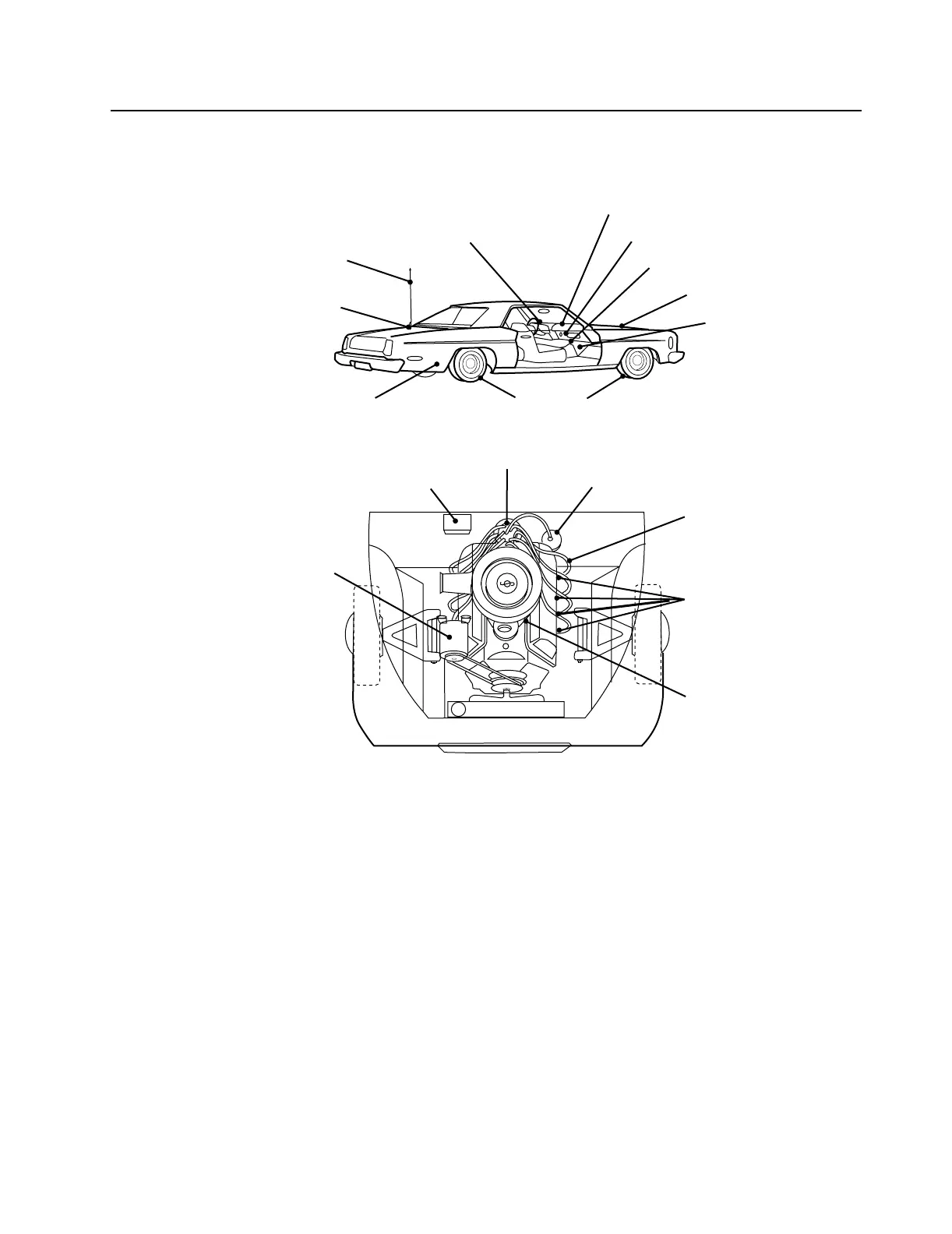
Noise Sources 17
It is impractical to prevent all arcing in the standard vehicle electrical system. In an 8-cylinder engine
running at 2,000 RPM, arcing occurs across the spark plugs at a rate of 8,000 sparks per minute or
133 sparks per second. Electrical motors and generators also produce arcs.
7.3 Conducted Noise
Conducted noise enters the radio through the points where the radio is attached to the vehicle’s
electrical system such as battery cables, ignition switch, chassis ground etc. It can be generated by
electrical transients, electrical motors, poor grounding points, or inadequate electrical system filtering
(from alternators, generators, voltage regulators, or weak batteries). Conducted noise can degrade
both transmit and receive performance of a mobile radio.
7.4 Induced Noise
Induced noise enters the radio through the proximity of radio wiring to other wiring in the vehicle.
Electrical currents through the standard vehicular wiring can induce undesirable noise signals into the
radio cabling. Communication is degraded simply because the wiring provides a transformer-type
coupling action without any actual physical connection. Induced noise can degrade both transmit and
receive performance of a mobile radio.
Figure 7-1. Noise Sources
Spark Plugs
Idle Stop
Solenoid
FL0830260-O
Spark Plug
Wires
Alternator or
Generator
Voltage
Regulator
Distributor Ignition
Coil
Wheel Static
Electric Fuel Pump
Antenna Ground
or Location
Radiated Noise Pick-up
Inadequate Terminal
or Fuse Block Filtering
Windshield Wiper Motor
Heater Air Conditioner Blower
Electric Windows Motors
Hood Static
Power Seat Motor

 Loading...
Loading...