A REFERENCE GUIDE FOR OPTIMIZING DELL™ MD1000 SAS SOLUTIONS VER A00
PAGE 29 5/06/2005
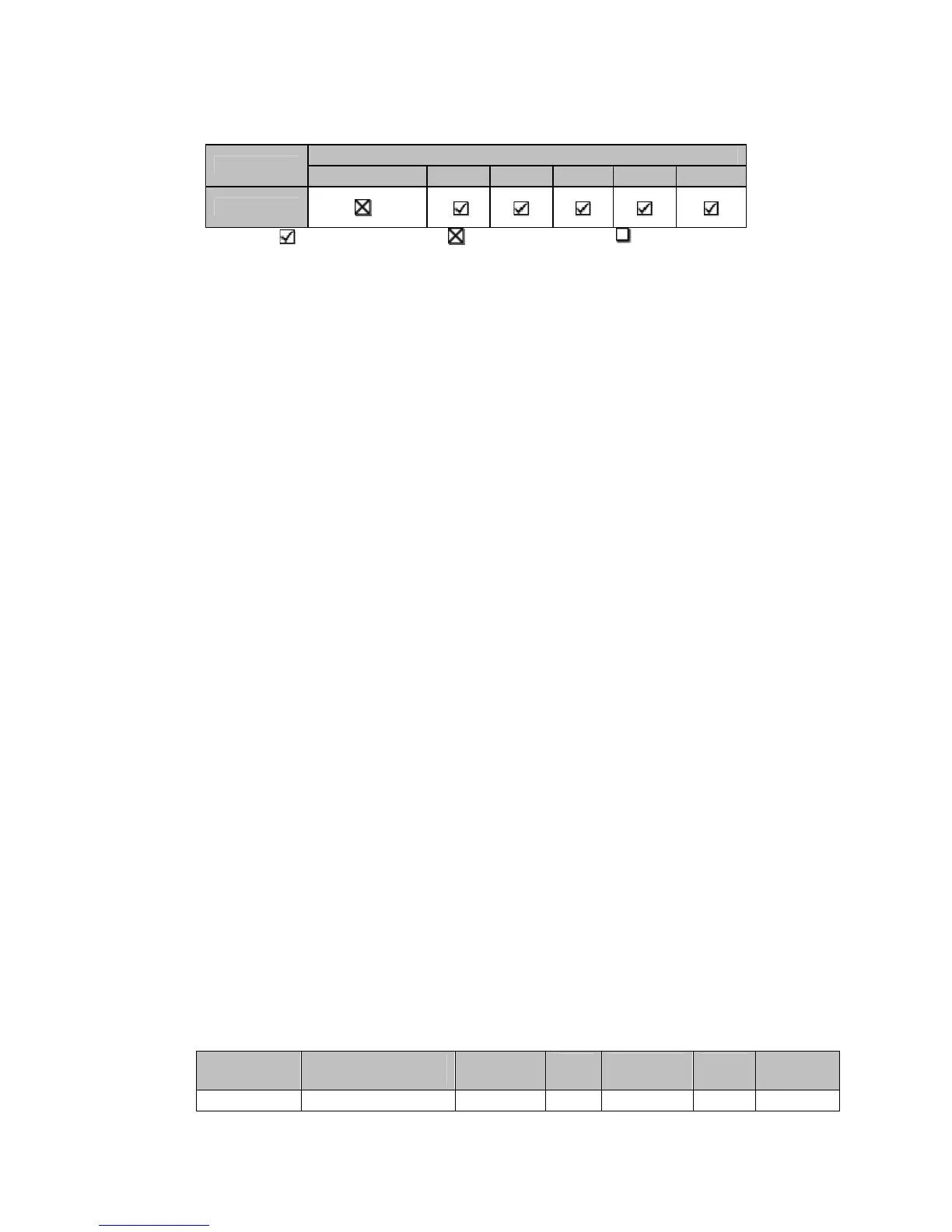
Table 9: Web RAID Guidelines
RAID Level
Application
Concatenated 0 1 10 5 50
Database
Recommended Not Recommended Possible
Recommended:
• RAID 10 – Recommended for enterprise web server solutions where availability and
redundancy and performance are the highest priority, usually for stand-alone portal sites
that are critical to the organization’s business.
• RAID 5 – Recommended for web servers that require maximum storage capacity and
moderate data protection and performance.
• RAID 50 – Recommended for those solutions that require a balance between storage
capacity and performance.
• RAID 0 – Recommended for solutions where the web server will be part of a group of web
servers that service a large internet portal and performance is the highest concern. In this
situation, availability and redundancy are addressed by the cluster group and do not need
to occur at the disk level.
• RAID 1 – Good solution for small websites which do not require high storage capacity.
Not recommended:
• Concatenated - This solution is not recommended due to lack of redundancy and data
protection
Note: While this configuration is not recommended, it can be configured and utilized.
Database or Online Transaction Processing Servers
Database servers can range from simple workgroup databases like Microsoft
®
Access with a few
hundred users to mission-critical enterprise databases like Oracle or SQL Server with thousands of
users. Database applications will always benefit from some data protection while other
requirements such as performance and availability will vary. As a general rule, the more critical the
database, greater is the need for data protection. Additionally, the performance requirements
increase relative to the number of users accessing the database.
Online Transaction Processing (OLTP) oriented servers are used in a number of industries for the
entry and retrieval of transactions. For example, OLTP is common in banking, airlines, mail-order,
and supermarkets. These servers are generally mission-critical and require maximum availability
and redundancy possible.
Table 10: Database or OLTP General IO profile
I/O Profile
(Read/Write)
I/O Profile
(Sequential/Random)
Bandwidth
I/O
Size
Latency
Sensitivity
Growt
h Rate
Criticality
80/20 Random Moderate 8k Moderate Low High

 Loading...
Loading...











