• The minimum angle of inclination of the sensor depends on the process fitting. See
Figure 1-2 and Table 1-3.
• For clean-in-place (CIP) applications, Micro Motion recommends using the
generally-accepted flow velocity of at least 1.5 m/s for cleaning the sensor.
• If the process piping must be larger than the sensor, eccentric reducers may be used
to ensure full drainability. In this case, the process end connections for the piping
and sensor must be the same size. See Figure 1-3.
Note
As part of the cleaning process, skid-based systems may be purged with nitrogen at the end
of the cleaning cycle. When using eccentric reducers, it is possible to trap gas in the section of
process piping adjacent to the reducer. Sensor performance can be impacted by intermittent
flow of the captured gas in a liquid fluid stream.
• The gap between the electronics housing and sensor body should be inspected
periodically. Manually clean this gap when necessary.
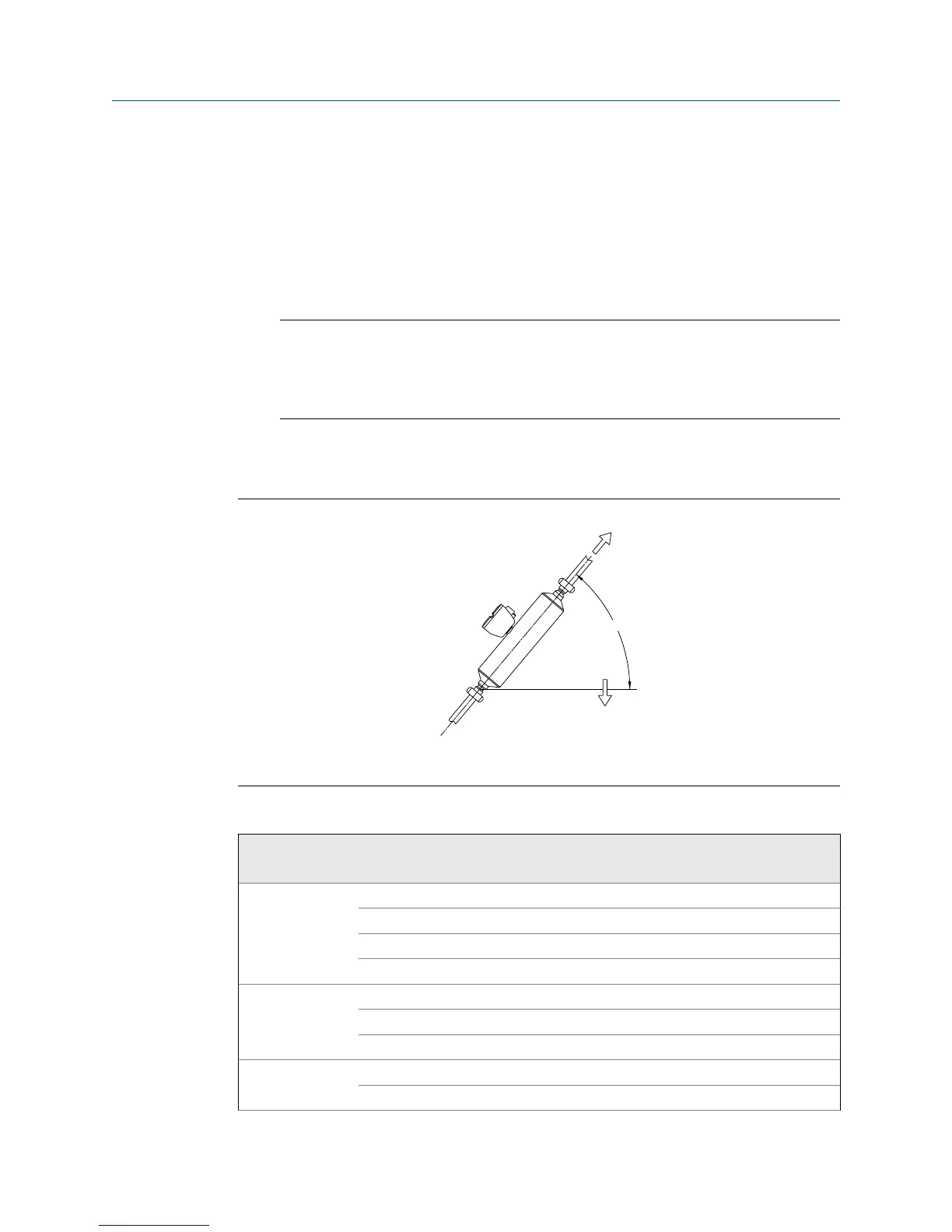
Sensor inclinationFigure 1-2:
A. Angle of inclination
B. Direction of gravity
Minimum angle of inclinationTable 1-3:
Model
Fitting
code Description Min. angle
T025F, T025T 621 1/2-inch Tri-clamp compatible sanitary clamp 47°
670 DN10 DIN 11851 sanitary coupling 47°
671 DN15 DIN 11851 sanitary coupling 47°
676 DN15 DIN 11864-1A sanitary coupling 47°
T050F, T050T 621 1/2-inch Tri-clamp compatible sanitary clamp 0°
671 DN15 DIN 11851 sanitary coupling 47°
676 DN15 DIN 11864-1A sanitary coupling 47°
T075F, T075T 622 3/4-inch Tri-clamp compatible sanitary clamp 0°
623 1-inch Tri-clamp compatible sanitary clamp 47°
Planning
4 Micro Motion T-Series

 Loading...
Loading...











