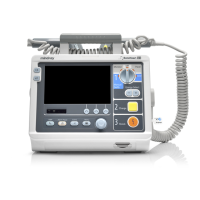
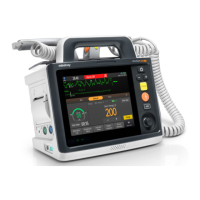
5 - 12 Defibrillator/Monitor Operator’s Manual
Intermittent Signal 1. Check that cables are properly connected.
2. Check that electrodes are not detached or dry. Perform skin preparation
again as described in5.4Preparing for ECG Monitoring and Measurement.
3. Check that the patient cable or leadwires are not damaged. Change
them if necessary.
Excessive alarms: heart rate, lead fault 1. Check that electrodes are not dry. Perform skin preparation again and
replace the electrodes. For details, refer to 5.4Preparing for ECG
Monitoring and Measurement.
2. Check for excessive patient movement or muscle tremor. Reposition the
electrodes. Replace with fresh and moist electrodes if necessary.
Low Amplitude ECG Signal 1. Check that the ECG gain is not set too low. Adjust the gain as required.
For details, refer to 5.6.5Changing ECG Waveform Size.
2. Perform skin preparation again and re-place the electrodes. For more
information, refer to 5.4Preparing for ECG Monitoring and Measurement.
3. Check electrode application sites. Avoid bone or muscular area.
4. Check that electrodes are not dry or used for a prolonged time. Replace
with fresh and moist electrodes if necessary.
No ECG Waveform 1. Check that the ECG gain is not set too low. Adjust the gain as required.
For details, refer to 5.6.5Changing ECG Waveform Size.
2. Check that the leadwires and patient cables are properly connected.
Change cable and lead wires.
3. Check that the patient cable or leadwires are not damaged. Change
them if necessary.
Base Line Wander 1. Check for excessive patient movement or muscle tremor. Secure
leadwires and cable.
2. Check that electrodes are not detached or dry and replace with fresh
and moist electrodes if necessary. For details, refer to 5.4Preparing for
ECG Monitoring and Measurement.
3. Check for ECG filter setting. Set ECG Filter mode to [Monitor].
Problem Corrective Actions
 Loading...
Loading...