2/5
Technical data sheet: S000113312EN-1 Updated: Created: 13/01/2021
Cat. No(s): 0 035 45
KNX routeur IP DIN
1. USE
Legrand KNX IP Routers are similar to TP line couplers, except that they
use Ethernet for the main line. However, it is also possible to directly
integrate KNX end devices via IP, making Ethernet respectively IP (Internet
Protocol) a KNX medium.
LEGRAND KNX IP Router is a tunnelling and routing device. It can be used
as line or backbone coupler and provides a data connection between the
upper KNXnet/IP line (main line or backbone) and the lower TP KNX bus
line (sub line).
It also provides with the tunnelling protocol a connection point for ETS to
enable commissioning and monitoring.
IP Router can also connect two separate installations/systems.
Following highlights are characterising LEGRAND KNX IP Router:
• Support of long messages up to 250 byte. In combination with
LEGRAND IP Router line coupler and USB interface "UIM-KNX 42" long
messages are made possible (e.g. energy metering applications).
• It provides the tunnelling protocol, a connection point for ETS to enable
commissioning and monitoring (4 parallel connections are possible).
• IP Router can be used for replacing a line coupler or an area coupler.
The best advantage of this change is using LAN as a fast medium for
exchange of telegrams between the lines and/or areas.
• sending IAK on own message: sending of immediate acknowledged
(IACK) on a frame that is sent by the LEGRAND KNX device itself.
When the IP Router sends a message and there is nobody to
acknowledge this message, the it would repeat the last message up to
3 times. In case there is an IACK, there will be no repetition. The failure
mechanism in case of a negative IACK or BUSY is still maintained.
• switching off the filter table with a button on the device without
reconfiguring the device with ETS, necessary for fast diagnostic on site.
It can temporarily disable filtering of messages by pressing a button.
This eases commissioning and debugging of the system. The temporary
access to other lines is possible without download from ETS.
• Automatically switching on filter tables and filtering of device oriented
tables after time out. Time out is ETS configurable.
No forgetting of reactivating the tables anymore.
• Routing of all physically addressed messages (no filtering of device
oriented messages), no matter of own physical address, on press of a
button on the device without reconfiguring the device with ETS.
• High internal amount of communication buffers capable smoothing
peeks in communication load.
• Detailed possibility for diagnosis by displaying all operational states
with 6 duo LEDs. (Bus OK (each line), traffic (each line), errors/faulty
communication NACK, BUSY on the bus (each line), state of the filter
table …)
• UPnP available to discover the device in IP network. The ETS can
discover the device as communication interface through Eibnet/IP
Search Request.
• WEB interface: currently providing device settings and an opportunity to
switch on to program mode.
1.1 Communication Objects
IP Router has no KNX communication objects.
1.2 IP Router as Programming Interface
IP Router can be used together with the ETS as a programming
interface. The device provides an additional physical address for this
purpose which can be used for a tunneling connection.
1.3 Tunneling
The presence of the Internet Protocol (IP) has led to the definition of
KNXnet/IP.
KNXnet/IP provides the means for point-to-point connections -KNXnet/
IP Tunnelling- for ETS and/or between a supervisory system and a KNX
installation.
KNXnet/IP Device Management provides configuration of KNXnet/IP
devices through the KNX network effectively reducing the time required
for configuration.
1.4 Routing
Routing is how lines or areas may interconnect using IP networks via
KNXnet/IP.
KNXnet/IP Routing defines how KNXnet/IP routers communicate with
each other using IP networks.
1. USE continued
1.5 Coupler
The basic functionality of IP Router is coupling the Ethernet with KNX-TP
line(s).
IP Router provides galvanic isolation between the two connected lines.
Due to the flexibility of IP Router, the coupler can be used as a line
coupler e.g. to connect trough Ethernet several TP lines together, as a
backbone coupler to connect trough Ethernet several TP areas or to
connect different TP installations/systems.
The main task of IP Router is filtering the traffic according the
installation place in the hierarchy or according to the built-in filter tables
for group oriented communication.
The IP Router provides outstanding features compared to other similar
products, for example support for long messages (up to 250 byte
length) and a configurable one button activation of special functions
(e.g. transmit all group telegrams). These are helpful during installation,
during run time and for trouble shooting. The high informative 6 duo
LED display shows accurate the bus status on each line. This helps
identifying common communication problems due to bus load or
retransmissions on both lines.
2. TECHNICAL CHARACTERISTICS
2.1 Electrical characteristics
• Voltage: 230V~
• Frequency: 50/60 Hz
2.2 Connections characteristics
• IP Line RJ45 socket for 10/100BaseT
• KNX Line BUS connection terminal
2.3 Consumption
• BUS: DC 21…30V SELV
• Current consumption: < 20 mA
2.4 Mechanical characteristics
• IP20
• Safety class III
• Number of modules: 2
• Weight: 68 g
2.5 Climate characteristics
• Operating temperature: -5°C to +45°C
• Storage temperature: -20°C to +60°C
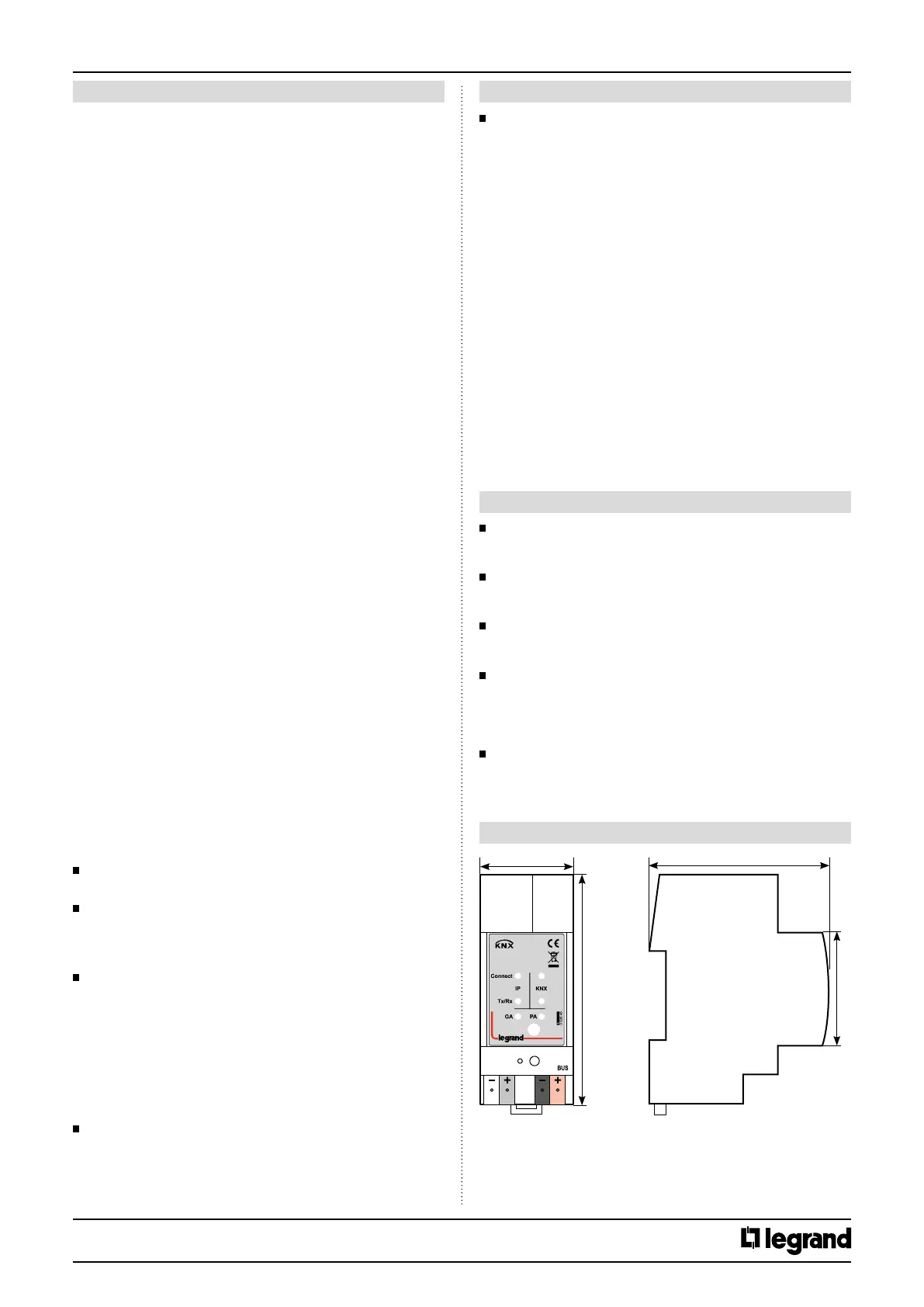
3. DIMENSIONS
36 mm
70 mm
90 mm
45 mm
 Loading...
Loading...