MATRIX 400™ QUICK GUIDE
15
OPTICAL ACCESSORY SELECTION
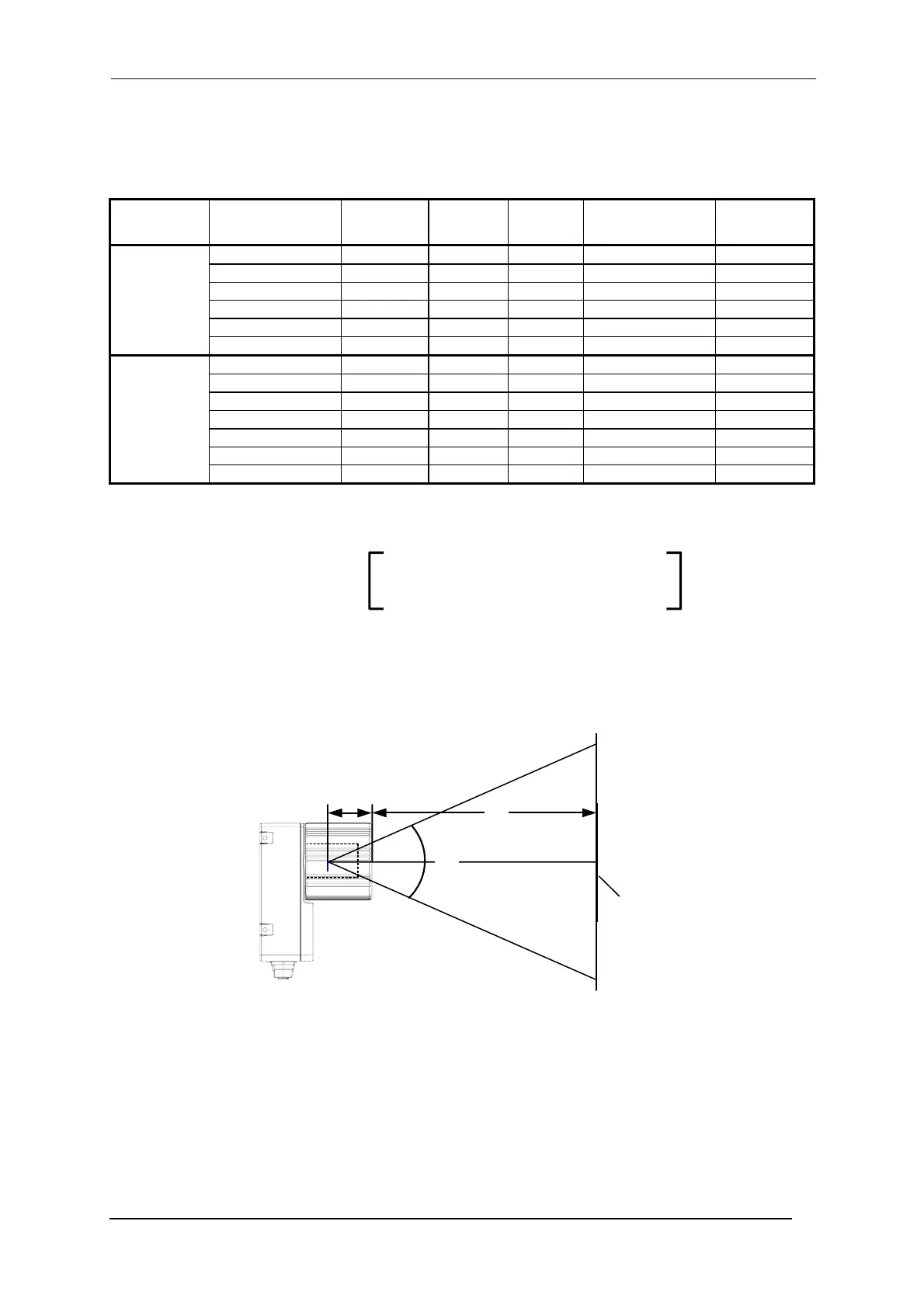
Refering to Figure 18 and the formula below, use the data in the following table to calculate the FOV for your
application.
Model Lens
Viewing Angle
Horizontal
Viewing
Angle
Vertical
Viewing
Angle
Diagonal
Min Focus Distance
mm
Lighting System
LNS-1109 9mm 48.5° 39.5° 60° 85 LT-002
LNS-1112 12.5mm 37° 30° 46.5° 85 LT-002
LNS-1116 16mm 28.5° 23° 36° 85 LT-001
LNS-1125 25mm 18.5° 15° 23.5° 135 LT-001
LNS-1135 35mm 13° 10,5° 16.5° 235 LT-006
400-400-0x0
(SXGA)
LNS-1150 50mm 9° 7° 11.5° 500 LT-006
LNS-1006 6mm 59.5° 46.5° 71° 85 LT-002
LNS-1109 9mm 40.5° 31° 49.5° 85 LT-002
LNS-1112 12,5mm 31° 23.5° 38° 85 LT-002
LNS-1116 16mm 24° 18° 30° 85 LT-001
LNS-1125 25mm 15° 11.5° 19° 135 LT-001
LNS-1135 35mm 11° 8.5° 13.5° 235 LT-006
400-600-0x0
(UXGA)
LNS-1150 50mm 7.5° 5.5° 9.5° 500 LT-006
The viewing angle has a tolerance of ± 1° depending on the focus distance.
FOV
x
= 2 (d + 35 mm) tan (α
x
/2)
where:
FOV
x
= horizontal, vertical or diagonal FOV
α
x
= horizontal, vertical or diagonal viewing angles.
d = focus distance
d
35 mm
FOV
plane
Figure 18 – Reading Distance References
Example:
The FOV for a Matrix 400-600-0x0 base using the 16 mm lens at a focus distance of 200 mm is:
FOV
H
= 2 [(200 mm + 35 mm) tan (24°/2)] = 100 mm
FOV
V
= 2 [(200 mm + 35 mm) tan (18°/2)] = 74 mm

 Loading...
Loading...