9
4.1.3.1.3 Dipole Vector Manual
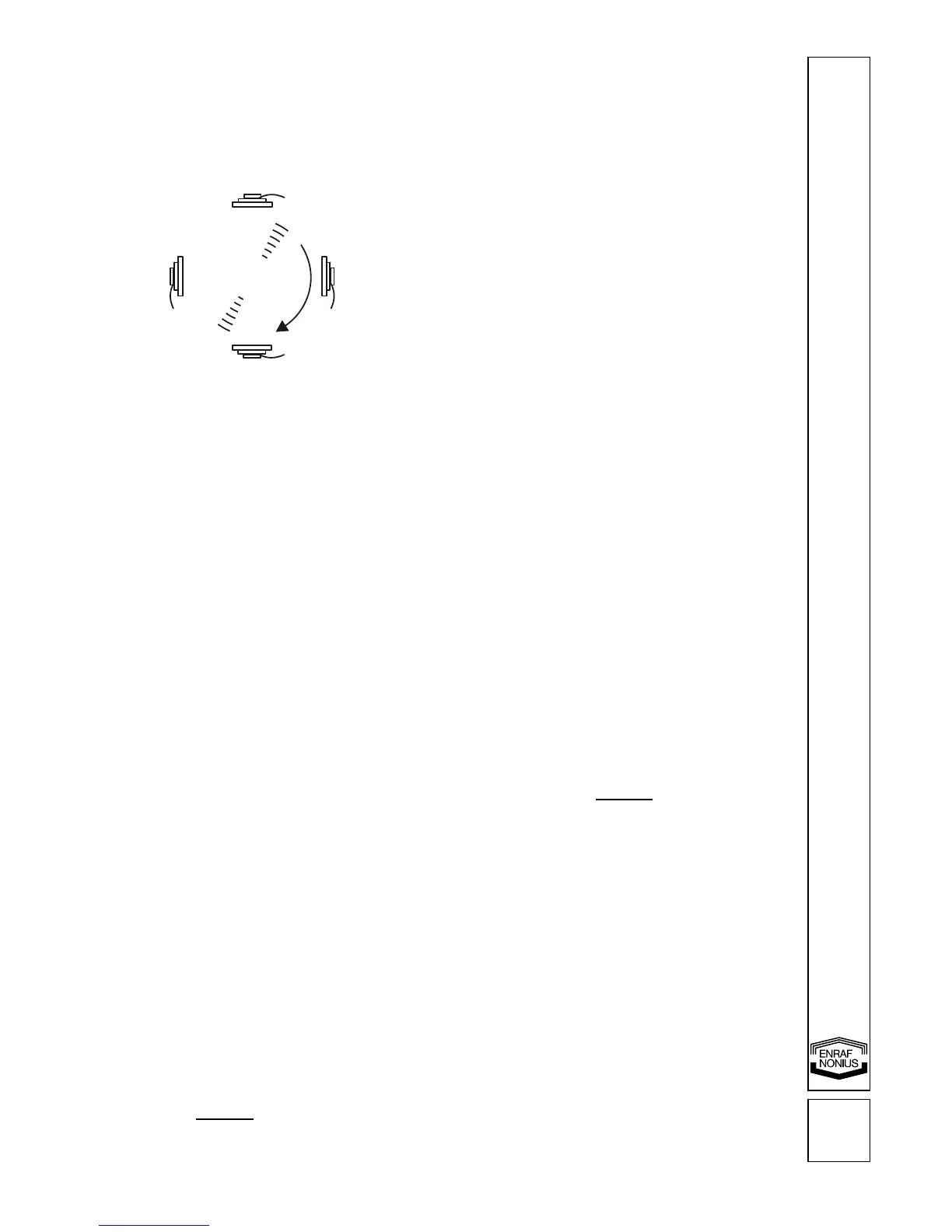
With the dipole vector technique the currents from the two electrode pairs are vectorially summed
in the tissue. The effect is that stimulation only occurs into the direction of the resulting vector,
which can be adjusted over a range of 360º. Amplitude modulation occurs in the equipment and
the modulation depth is 100%.
Stimulation with 100% modulation depth only occurs into the
direction of the vector.
The advantage of this method is that the direction of the stimulation can be adjusted electronically
after positioning the electrodes.
4.1.3.1.4 Dipole Vector Automatic
With the automatic dipole technique the dipole vector described above is rotated at an adjustable
speed. If the current amplitude is increased exceeding the motorial threshold, the tissue will
contract and relax rhythmically. The automatic dipole vector current is ideally suited for areas
where mechanical pressure (massage) is not desirable.
Parameters 4 Pole Interferential Currents:
Carrier frequency, expressed in kHz, is the base frequency of the alternating current.
Beat frequency, expressed in Hz, defines the channel frequency difference in classical interferential
mode and the rate at which the amplitude is internally modulated in the vector modes.
Frequency Modulation, expressed in Hz, defines a variable frequency range that is summed to the Beat
frequency i.e when the Beat frequency is set to 80 Hz and the Frequency modulation is set to 40 Hz, the
final frequency will vary from 80 – 120 Hz. Frequency modulation is often used to prevent accommodation
to stimulation or to improve patient tolerance.
Modulation Program defines the time and sequence in which the frequency will sweep through the
Frequency modulation range. See for the available Modulation programs fig 4.1.4.12.
Balance defines the difference in current amplitude between the two channels. Only available in classical
interferential mode.
Vector position adjustment defines the angle of the dipole vector with respect to the position of the
electrodes.
Rotation Speed, expressed in s, defines the time elapsed during one revolution of the vector in
automatic dipole vector mode.
4.1.3.2 Biphasic Pulsed Currents (TENS)
4.1.3.2.1 Asymmetrical and Alternating Asymmetrical
The asymmetrical biphasic pulsed current waveform is often used in TENS (Transcutaneous Electrical
Nerve Stimulation) applications. This waveform is characterized by variable phase duration and variable
pulse frequency. Its typical amplitude, duration, and rate of rise and decay are unequal for each phase
with respect to the baseline. The waveform is fully balanced, i.e. the phase charges of each phase are
equal. See fig 4.1.4.4.1 for a graphical representation.

 Loading...
Loading...