Do you have a question about the Intel D945PLRN and is the answer not in the manual?
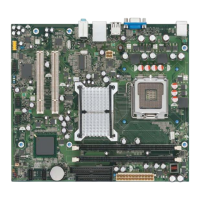
Provides a summary of the board's features, including form factor, processor support, memory, chipset, and interfaces.
Details the types of processors supported by the motherboard, including Pentium D, Pentium 4, and Celeron.
Describes supported memory types, configurations, capacity limits, and features like DDR2 SDRAM and Serial Presence Detect.
Details the Intel 945PL chipset components, including the Memory Controller Hub (MCH) and I/O Controller Hub (ICH7).
Details the PCI Express x16 and x1 connectors, their transfer speeds, and supported features like ASPM and wake events.
Describes the legacy I/O features, including serial, parallel, diskette drive, and PS/2 interfaces.
Explains the Intel High Definition audio subsystem, codec, features like jack sense, and audio connectors.
Details the 10/100 Mbits/sec LAN subsystem, including the ICH7, PLC device, RJ-45 connector, and software.
Covers hardware management features like chassis intrusion detection, fan monitoring, and thermal/voltage monitoring.
Details power management implementation through ACPI and hardware support, including system states and wake-up events.
Provides a map of system memory addresses, including extended, runtime BIOS, and conventional memory ranges.
Lists the fixed I/O addresses for various components like IDE channels, COM ports, and LPT ports.
Details the PCI configuration space for various devices, including graphics ports, audio controllers, USB, and LAN.
Explains interrupt routing via PIC or APIC and lists system resources associated with IRQ numbers.
Describes the board's connectors, categorized into back panel I/O and component-side connectors.
Details the location and function of the jumper block used for BIOS Setup configuration modes (Normal, Configure, Recovery).
Covers mechanical aspects like form factor (ATX) and I/O shield dimensions and requirements.
Discusses DC loading characteristics, add-in board power requirements, fan connector capabilities, and power supply considerations.
Addresses thermal management, including chassis airflow requirements, heatsink types, and component temperature limits.
Lists environmental specifications for temperature, shock, and vibration resistance.
Covers safety regulations, EU Declaration of Conformity, product ecology statements, EMC regulations, and certification markings.
Introduces the Intel BIOS, its storage in SPI Flash, update utilities, and accessing the BIOS Setup program.
Details the organization of the BIOS stored in the Serial Peripheral Interface Flash Memory (SPI Flash).
Explains how the BIOS automatically configures PCI devices and supports PCI IDE connections.
Describes SMBIOS as a management method for computer systems, detailing stored information like BIOS revision and asset tags.
Explains how legacy USB support enables USB device usage before OS drivers are available, for BIOS entry and OS installation.
Covers utilities for updating the BIOS, including Intel Express BIOS Update and Flash Memory Update.
Details choices for booting from diskette, hard drives, CD-ROM, or network, and changing boot devices during POST.
Provides techniques to improve system boot speed by optimizing peripheral selection and BIOS boot parameters.
Explains BIOS security features, including supervisor and user passwords for accessing Setup and controlling booting.
Describes the function of the onboard speaker for providing audible error codes (beep codes) during POST.
Lists beep code patterns and their corresponding frequencies for recoverable errors during POST.
Lists common BIOS error messages and provides brief explanations for issues like low battery or bad checksum.
Explains POST codes generated to I/O port 80h for diagnosing POST failures and locating errors.
| Form Factor | ATX |
|---|---|
| Socket Type | LGA 775 |
| Memory Type | DDR2 |
| Memory Slots | 2 |
| Maximum Memory | 4 GB |
| SATA | 4 x SATA 3Gb/s |
| Chipset | Intel 945PL |
| Supported CPU | Intel Pentium 4, Pentium D, Celeron D |
| Expansion Slots | 1 x PCI Express x16, 3 x PCI |
| IDE | 1 x IDE connector |
| LAN | 10/100 Mbps Ethernet |
| USB Ports | 8 x USB 2.0 |











 Loading...
Loading...