TECHNOLOGY
EN / Alpha alternator - Alpha Pro II regulator / January 2013
7
3 HOW IT WORKS
This user’s manual describes the installation and
operation of the Alpha Alternator together with the
Alpha Pro II regulator from Mastervolt. This charging
system is designed to provide a high output power at
low RPM, which is typical for marine applications. It
consists of the following main components (See
figure 1):
1 Alpha alternator (included)
2 Alpha Pro II charge regulator (included)
3 Battery fuses (10A fuse included)
4 Batteries (not included)
5 Temperature sensor (included)*
*The picture shows an installation without
MasterShunt. If you have a MasterShunt installed,
the Alpha Pro II temperature sensor is better
mounted on the alternator.
Fig.1: Basic charging system consisting of the
Alpha Alternator and the Alpha Pro II regulator
3.1 ALPHA ALTERNATOR
Mastervolt Alpha alternators are specially designed
to provide high power even at low RPM. A pulley
ratio of 1:2 – 1:3 and an engine idle speed of around
700-800 rpm will generate substantial current for
charging the battery sets and powering the
connected equipment.
Mastervolt alternators are resistant to the high
temperature of the engine room, allowing the engine
to serve as the energy source for onboard
consumers and as a quick charger for the service
and starter batteries.
3.2 ALPHA PRO II REGULATOR
The Alpha Pro II voltage regulator controls the
alternator’s output voltage. It is designed for optimal
recharging of both wet, gel, AGM and li-ion batteries.
Battery charging is accomplished in three automatic
stages: BULK, ABSORPTION and FLOAT. Simple,
automatic operation is made possible by the
microprocessor that is the brain of the Alpha Pro II
regulator.
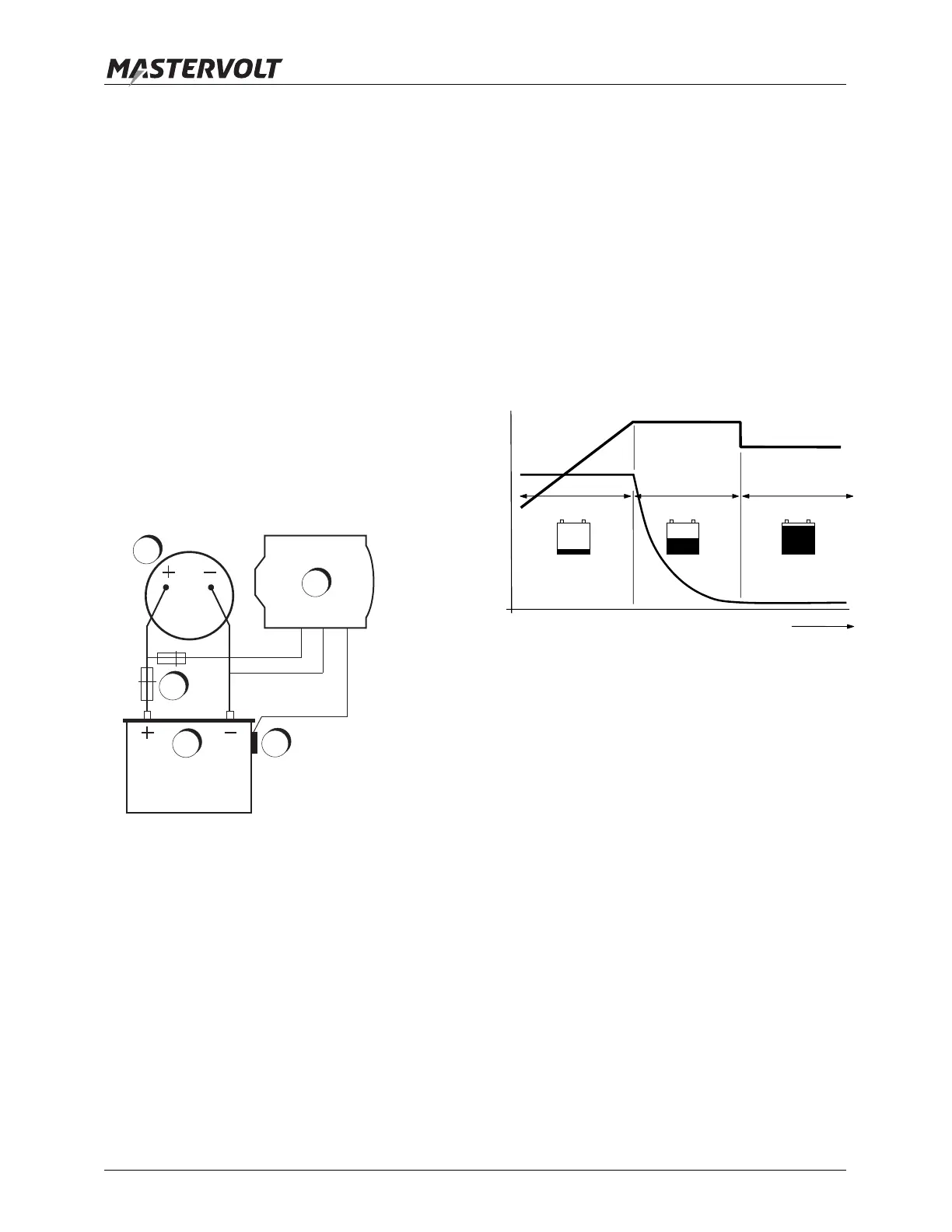
3.2.1 Three step charging system
Figure 2: Three step plus charge system
See figure 2. The first step of the three step plus
charge system is the BULK phase (A), in which the
output current of the charging system is limited by
the maximum output current of the alternator and the
engine RPM. At this stage the major part of the
battery capacity is rapidly charged. The current
charges the batteries and the voltage will rise to the
absorption voltage. Refer to the specifications for the
charging voltages for different batteries.
The duration of this phase depends on the ratio of
charging capacity to battery capacity and on the
degree to which the batteries were discharged to
begin with.
The bulk phase is followed by the absorption phase.
(B). The absorption charge starts when the voltage
on the batteries has reached the absorption voltage,
and ends when the battery is fully charged. Battery
voltage remains constant throughout this stage, and
the charge current depends on the state of charge of
the battery, the battery type, the ambient
temperature, and so on. With a wet cell battery this
stage lasts about four hours, with gel, AGM and li-
ion batteries around three.
CHARGE CURRENT
BATTERY VOLTAGE
BULK
ABSORPTION
FLOAT
TIME

 Loading...
Loading...