7
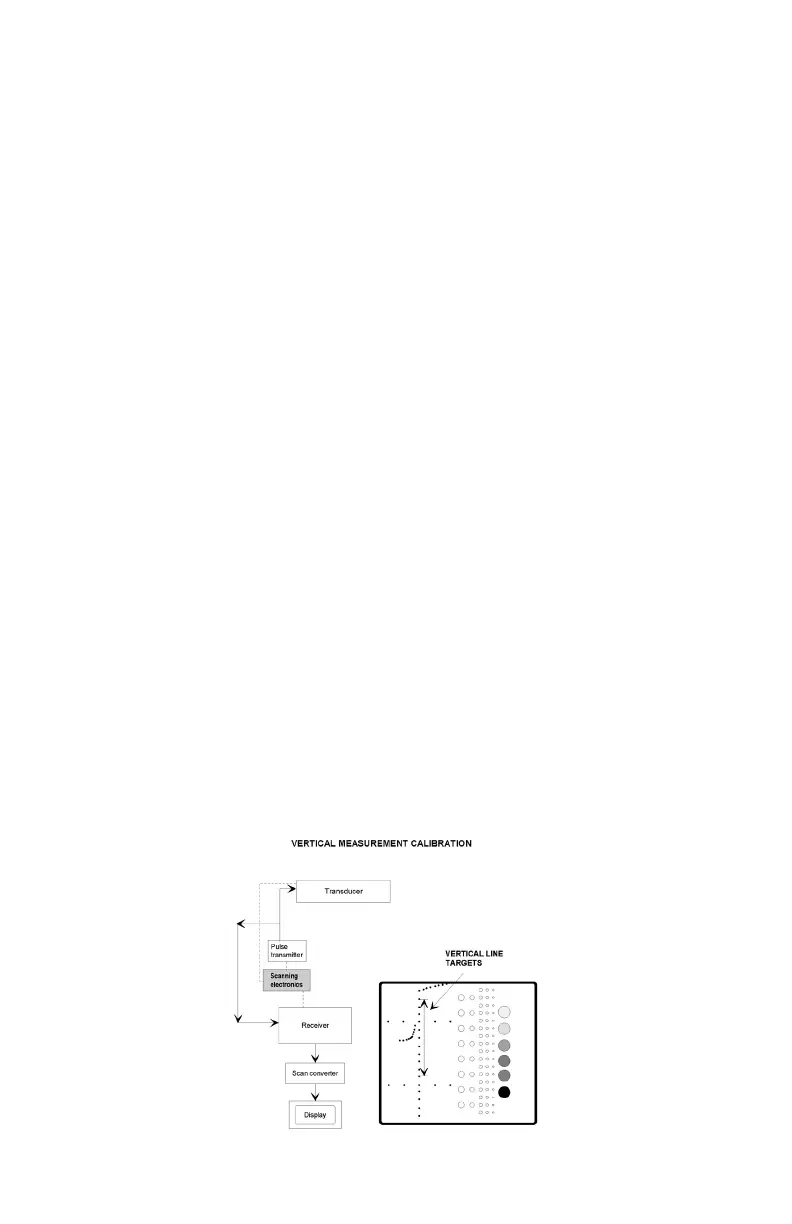
VERTICAL DISTANCE MEASUREMENTS
Vertical distance measurements obtained along the axis of the sound beam. The
accurate representation of the size, depth and volume of a structure is a critical
factor in a proper diagnosis. Most imaging systems use depth markers and/or
electronic calipers to obtain these measurements. The phantom is scanned and a
distance measurement obtained using the timing markers and/or electronic cali-
pers. The resulting measurement is then compared to the known distance between
the line targets in the phantom. The accuracy of vertical distance measurements is
dependent upon the integrity of the timing circuitry of the imaging system. Testing is
performed as follows:
1. Place the phantom on a clean, at surface with scanning surface #1 positioned
for use
2. Apply an adequate amount of low viscosity gel or water to the scan surface. If
water is used, ll the scanning well slowly to avoid introduction of air bubbles.
3. Adjust the instrument settings (TGC, output, etc.) to establish baseline values
for "normal" scanning. If the bottom of the phantom is seen, adjust the
gain settings until the image goes entirely black. Record these settings on the
quality assurance record. These setting should be used for subsequent testing.
4. Position the transducer over the vertical group of line targets until a clear image
is obtained. Freeze the display.
5. Using the electronic calipers or the timing markers measure the greatest
distance that can be clearly imaged between line targets.
6. Document the measurement obtained on the quality assurance record.
Results:
Vertical Spacing: 1.0 cm center to center ± 0.1 mm
If a discrepancy occurs which is greater than 1.0 mm, corrective action should be
considered by the individual Ultrasound Department.
 Loading...
Loading...