Do you have a question about the Miller Big Blue 300 P and is the answer not in the manual?
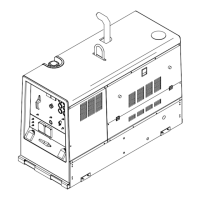
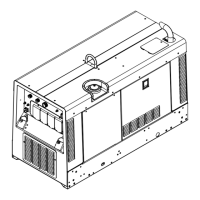
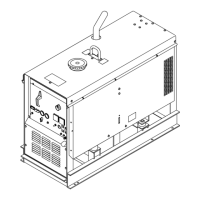
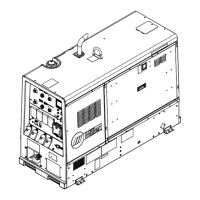
Identifies the unit as Big Blue 300 P PRO 300 CAT, an Engine Driven Welding Generator.
Lists the welding processes the generator supports, including Stick, TIG, MIG, Flux Cored, and Air Carbon Arc.
Emphasizes Miller's long-standing dedication to quality and customer service in welding equipment.
Explains the manual's role in user assistance, safety, and troubleshooting, mentioning ISO 9001 certification.
Highlights Miller's hassle-free warranty program for its power sources, including details on coverage.
Explains safety symbols (Danger, Warning, Notice) and general precautions for operating welding equipment.
Details the risks of electric shock from live parts and provides precautions like wearing protective gear and avoiding damp areas.
Warns about burns from hot parts and eye injuries from flying metal, recommending appropriate PPE.
Details risks like electric shock, hot parts, fumes, and flying metal associated with arc welding.
Addresses hazards from welding fumes and gases, emphasizing ventilation and respirator use, and noise-related hearing damage.
Covers dangers from arc rays causing burns and welding sparks causing fires or explosions, with prevention measures.
Warns about magnetic fields affecting medical implants and the explosion risk of damaged gas cylinders.
Covers engine-specific dangers like battery explosion, fuel fires, moving parts, hot engine components, and steam/coolant burns.
Warns against indoor generator use due to carbon monoxide and fire risks from exhaust sparks.
Outlines dangers of breathing compressed air and hazards from pressurized air systems and hoses.
Addresses hazards related to unit installation, falling units, overheating, flying sparks, and moving parts.
Addresses dangers associated with welding wire and the risk of overheating equipment due to overuse.
Warns about static discharge damage to PC boards and injury risks from trailer tilting.
Explains potential interference from HF radiation with electronic equipment and how to mitigate it.
Details how arc welding can cause interference and methods to reduce it, including cable management and location.
States warnings about chemicals in exhaust and battery components known to cause cancer or birth defects.
Reiterates warnings about cancer and birth defects from engine exhaust chemicals for gasoline and diesel engines.
Lists key safety standards and organizations relevant to welding, cutting, and compressed gases.
Discusses potential interference from HF and Arc Welding, and EMF health considerations.
Lists relevant safety standards and discusses EMF effects on medical devices and exposure reduction.
Explains the meaning of various warning labels found on the equipment, including setup, operation, and maintenance instructions.
Provides a comprehensive list of symbols used in the manual for controls, processes, measurements, and connections.
Details welding output ranges, generator power ratings, engine types, and fuel capacity.
Lists the unit's dimensions, weight, and operating angle limitations for safe handling and placement.
Presents graphical representations of voltage and amperage output capabilities for Stick, MIG, and TIG welding modes.
Shows a graph illustrating typical fuel usage based on DC weld amperes under 100% duty cycle conditions.
Explains duty cycle percentages and provides a chart showing weld amperes versus duty cycle to prevent overheating.
Displays a graph showing available AC power in amperes for 120V and 240V receptacles.
Provides instructions on safely moving the generator and considerations for its location and airflow clearance.
Details methods for securely mounting the generator using brackets or bolts, warning against welding on the base.
Explains the importance of grounding the generator to the vehicle frame to prevent electrical hazards.
Instructs users to find the unit's rating label, which provides essential information about its specifications.
Provides instructions for installing the exhaust pipe, including direction and safety considerations.
Guides users through the process of activating a dry charge battery, including electrolyte addition and charging.
Details the correct procedure for connecting the battery, emphasizing safety, especially connecting the negative cable last.
Outlines essential checks for engine oil, fuel, and coolant levels before starting the generator.
Explains how to correctly connect weld cables for Stick, TIG, MIG, and FCAW processes, emphasizing proper polarity and connection.
Provides a chart to help users select the correct weld cable size based on amperage, duty cycle, and cable length.
Describes how to connect remote controls and other devices to the RC14 receptacle for voltage/amperage adjustment.
Identifies and illustrates the various controls on the front panel of the welding generator.
Explains the function of engine controls like Preheat, Engine Control Switch, and Stop Lever for starting and stopping.
Details the purpose of the Fuel/Hour Gauge and Engine Indicator Light for monitoring engine status.
Describes weld controls including Remote Receptacle, Process/Contactor Switch, and Voltage/Amperage Control for setting output.
Explains how the DC Voltmeter and DC Ammeter display preset and actual output values for welding.
Details the function of the Process/Contactor Switch for selecting weld processes and output control modes.
Explains how to use Lift-Arc for DCEN GTAW welding, including arc start and end procedures like Crater-Out and Auto-Stop.
Describes how to connect and use remote controls for adjusting voltage and amperage, and how the Auto Sense Remote feature works.
Explains the display readings for engine hours, oil change intervals, fuel level, oil pressure, and coolant temperature, including reset procedures.
Identifies the different AC power receptacles (120V, 240V) and their protective circuit breakers/protectors.
Provides a schedule for routine maintenance tasks based on operating hours, covering checks, changes, and replacements.
Details maintenance schedules and part numbers for Perkins and CAT diesel engines, including fluid types and filter recommendations.
Guides users on cleaning or replacing the air cleaner primary and safety elements, dust cap, and ejector.
Explains how to inspect and clean the spark arrestor muffler, including removing debris from the cleanout hole.
Outlines the procedure for changing coolant and checking coolant levels in the radiator and recovery tank.
Describes how to adjust engine speed on standard models using the adjustment screw, emphasizing factory settings and warranty.
Explains how to adjust engine speed for idle operation on models with the optional automatic idle system.
Provides instructions for changing oil and filters, replacing fuel filters, and draining the fuel tank or sludge.
Identifies various fuses and circuit breakers that protect the generator's electrical systems and explains their functions.
Details how to inspect generator brushes for wear and replace them if damaged or below minimum length.
Explains the meaning of various help codes displayed on the voltmeter/ammeter to diagnose fault conditions.
Provides remedies for common welding problems like no weld output, erratic output, or low voltage/amperage.
Offers solutions for problems related to generator power output, such as no output or low output at receptacles.
Addresses engine problems like not cranking, not starting, hard starting in cold weather, and sudden stopping.
Covers engine issues like slow stopping, battery discharge, idle speed problems, and oil usage during run-in.
Presents the main circuit diagram for the welding generator, illustrating electrical components and connections.
Explains wetstacking in diesel engines during run-in and how to prevent it with proper operation.
Provides step-by-step instructions for performing the engine run-in procedure using a load bank to seat piston rings.
Details the process of running in the engine using a resistance grid for generator load, including monitoring and adjustments.
Guides on selecting equipment, emphasizing double-insulated tools and proper grounding.
Reiterates the importance of grounding the generator to the vehicle frame for electrical safety and static hazard prevention.
Explains how to properly ground the generator when supplying power to building electrical systems.
Details how to calculate power needs for resistive and non-resistive loads, using examples for watts and starting amperage.
Lists approximate starting and running watts for various types of industrial motors based on horsepower.
Provides approximate power requirements for common farm and home equipment like de-icers, pumps, and coolers.
Lists approximate starting and running watts for contractor tools and equipment such as drills, saws, compressors, and pumps.
Explains how to determine the starting amperage required for single-phase induction motors using a table and formula.
Advises on limiting generator load to 90% of capacity and the 5-second rule for starting motors to prevent damage.
Illustrates typical connections for supplying standby power to building systems using transfer switches and disconnects.
Provides guidelines and charts for selecting appropriate extension cord lengths based on current, load, and conductor size for 120V loads.
Offers guidance and charts for choosing correct extension cord lengths for 240V loads, considering current, load, and conductor size.
Shows an exploded view of the main assembly with numbered parts corresponding to the parts list.
Details the terms, periods, and conditions of Miller's limited warranty for welding equipment, including exclusions.
Lists items and conditions not covered by the warranty, such as consumable parts, improper installation, and lack of maintenance.
Provides space for the user to record personal information about the equipment, like model and serial number.
Guides users on how to contact distributors for service, parts, training, and technical information.
| Model | Big Blue 300 P |
|---|---|
| Dimensions | 42 x 22 x 27 inches |
| Type | Welding Generator |
| Welding Amperage Range | 30-300 A |
| Output Current Range | 20 - 300 Amps |
| Duty Cycle | 100% |
| Fuel Capacity | 12.5 gal |
| Input Voltage | Not applicable |
| Frequency | Not applicable |







 Loading...
Loading...