© 2014 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public. Page 3 of 33
Purpose of This Document
This document gives an overview of RAID technology and describes the various RAID levels, as well as the RAID
levels supported on Cisco UCS
®
C220 and C240 M3 Rack Servers. It also describes how to work with the Cisco
®
Integrated Management Controller (Cisco IMC), including creating RAID volumes and hot spares and replacing a
drive. In addition, it discusses how to migrate the existing RAID level using the WebBIOS utility and how to use the
LSI MegaCLI utility.
RAID Overview
A redundant array of independent disks (RAID) is a group, or array, of independent physical drives that provides
high performance and fault tolerance. The RAID drive group appears to the host computer as either a single unit or
multiple virtual units. I/O is expedited because several drives can be accessed simultaneously.
RAID drive groups provide greater data storage reliability and fault tolerance than single-drive storage systems.
Data loss resulting from a drive failure can be prevented by using the remaining drives to reconstruct missing data.
RAID has become popular because it improves I/O performance and increases storage subsystem reliability.
RAID Levels Supported by Cisco UCS C220/C240 M3 Rack Servers
The RAID levels supported on any Cisco UCS C-Series server vary by RAID controller and can be verified in Cisco
IMC.
Example: RAID levels supported on two different controllers.
Cisco UCS RAID SAS 2008M-8i Mezzanine Card
LSI MegaRAID SAS 9271CV-8i
Verifying the Supported RAID Levels in Cisco IMC
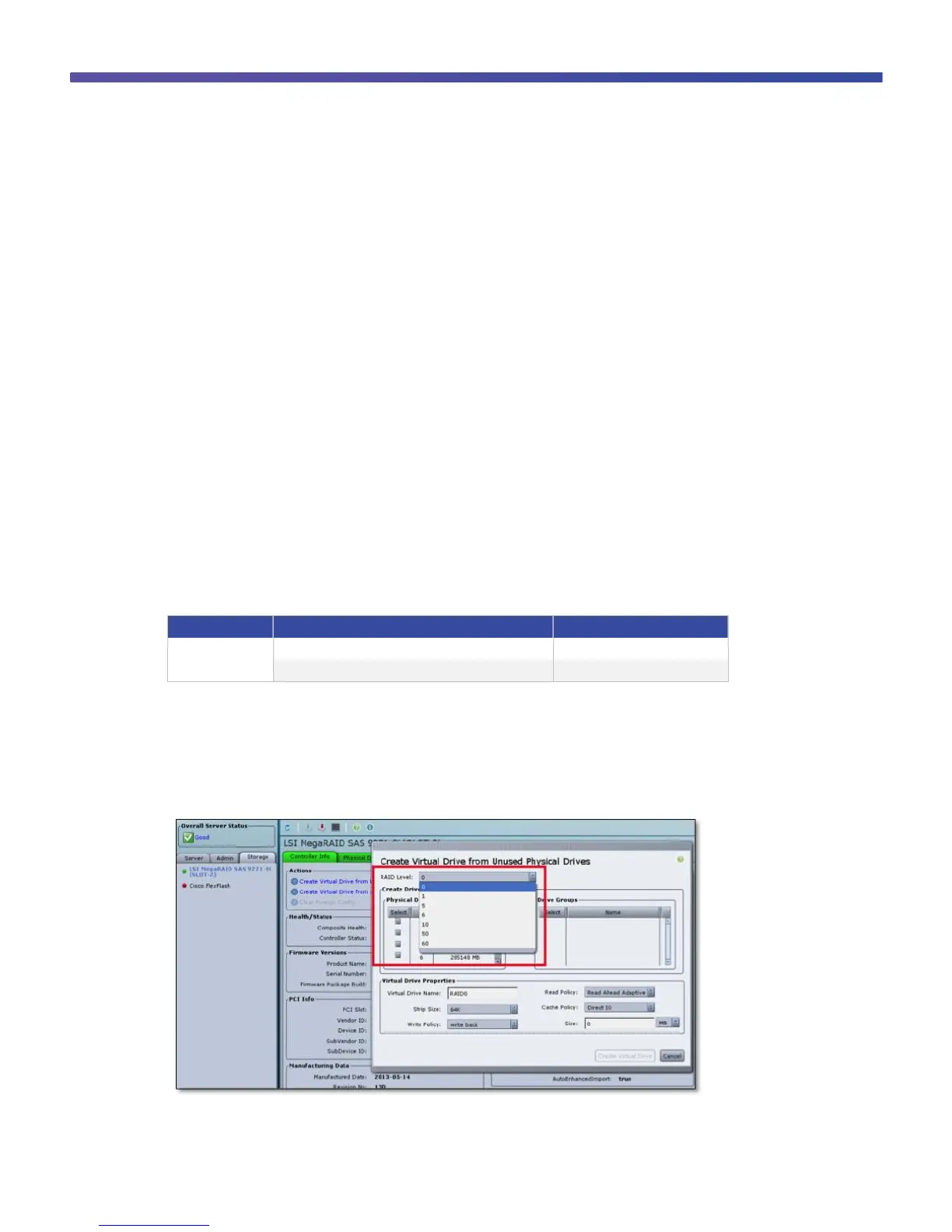
●
Log in to Cisco IMC, navigate to the Storage tab, and click Create Virtual Drive from Unused Physical
Drives. The supported RAID levels can be seen in the drop-down menu next to “RAID Level” (Figure 1).
Figure 1. Verifying the Supported RAID Levels
 Loading...
Loading...




