Appendix - 79
MELSEC-Q
APPENDICES
FIXED-FEED
This is the feeding of a set dimension for
cutting sheet and bar workpieces into the
designated dimensions. Incremental system
positioning is often used. The current value is
not incremented, even when the feed
operation is repeated.
FLASH MEMORY
This battery-less memory can be used to store
parameters and positioning data for backup.
Because it is battery-less, battery maintenance
is not required
FLAT TYPE MOTOR (PANCAKE MOTOR)
About 100mm shorter in axial dimension than
the standard motor. Used when the servo
motor is installed in a small space.
FLS SIGNAL (Forward Limit Switch Signal)
This is the input signal that notifies the user
that the upper limit switch (b contact
configuration, normally ON) outside the
movement range at which positioning control is
carried out was activated.
The positioning operation stops when the
external FLS signal (b contact) turns OFF
(non-continuity status).
FORMATTING
The initialization of a disk.
An operation to write rules, contents, etc., to a
disk.
In the above case, the disk memory capacity
will only decrease by the amount of the
formatting.
G CODE
These are standardized (coded) 2-digit
numerical values (00 to 99) designating
various control functions of the NC module.
Also called G functions.
Example :
G01 Linear interpolation
G02 Circular interpolation CW (clockwise)
G04 Dwell
G28 OPR
G50 Max. spindle speed setting
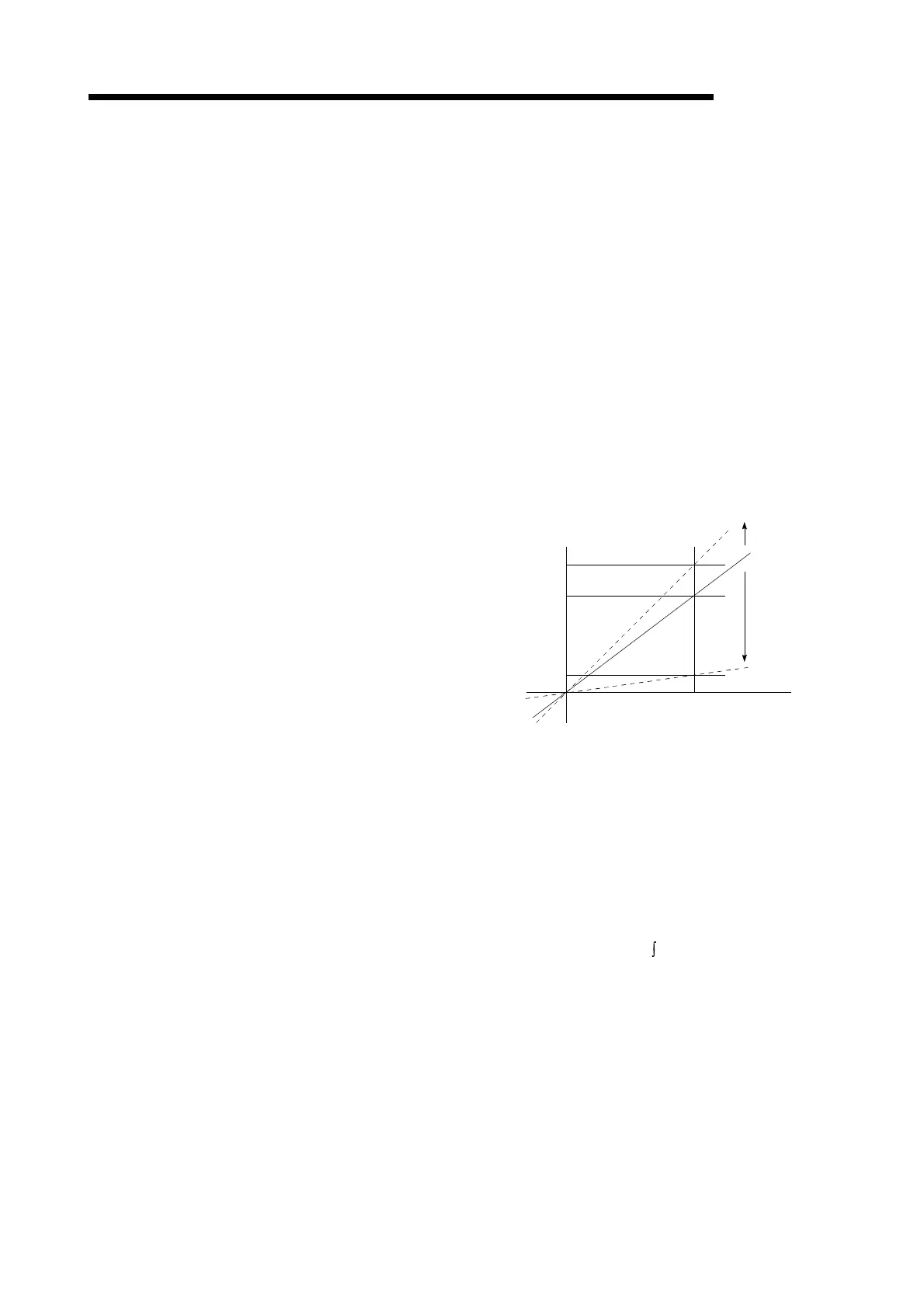
GAIN
The changing of the ratio between two values
having a proportional relation. Seen on a
graph, the changing of the incline of the
characteristics.
13
10
2
10
Raising
the gain
Output Lowering
the gain
Input
For example, when 10 is output for an input of
10, the output can be changed to 12, 5, etc.,
by changing the gain.
GD
2
The inertia moment. The sum total of the mass
(dm) of each small area configuring an object
multiplied by the square of the distance (r) of
each of those areas from a given straight line.
The relation with I =
r
2
dmGD
2
is given by 4gI,
with "g" being gravitational acceleration.

 Loading...
Loading...











