an
environment. Some definitions
of
these
parameters are given
below and the relationship between them is shown in Fig. 4.7.
SaMated
vapo~e
8
I
I
I
I
I
I
----------lA
Air temperature
I
I
I
I
I
I
c
Relative AC
Humidity = BC
oc
841256
Fig. 4.7. Relationship between various
Humidity
Parameters
4.5.1. Definition
of
Humidity Terms
Dew Point: The temperature at which atmospheric water vapour starts to condense
when the air is
cooled.
Relative
Humidity: The ratio
of
the prevailing partial pressure
of
water vapour to the
pressure
of
saturated water vapour at the prevailing temperature.
4.5.2. Use of the Humidity Transducer
The Humidity Transducer MM
0037 is a
dew-point
temperature measurement system.
Other parameters such as vapour pressure and relative humidity are calculated from this
measurement. However,
if
relative humidity measurements are required,
it
is also neces-
sary
to
connect the
Air
Temperature Transducer MM 0034
to
the Analyzer.
The MM 0037 Transducer operates on the principle
of
cooling a
mirror
to
determine the
dew point. This technique uses a
relatively large amount
of
power, and
for
this reason
the dew point measurement is updated
only every third minute, in order to conserve
battery
life. However, the last measured value is always displayed by the· Analyzer. A
flashing LED on the "Dewpoint" pushkey indicates that a measurement is in progress.
If a HUMIDITY pushkey is activated immediately after the self-test program has been
completed, MEASURING will first appear on the Display, followed by the first measure-
ment, after this has been
completed. The dewpoint temperature displayed is the average
of
twelve measurements. Where one
or
more
of
these measurements deviates by more
than
0,5°C from the first measurement, the dewpoint is deemed unstable. Whenever this
37

 Loading...
Loading...











