Form I-RA/D 350/500, P/N 131090R12, Page 37
Oil Burner Troubleshooting
To diagnose malfunctions properly, the following test equipment is re-
quired:
1) An electrical test meter that can measure AC volts, ohms, and
amps;
2) A combustion analyzer kit to measure oxygen and/or carbon
dioxide, smoke, stack temperature, and draft; and
3) Two pressure gauges with scales of 0-100 PSIG and 0-30 PSIG.
Before test ring any heater, check the combustion chamber for an
excessive accumulation of unburned oil and restore to safe condition
before ring.
WARNING: Do not attempt to start the burner when
excess oil has accumulated, when the furnace is full of
vapor, or when the combustion chamber is very hot.
NOTE: Refer to the troubleshooting guide on page 38 to select the ap-
propriate troubleshooting chart.
Check the Indicator Lights
Light
Location (on the Electrical
Box)
Function
GREEN On the side next to discon-
nect (on/off) switch
Indicates that the main
power is on to the heater
GREEN On the xed-cover portion
above the ignition controller
Indicates that all limits have
been satised and the unit
is ready to operate
Troubleshooting
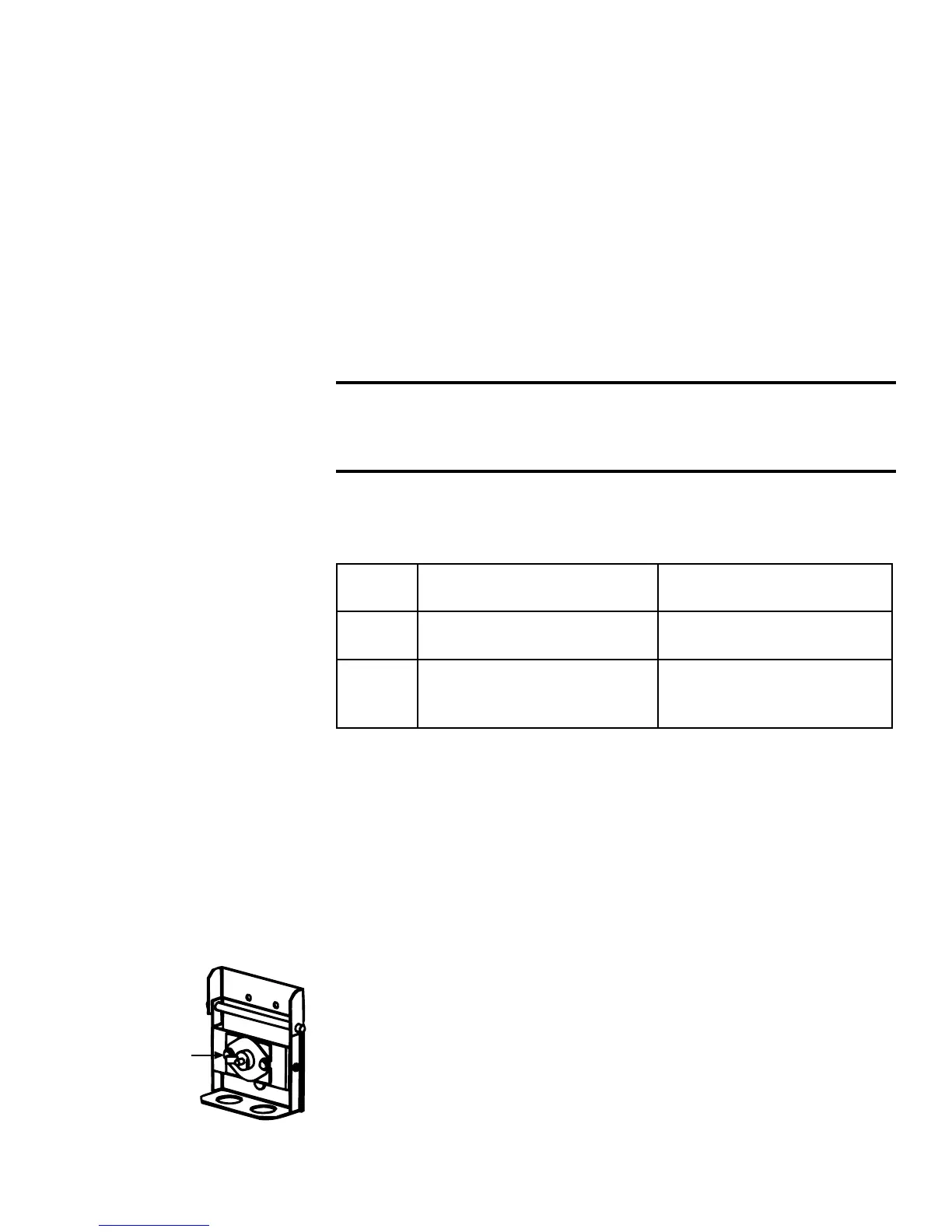
Viewport Cover
Backow
Sensor Switch
Description/Application - The backow sensor is a temperature-sen-
sitive switch that is designed to shutdown the heater when there is a
positive pressure in the combustion chamber The heater is designed to
operate with an overre draft of -0.01” to -0.02” w.c. Prolonged operation
at a positive pressure (
equal to or greater than 0.00” w.c.) can cause
overheating and accidental component failure. Undesirable positive
furnace pressure can be caused by any one or a combination of the fol-
lowing conditions:
• Totally or partially blocked ue gas venting system
• Improperly designed venting system
• Improper fuel-to-air ratio for combustion
• Excessive ash buildup on interior heat exchanger surfaces
• Blocked heat exchanger passages
• Improper atomization of the fuel
• Plugged or defective fuel nozzle
• Improperly adjusted fuel nozzle assembly
• Burning off-specication fuel
• Changes in outside ambient temperature
 Loading...
Loading...