ASDA-A2 Chapter 7 Motion Control
7-22 Revision February, 2017
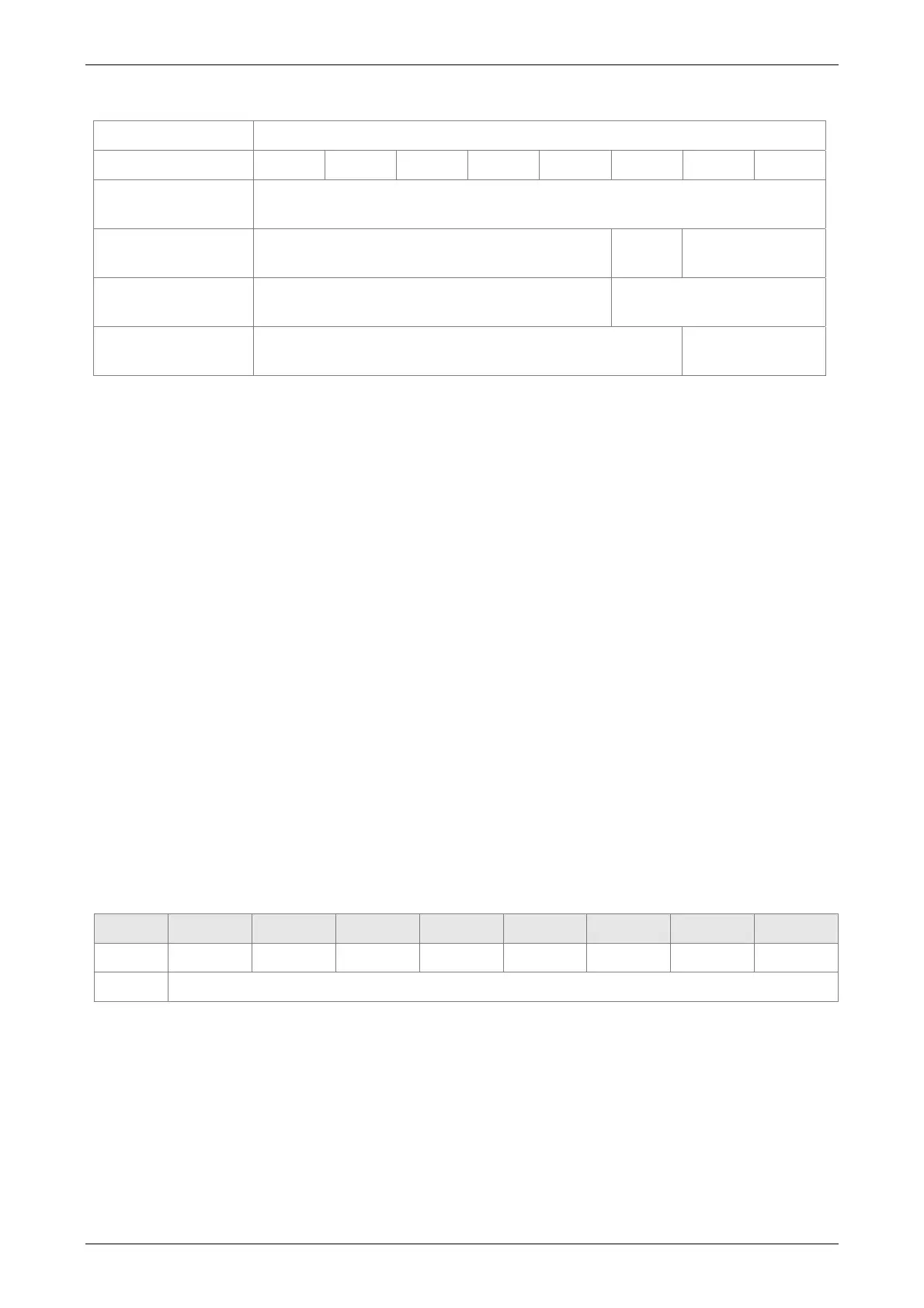
SOURCE: Settings of data source
SOURCE
Bit
31 ~ 28 27 ~ 24 23 ~ 20 19 ~ 16 15 ~ 12 11 ~ 8 7 ~ 4 3 ~ 0
SOUR = 00 means
constant
Para_Data
SOUR = 01 means
parameter Px-xx
Rsvd (0x0000 0) P_Grp P_Idx
SOUR = 10 means
data array
Rsvd (0x0000 0) Array_Addr
SOUR = 11 means
monitoring variable
Rsvd (0x0000 00) Sys_Var
P_Grp, P_Idx: specified parameter group and number
Array_Addr: specified the position of data array
Para_Data: the written constant
Sys_Var: monitor parameter code. Refer to P0-02 for its setting.
When Rsvd is not 0, it will display AL.213. When P_Grp exceeds the range, it will display AL.207.
When displaying AL.209, it means P_Idx exceeds the range.
When Array_Addr exceeds the range, it will display AL.213. And AL.231 is for Sys_Var exceeding
the range.
Note: 1. Even when the written parameter is retained, the new value will not be written into
EEPROM. Too frequent written will not shorten the lifetime of EEPROM.
Note: The aim of writing parameters via PR procedure is for turning ON/OFF or
adjusting some functions. (E.g. according to different positioning command to
adjust P2-00, Position Loop Gain.) This procedure will continuously repeat during
the operation. If the data is all written into EEPROM, it will shorten the lifetime of
EEPROM. In addition, if P2-30 is set to 5, the modified parameters (either from
panel or communication) will not be saved and is inconvenient to use. Thus, this
new function is added.
3. If writing parameters fails, alarm AL.213~219 will occur (Refer to Chapter 11 of the manual)
and the next PR which is enabled by AUTO function will not be executed.
10) Special Function: TYPE = 0xA, Indexing command.
Bit
31 ~ 28 27 ~ 24 23 ~ 20 19 ~ 16 15 ~ 12 11 ~ 8 7 ~ 4 3 ~ 0
DW0 - OPT2 DLY SPD DEC ACC OPT 0xA
DW1 DATA (32-bit): Indexing Coordinate Command, Unit: PUU