20070201
5-3-3
Drawing a Graph
u To store an X = constant expression *
1
Example To store the following expression in memory area X4 : X = 3
3 (TYPE)4 (X=c) (Specifi es X = constant expression.)
d (Inputs expression.)
w (Stores expression.)
• Inputting X, Y, T, r , or
θ
for the constant in the above procedures causes an error.
u To store an inequality *
1
Example To store the following inequality in memory area Y5 : y > x
2
− 2 x − 6
3 (TYPE)6 (g )1 (Y>) (Specifi es an inequality.)
vx -c v -g (Inputs expression.)
w (Stores expression.)
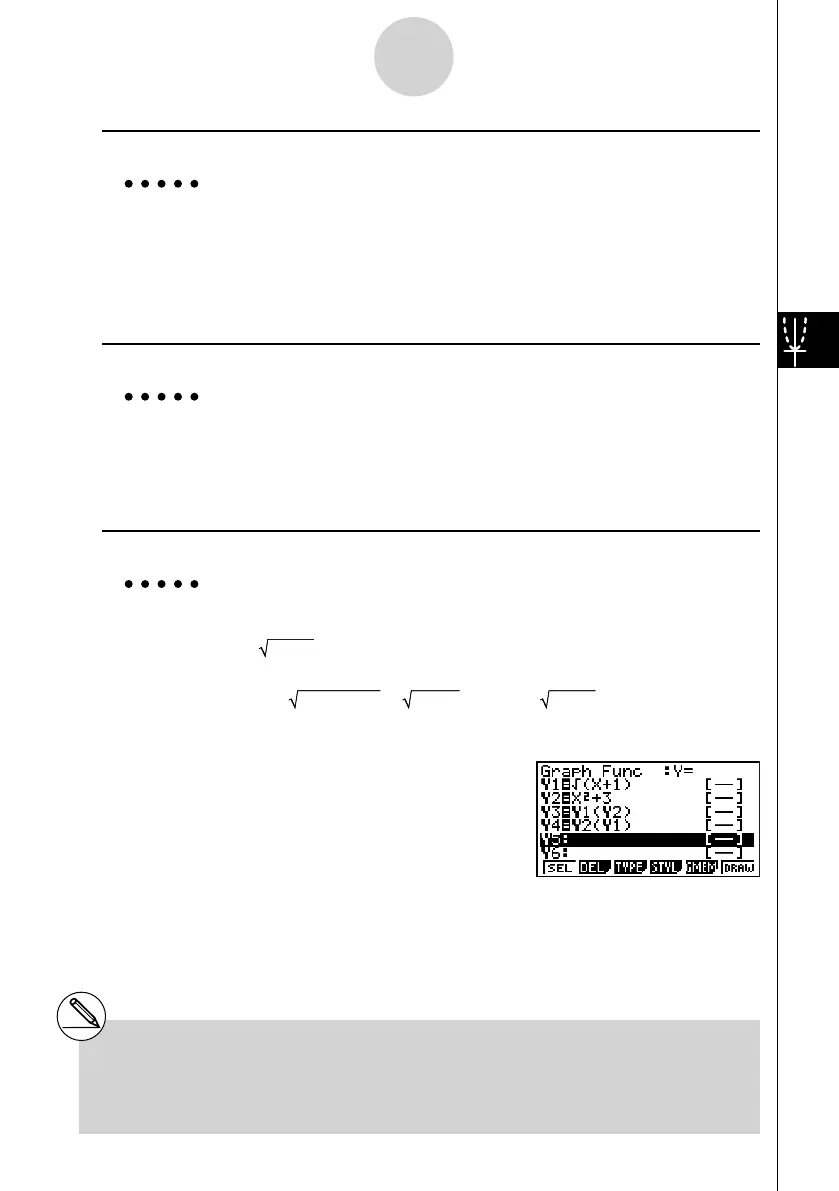
u To create a composite function
Example To use relations in Y1 and Y2 to create composite functions for Y3
and Y4
Y1 = (X + 1), Y2 = X
2
+ 3
Assign Y1
°
Y2 to Y3, and Y2
°
Y1 to Y4.
(Y1
°
Y2 = ((x
2
+ 3) +1 ) = (x
2
+ 4) Y2
°
Y1 = ( (X + 1))
2
+ 3 = X + 4 (X > −1))
Input relations into Y3 and Y4.
3 (TYPE)1 (Y=)J 4 (GRPH)
1 (Y)b( 1 (Y)c) w
J 4 (GRPH)1 (Y)c
( 1 (Y)b) w
• A composite function can consist of up to fi ve functions.
*
1
A function cannot be stored into a memory
area that already contains a function of a
different type from the one you are trying to
store. Select a memory area that contains a
function that is the same type as the one you are
storing, or delete the function in the memory area to
which you are trying to store.
 Loading...
Loading...











