[page 24] | gpelectric.com
OPERATION
5.5 POWER OUTPUT
The Inverter will operate most AC loads within its power rating. When determining whether a
microwave oven can be operated by the Inverter, remember that the power commonly advertised
for microwave ovens is the cooking power (the power delivered to the food), not the power
actually consumed by the microwave oven. The microwave oven will consume 40% to 100%
more than its advertised cooking power. Check the rating sticker on the back of the oven to
determine its actual power draw.
Some induction motors used in refrigerators, freezers, pumps, and other motor operated
equipment require very high surge currents to start. The Inverter may not be able to start some
of these motors, even though their rated current draw is within the Inverter.
If the motor refuses to start, observe the battery voltage indicator while trying to start the motor.
If the battery voltage indicator drops below 11V while the Inverter is attempting to start the
motor, this may be why the motor will not start. Make sure that the battery connections are
good and that the battery is fully charged. If the connections are good and battery is charged,
but the voltage still drops below 11V, you may need to use a larger battery.
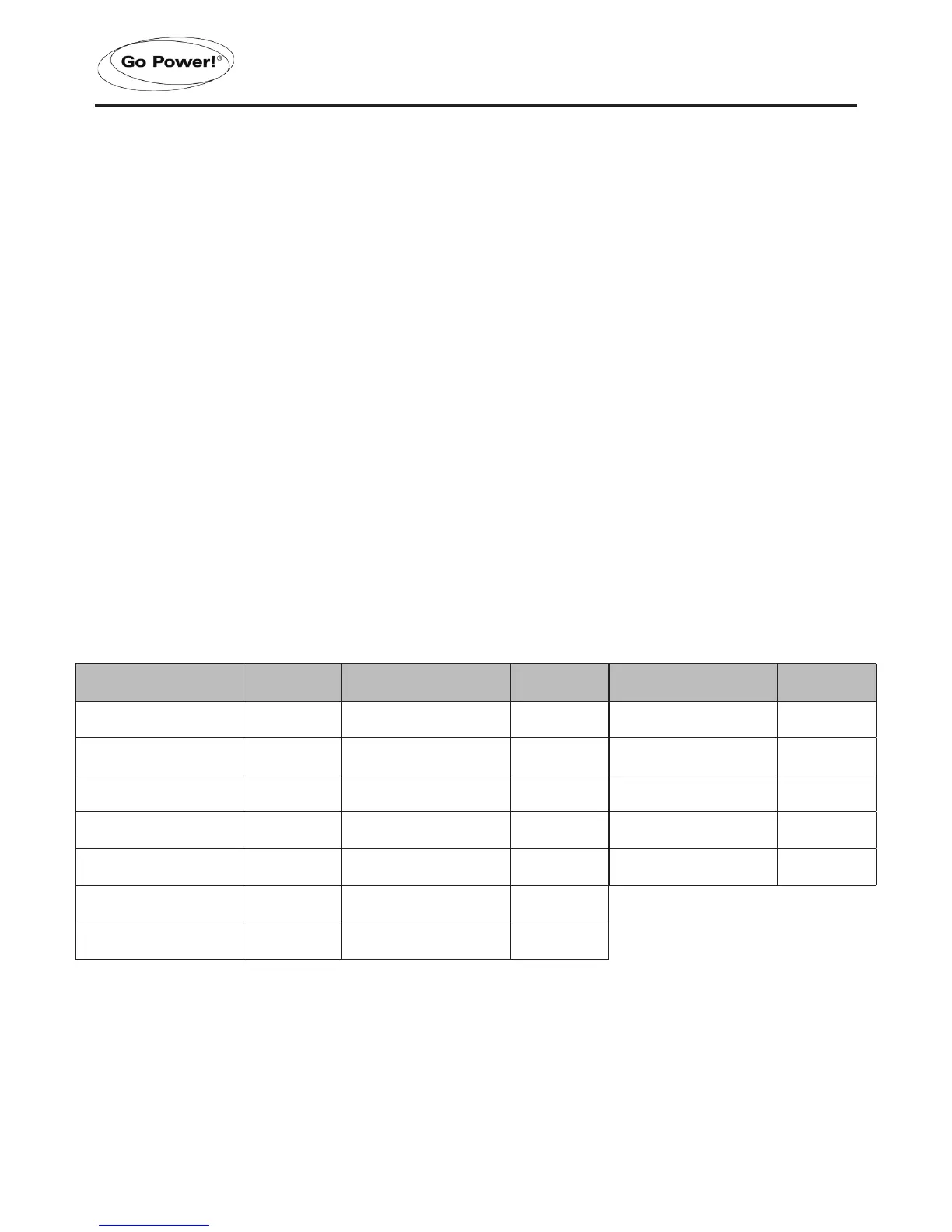
The following table shows the typical power consumption of common devices. Actual device
wattage requirements will vary. Some devices listed may require a pure sine wave Inverter
instead or proper operation.
Device Wattage
Laptop 50
Stereo 200
Mixer 200
Table Fan 200
Computer 250
Small Refrigerator 350
Jigsaw 350
Device Wattage
Belt Sander 350
3/8” Drill 350
Blender 350
Food Processor 400
Reciprocating Saw 600
Vacuum 750
Chest Freezer 800
Device Wattage
Coffee Maker 850
Iron 1050
Mini Microwave 1200
Hair Dryer 1200
10” Saw 1350

 Loading...
Loading...