25 Operation and Adjustment Manual
fromthemoonareeffectivelyparallel.
Additionally,whenyoulookstraightatthemoon,your
lineofsightis“collimated”orparalleltothemoon‐
beams.Youcanwalkbackandforthhoweverfaryou
want(makelateralshifts),butyouwillnotneedtorotate
yourheadbackandforth
tokeepyoureyesalignedto
themoon—themoonappearstomoverightalongwith
you.
Usingthisthoughtexperiment,youmightbegintosee
howcollimatedinstruments,whoselinesofsightare
parallel,arenotnecessarilyonthesameexactlinein
space.Oneinstrumentcanmovebackand
forthlater‐
ally,withtheimagefromtheotherinstrument
(analogoustothemoon)stillappearingtobeinthesame
relativeposition.It’simportanttorememberthischaracteristicof
collimationsothatyoudon’tfoolyourselfintothinkingthatcolli‐
matedinstrumentsactuallysharethesamephysicallineofsight.
Thebottomlineis:collimated,butnotnecessarilycollinear,linesof
sightareexactlyparallel,liketherailsonasectionoftraintrack;
parallelbutnotoccupyingthesamephysicalspace.Thiscollimation
procedureisveryusefulfortransferringreferencelinesfromone
instrumenttoanother.
Let’sdiscusshowtocollimatetwoinstruments.Incollimation,one
instrumentremainsstationary,andisfocusedatinfinity.Thisis
designatedasthereferenceinstrument,becauseitrepresentssome
referencelinethatisofimportance(e.g.,ashaftorborecenterline,
etc).Then,collimationoccurswhentheopticalaxisofasecond
(“working”)instrumentisbroughtintoparallelalignmentwiththe
referenceinstrument.
Tocollimatethe“working”instrumenttothereferenceinstrument,
performthestepsbelow.Again,thisisabuck‐inprocess.
1. Illuminatethereferenceinstrument.Makesurethatthe
referenceinstrumenthasalightsourcewhichisillumi‐
nated
sothatitsreticleisbacklit.
2. Focusatinfinity.Focusthereferenceinstrumenttoin‐
finityusingamirrorasdescribedpreviously.
3. Pointtothereferenceinstrument.Pointtheworkingin‐
strumentatthefaceofthereferenceinstrumentandfocus
onitsobjectiveend.Lockthehorizontalandverticaltan‐
gentscrewsontheworkinginstrument.
4. Centertransitonthe“far”target.Nowfocusthework‐
inginstrumentatinfinity.Thefocusisnowsetsothat
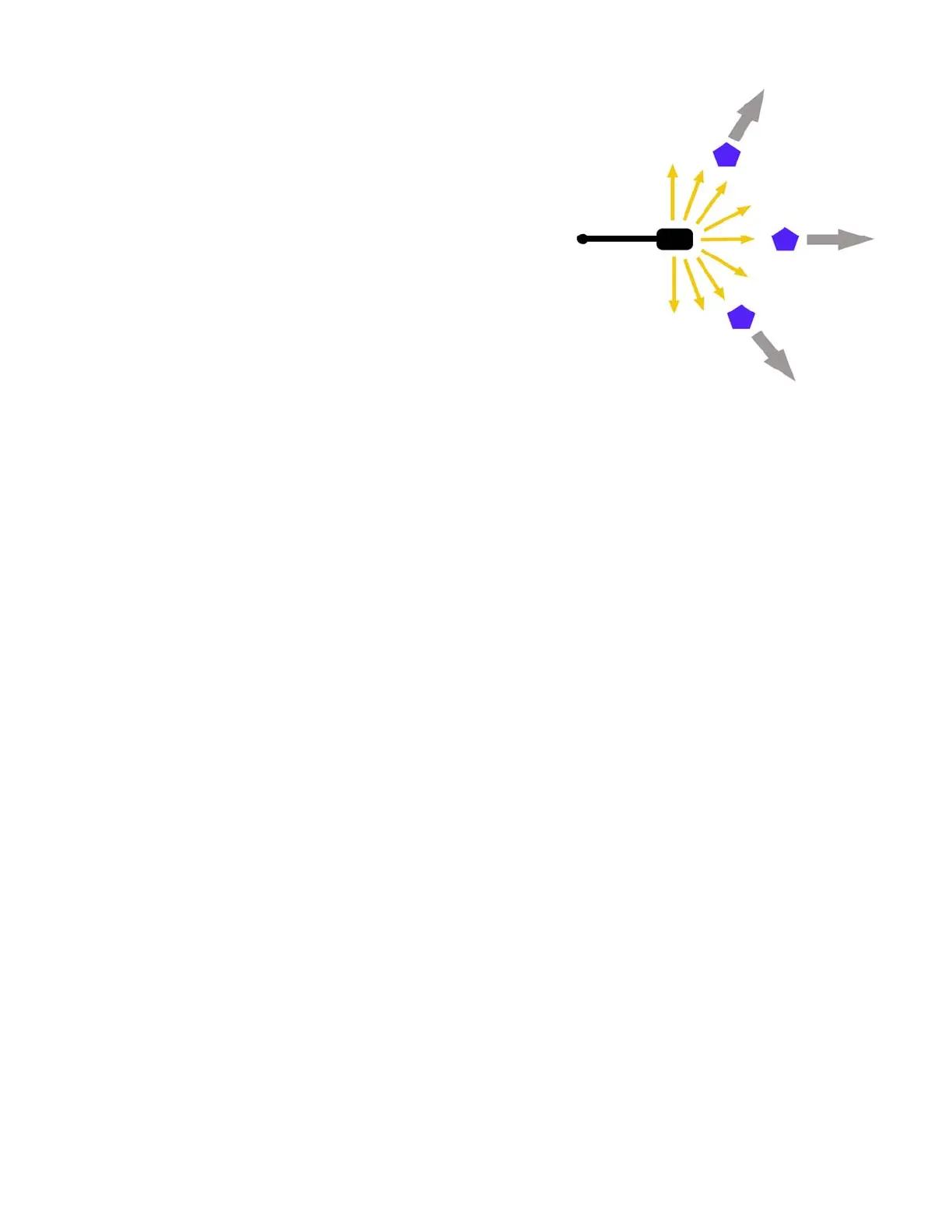
Astreetlightfromabove:
shadows(grayarrows)cast
byanobjectnearalight
sourceareparalleltothe
lightrayswhichtravel
fromthatlightsourceto
theobject.
Figure3.9
 Loading...
Loading...