© National Instruments | 7-13
X Series User Manual
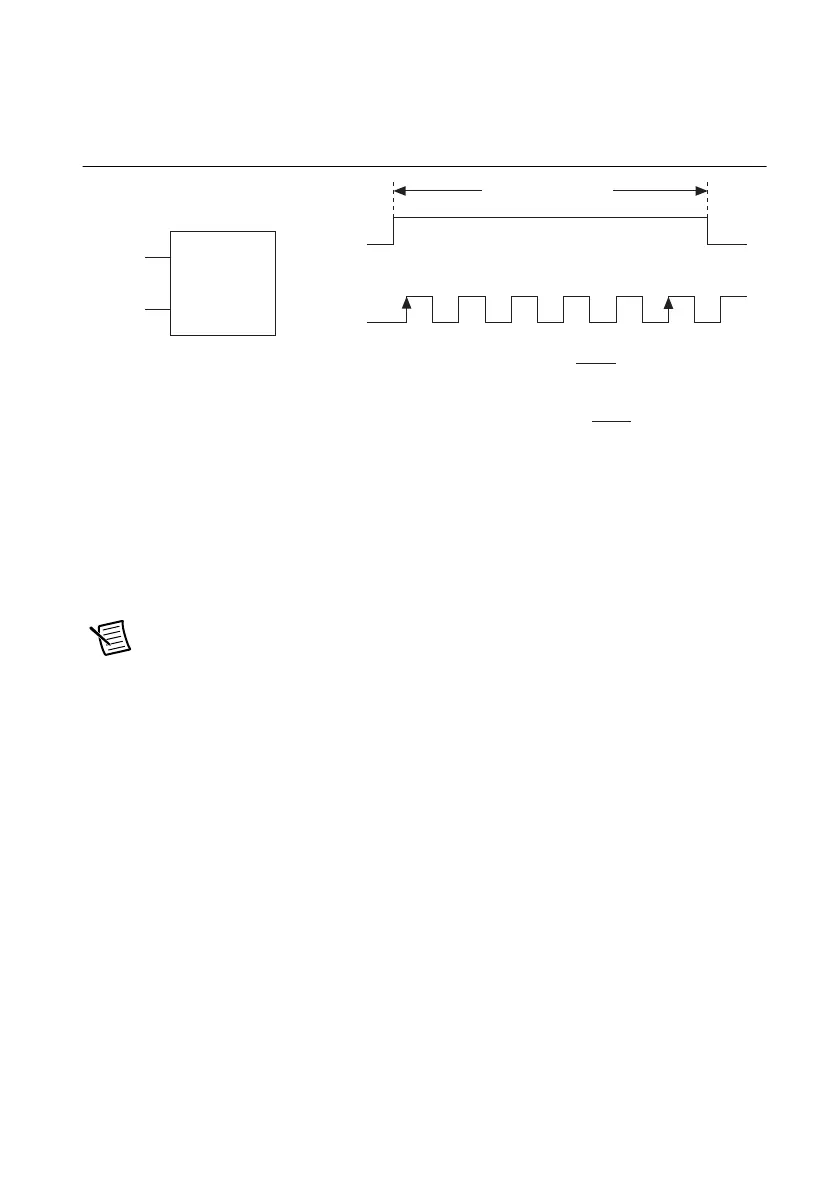
Figure 7-13 illustrates this method. Another option is to measure the width of a known period
instead of a known pulse.
Figure 7-13. High Frequency with Two Counters
Large Range of Frequencies with Two Counters
By using two counters, you can accurately measure a signal that might be high or low frequency.
This technique is called reciprocal frequency measurement. When measuring a large range of
frequencies with two counters, you generate a long pulse using the signal to measure. You then
measure the long pulse with a known timebase. The X Series device can measure this long pulse
more accurately than the faster input signal.
Note Counter 0 is always paired with Counter 1. Counter 2 is always paired with
Counter 3.
Pulse
fx
Pulse
fx
Gate
Source
12…
N
Pulse-Width
Measurement
T =
N
fx
Frequency of fx =
T
Width of
Pulse
N
Width of Pulse (T )

 Loading...
Loading...