22
Sound basics
Sound travels approximately 344 m/s (1130 ft/s). It takes 3 ms for sound to travel
1 meter (3,3 ft).
In free-eld conditions (no walls, oor, or ceiling) the sound volume drops 6 dB
when the distance doubles.
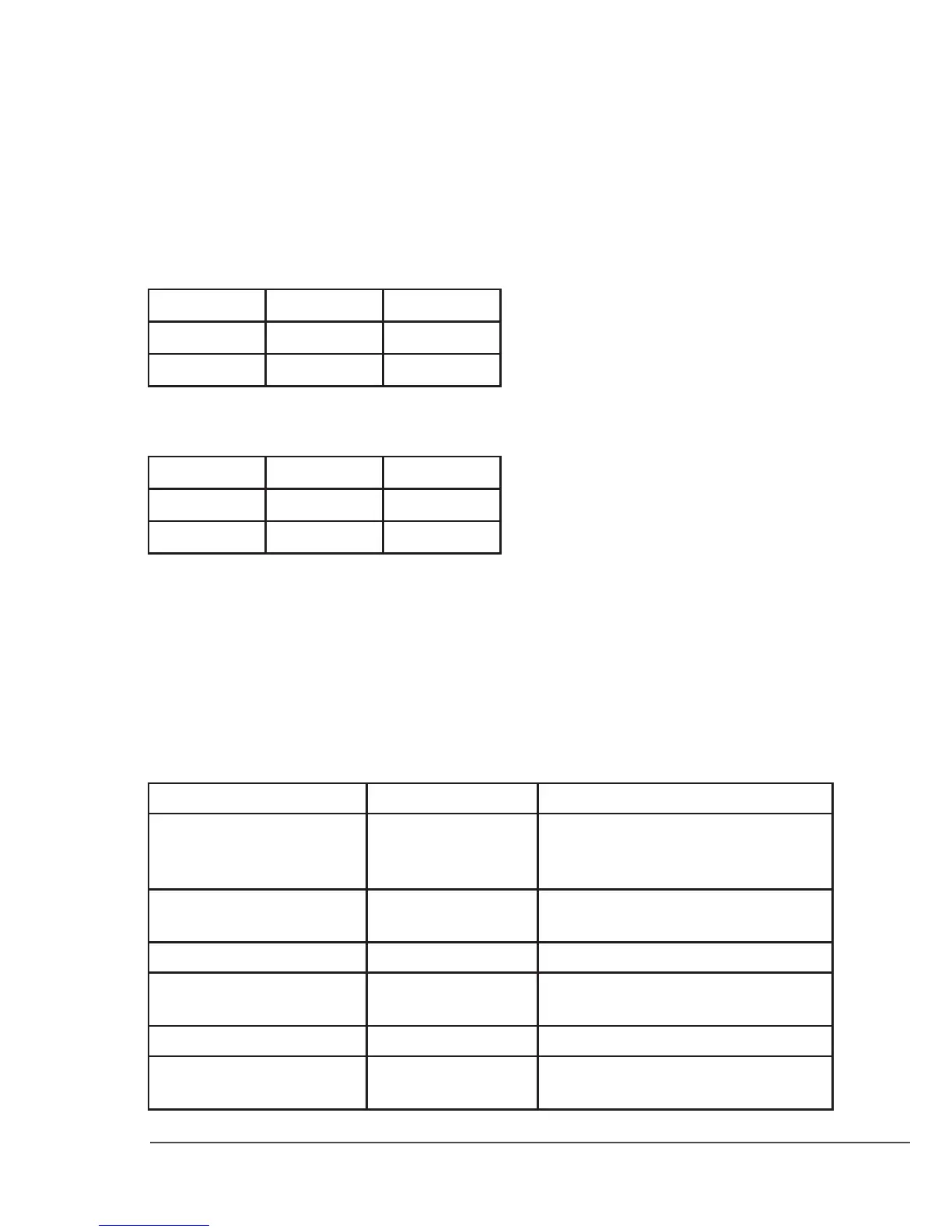
1 m 100 dB 0 dB
2 m 94 dB -6 dB
4 m 88 dB -12 dB
Sound level increases by 3 dB when the amplier power doubles.
100 W 85 dB 0 dB
200 W 88 dB +3 dB
400 W 91 dB +6 dB
The industry standard reference sound pressure level (SPL) for cinema and TV
sound production work is between 82 and 85 dB at the listening position.
Frequency spectrum
The audible frequency spectrum covers 10 octaves (up to 40 Hz, 80, 160, 320,
640, 1’280, 2’560, 5’120, 10’240, 20’480 Hz) which can conveniently divide the
spectrum as follows.
Subsonic bass frequencies below 16 Hz Not audible for humans.
Very low frequencies 16 Hz – 40 Hz
40 Hz – 80 Hz
Lowest audible octave for humans.
Music low frequencies, kick drums, bass
instruments
Low frequencies 80 Hz – 160 Hz
160 Hz – 320 Hz
Low register of a grand piano.
Middle C of a piano.
Midrange frequencies 320 Hz – 1’280 Hz Music midrange frequencies
Upper midrange frequencies 1’280 Hz – 2’560 Hz
2’560 Hz – 5’120 Hz
Low-order harmonics of most instruments.
The ear is the most sensitive in this range.
High frequencies 5’120 Hz – 10’240 Hz Brightness and harmonics
Extremely high frequencies 10’240 Hz – 20’480 Hz Highest harmonics. Inaudible to humans
above 20 kHz

 Loading...
Loading...