Implementing Multicast Routing on Cisco IOS XR Software Cisco ASR 9000 Series Routers
Information About Implementing Multicast Routing
MCC-19
Multicast Configuration Guide
OL-
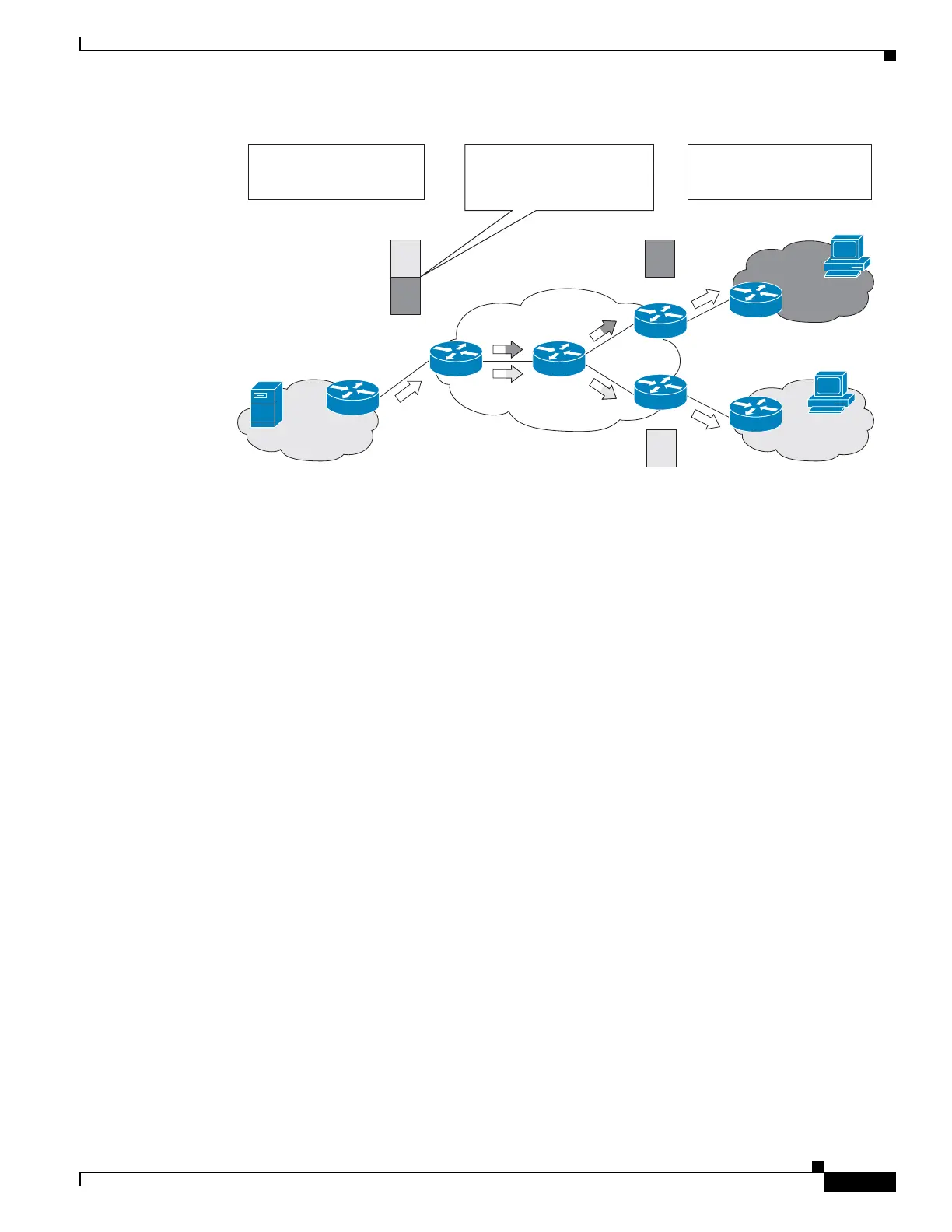
Figure 8 Receiver MVRF at the Source PE Router Receiver
For more information, see also Configuring MVPN Extranet Routing, page MCC-52 and Configuring
MVPN Extranet Routing: Example, page MCC-91.
RPF Policies in an Extranet
RPF policies can be configured in receiver VRFs to bypass RPF lookup in receiver VRFs and statically
propagate join states to specified source VRF. Such policies can be configured to pick a source VRF
based on either multicast group range, multicast source range, or RP address.
For more information about configuration of RFP policies in extranets, see Configuring RPL Policies in
Receiver VRFs to Propagate Joins to a Source VRF: Example, page MCC-93 and Configuring RPL
Policies in Receiver VRFs on Source PE Routers to Propagate Joins to a Source VRF: Example,
page MCC-96.
Multicast Source Discovery Protocol
Multicast Source Discovery Protocol (MSDP) is a mechanism to connect multiple PIM sparse-mode
domains. MSDP allows multicast sources for a group to be known to all rendezvous points (RPs) in
different domains. Each PIM-SM domain uses its own RPs and need not depend on RPs in other
domains.
An RP in a PIM-SM domain has MSDP peering relationships with MSDP-enabled routers in other
domains. Each peering relationship occurs over a TCP connection, which is maintained by the
underlying routing system.
MSDP speakers exchange messages called Source Active (SA) messages. When an RP learns about a
local active source, typically through a PIM register message, the MSDP process encapsulates the
register in an SA message and forwards the information to its peers. The message contains the source
and group information for the multicast flow, as well as any encapsulated data. If a neighboring RP has
local joiners for the multicast group, the RP installs the S, G route, forwards the encapsulated data
contained in the SA message, and sends PIM joins back towards the source. This process describes how
a multicast path can be built between domains.
VPN-A
VPN-A
VPN-B
Source
Receiver
Receiver
281305
PE1
CE
CE
CE
P
PE3
PE2
MVRF for VPN-A
MVRF for VPN-B
MVRF for VPN-A
MVRF for VPN-B
Packets received in MVRF for
VPN-A from the source
Packets are independently
replicated and encapsulated in
the MVRF for VPN-A and
VPN-B
PE2 and PE3 decapsulate and
forward the packets to the
respective MVRFs

 Loading...
Loading...















