I 0667 - 13GB
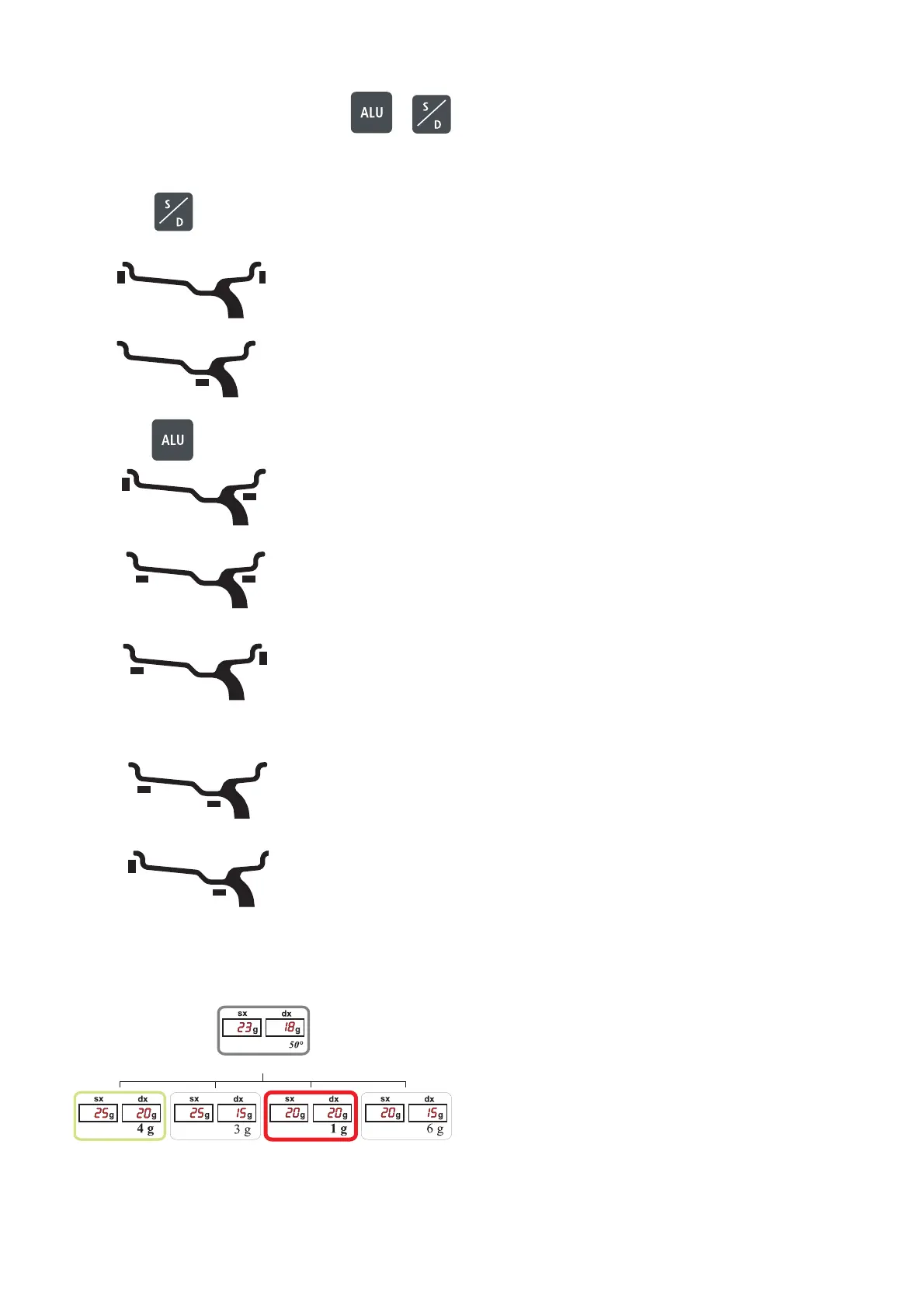
5.9 - DYNAMIC, STATIC, AND MANUAL ALU MODES
From the measurement screen, press or button to select the type required. The 5-LED displays show
the position where to apply the weights. If a spin has already been performed, the processor automatically recalcula-
tes, for each change of mode, the amounts of unbalance according to the new calculation.
Button
DYNAMIC Balancing of steel or light metal rims with
application of clip-on weights on the rim edges.
STATIC The static mode is necessary for motorcycle
wheels or when it is not possible to place the
counterweights on both sides of the rim.
Button
for manual ALU modes
Combined application: adhesive weight outside
and clip-on weight inside.
Combined balancing of alloy rims with application of
adhesive weights on the rim shoulders.
Combined application: adhesive weight inside
and clip-on weight outside.
Automatic ALU modes (see
5.2. AUTO SELECT)
ALU M Balancing of light metal rims with hidden application
of adhesive weights.
ALU 3M Combined application: clip-on weight inside and
hidden adhesive weight on outside (Mercedes).
This program is designed to improve the quality of
balancing without any mental effort or loss of time by
the operator. In fact by using the normal commercially
available weights, with pitch of 5 in every 5 g, and by
applying the two counterweights which a conventional
wheel balancer rounds to the nearest value, there could
be a residual static unbalance of up to 4 g. The damage of
such approximation is emphasized by the fact that static
unbalance is cause of most of disturbances on the vehicle.
This new function, resident in the machine, automatically
indicates the optimum entity of the weights to be applied
by approximating them in an “intelligent” way according
to their position in order to minimize residual static
unbalance.
Initial unbalance
phase shift
Possible approximations
residual static residual static
residual static
Choice with minimum
static residual
With conventional
wheel balancer
residual static
5.10 - MINISTAT - AUTOMATIC MINIMIZATION OF STATIC UNBALANCE
 Loading...
Loading...