MEA INC
2600 American Lane | Elk Grove Village, IL 60007 | USA
T +1 847 766 9040 | F +1 847 350 1951
COMPLETE CONTROL
www.meaincorporated.com
MEA Incorporated | Hawk Actuator Instruction and Operation Manual
02/2018
16
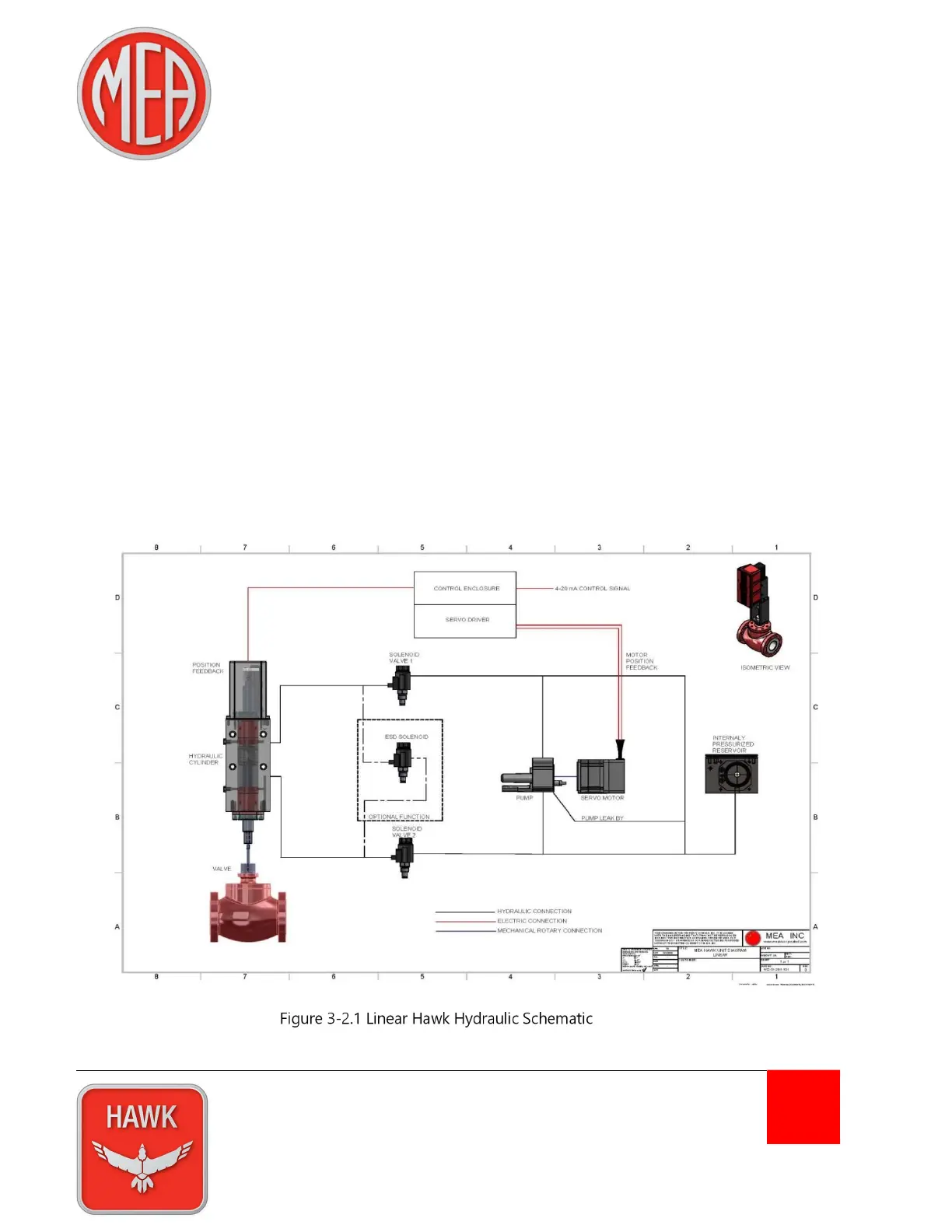
3-2 Linear Actuator
The linear version of the Hawk actuator consists of a single, double-acting, equal displacement cylinder,
which in combination with pressurized fluid from the HPS, creates linear movement of the driven device.
In Control mode, the actuator receives a desired position signal from the DCS. This signal is compared to
the current position signal provided by the actuator’s position feedback. The difference between the
desired position and current position is the deviation. If this deviation exceeds the user defined deadband
the servo driver begins the process of moving the actuator by first energizing the motor, which in turn
spins the pump. For a brief period, less than 80 ms, the pump builds pressure in the system before the
solenoids are energized. Once sufficient system pressure is generated, the solenoids open and the
hydraulic fluid moves the cylinder and the driven device.
Ultimately, the actuator will move the driven device in the direction that will decrease the deviation to 0%
± the deadband. Once reaching this position the servo motor and solenoids will de-energize and the
actuator will remain in place until the next deviation occurs.
Figure 3-2.1 Linear Hawk Hydraulic Schematic
 Loading...
Loading...