12 Dell EMC Networking with Isilon Front-End Deployment and Best Practices Guide | version 1.0
• If none of the layer 2 limitations are a concern, it may ultimately come down to a matter of preference.
This guide provides examples of both topologies.
In addition to the considerations for the L2 topology, some options need to be considered in the L3 topology.
The primary design choice will be in the dynamic routing protocol that best fits the environment. BGP may be
selected for scalability and is well suited for very large networks, while OSPF is an interior gateway protocol
that provides routing inside an autonomous network. OSPF routers send link-state advertisements to all other
routers within the same autonomous system areas. This generally causes more memory and CPU usage than
BGP. However, OSPF may offer faster convergence. OSPF is often used in smaller networks.
Design choices that are common in both topologies include:
• Whether to use LACP or non-LACP configurations downstream.
• Configuring each leaf pair in a Virtual Link Trunking (VLT).
• Dell EMC recommends that RSTP always is configured as a best practice. Although configuring VLT
will create a loop free topology, RSTP will prevent loops if there is a misconfiguration in the network.
4.2 Oversubscription
Oversubscription is equal to the total amount of bandwidth available to all servers connected to a leaf switch
divided by the amount of uplink bandwidth. In a leaf-spine network, oversubscription occurs at the leaf layer.
Oversubscription = total bandwidth / uplink bandwidth
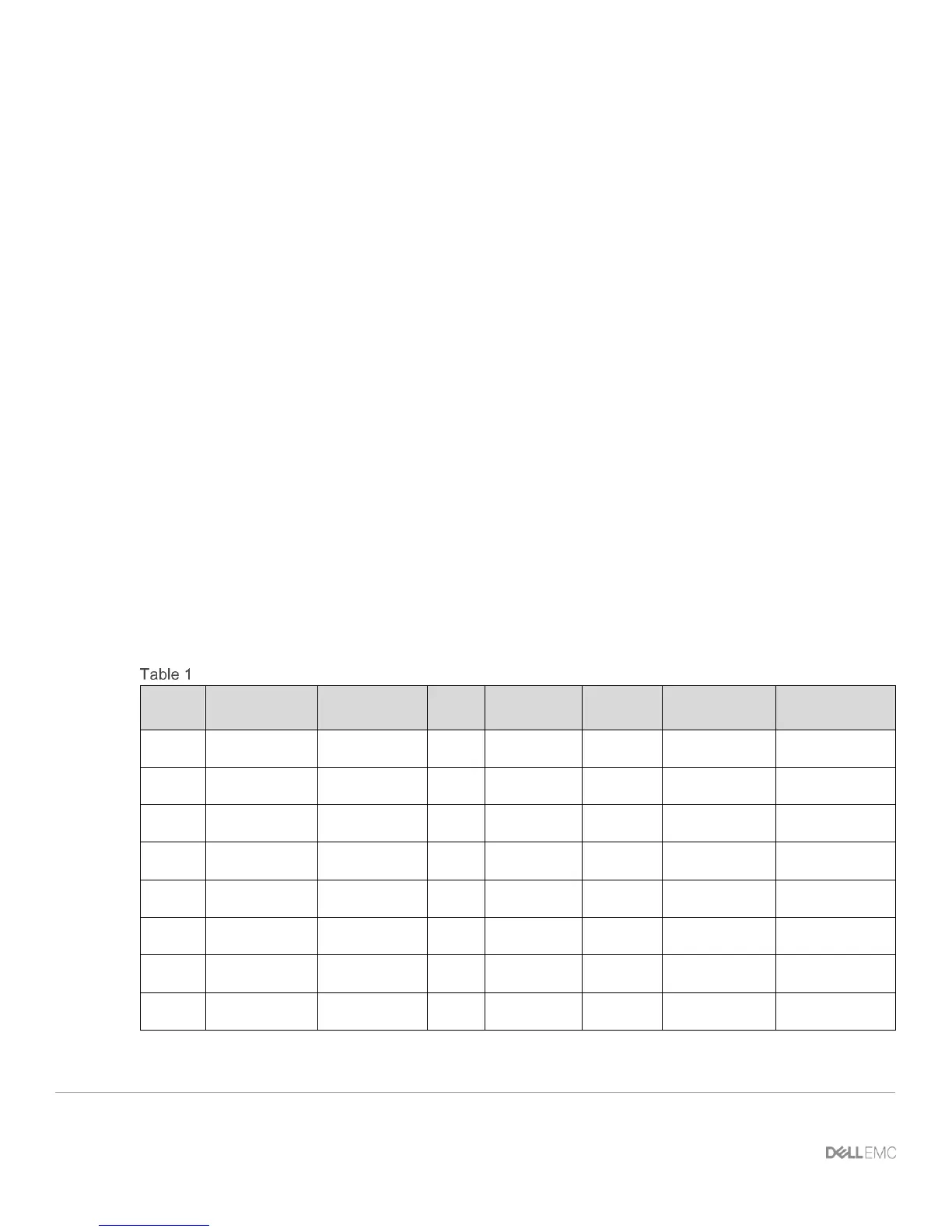
Other configurations are using available servers, storage and leaf switches that also could be used to manage
the subscription rates. The following are examples of oversubscription ratios based on downlink/uplink
bandwidth.
Oversubscription ratios based on uplink/downlink availability

 Loading...
Loading...











