E-Mail: keiths@interfaceforce.com
Technical changes reserved
TS Series Reaction Torque.doc
Internet: www.interfaceforce.com
5.5 Extension Cable
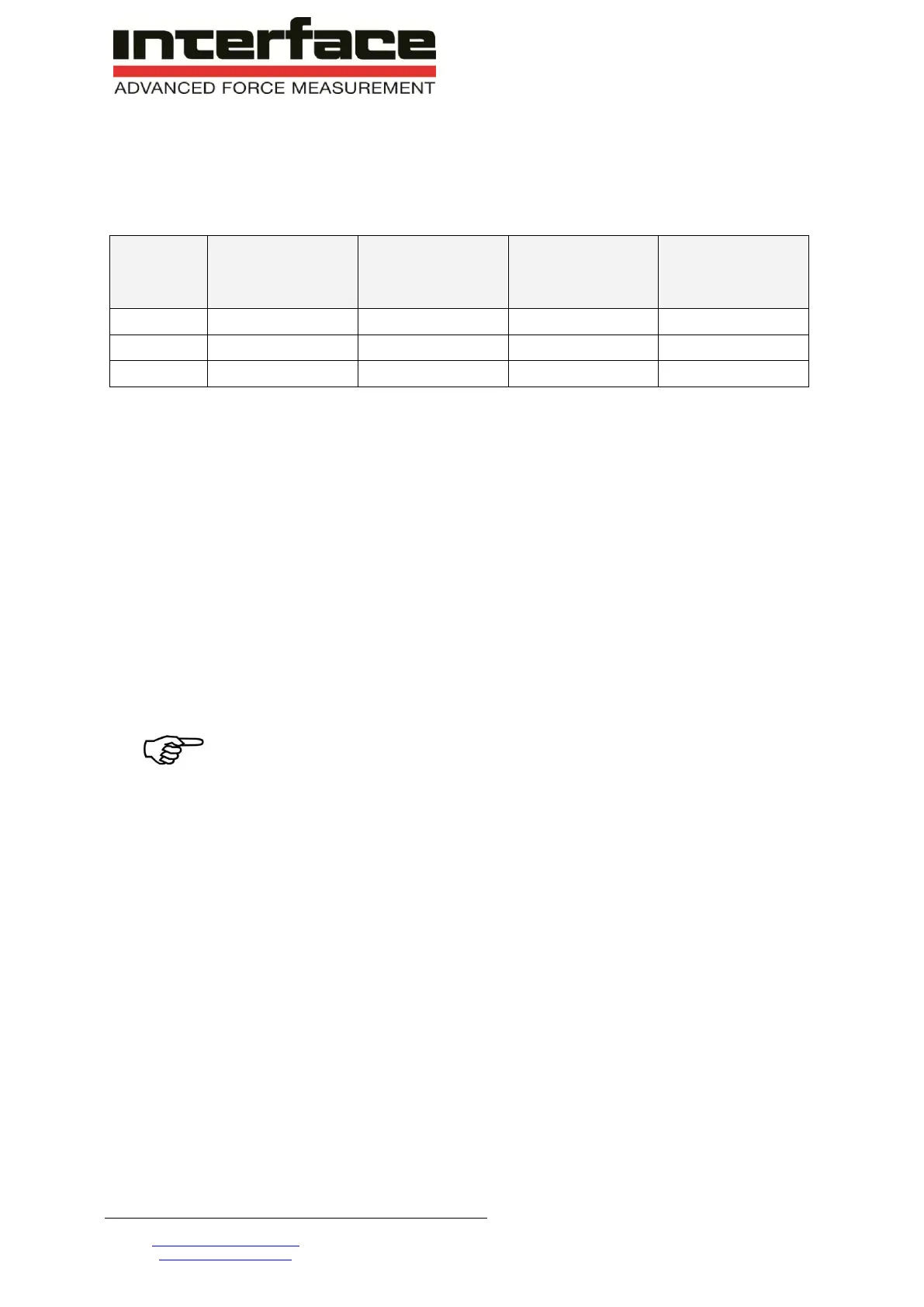
Caution: depending on bridge resistance and wire cross section, the measuring cable length enters into
the characteristic value of the sensor. Therefore order the sensor together with the extension cable.
Dependence of the characteristic value on the cable length:
Deviation per m
cable length at
bridge resistance
350
Deviation per m
cable length at
bridge resistance
700
Deviation per m
cable length at
bridge resistance
1000
Cable resistance = 2 x resistance of the cable length (both feed lines of the sensor).
The sensors with the ordered cable length are calibrated together, Therefore the cable length does not
need to be considered in this case.
5.6 Running of Measuring Cables
Do not run measuring cables together with control or heavy-current cables. Always assure that a large
distance is kept to engines, transformers and contactors, because their stray fields can lead to
interferences of the measuring signals.
If troubles occur through the measuring cable, we recommend to run the cable in a grounded steel
conduit.
6 Measuring
6.1 Engaging
The warming-up period of the torque sensor is approx. 5 min. Afterwards the measurement can be
started.
The warming-up period of the torque sensor is approx. 5 min.
6.2 Direction of Torque
Torque means clockwise or clockwise torque if the torque acts clockwise when facing the shaft end. In
this case a positive electrical signal is obtained at the output.
Torque sensors can measure both clockwise and counter-clockwise direction.
6.3 Static / Quasi-Static Torques
Static and/or quasi-static torque is a slowly changing torque.
The calibration of the sensors occurs statically on a calibration device.
The applied torque may accept any value up to the nominal torque.
6.4 Dynamic Torques
6.4.1 General
The static calibration procedure of torque sensors is also valid for dynamic applications.
Note: The frequency of torques must be smaller than the natural frequency of the mechanical
measurement setup.
The band width must be limited to 70 % of the nominal torque.
 Loading...
Loading...