20070201
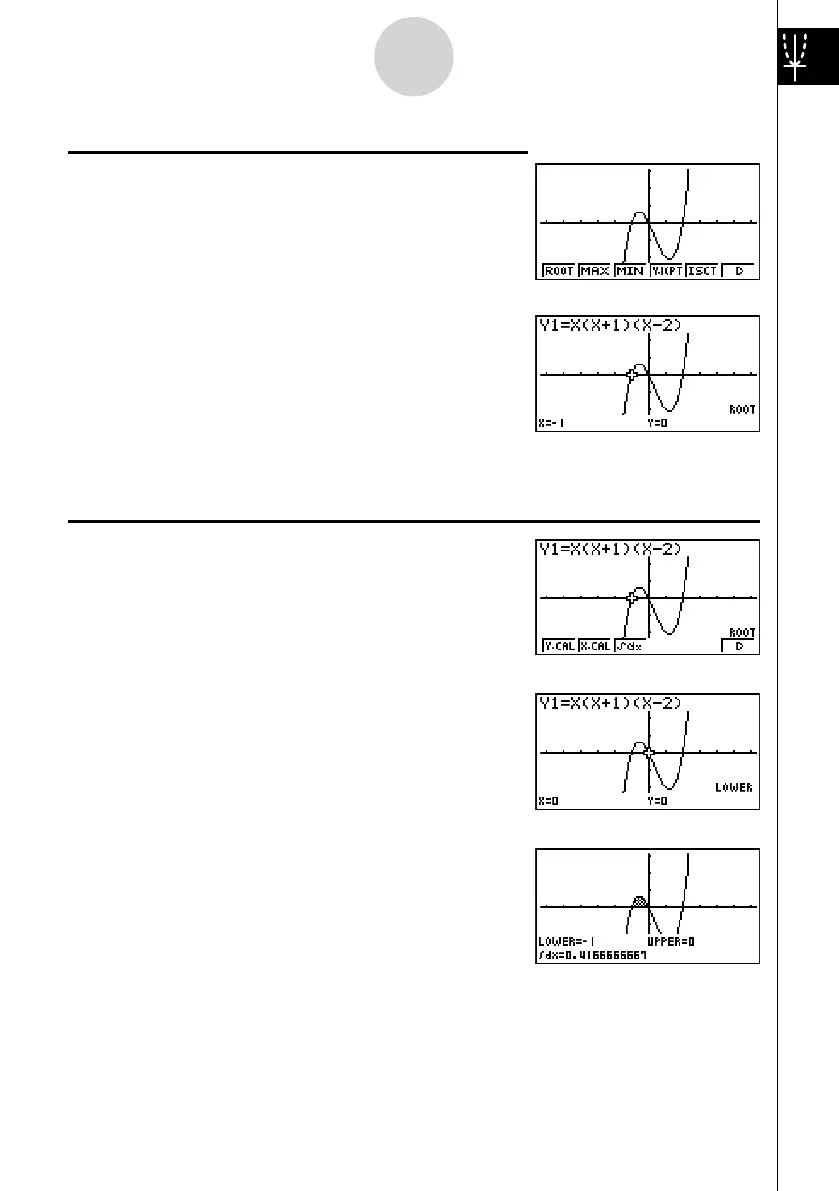
Example 2: To determine the roots of Y = X(X + 1)(X – 2)
1. Press
!5 (G-SLV).
2. Press 1 (ROOT).
Press
e for other roots.
Example 3: Determine the area bounded by the origin and the X = –1 root obtained for
Y = X(X + 1)(X – 2)
1. Press !5 (G-SLV)6 (g ).
2. Press 3 ( ∫ dx ).
3. Use d to move the pointer to the location where
X = –1, and then press
w . Next, use e to
move the pointer to the location where X = 0, and
then press
w to input the integration range,
which becomes shaded on the display.
7
Quick-Start
 Loading...
Loading...











