© National Instruments | 3-11
NI 6612 User Manual
Frequency Measurement
Frequency Measurement Considerations
The NI 6612 supports five methods for measuring frequency. Table 3-1 summarizes the five
frequency measurement methods.
In choosing a method, consider the measurement duration, timing, and number of counters.
Measurement duration can be either a fixed time or a fixed number of periods of the input signal.
That is, to calculate frequency, the counter can either:
• measure the number of periods (p) that occur during a specified time duration (t).
Figure 3-13 shows an example with a measurement duration of 100 µs.
• measure the time (t) it takes to observe a specified number of periods (p). Figure 3-14
shows an example with a measurement duration of three periods.
In both cases, the frequency, f, is given by:
Figure 3-13. Frequency Measurement Using Time
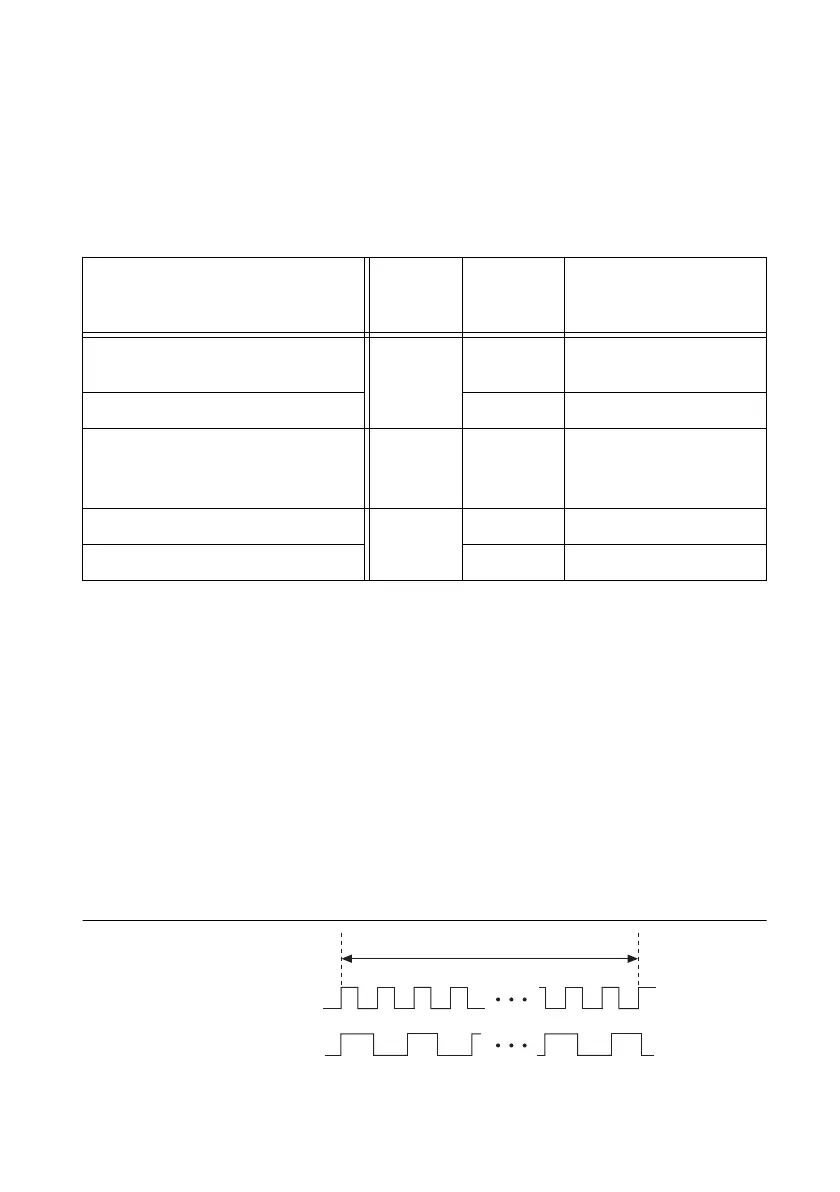
Table 3-1. Frequency Measurement Methods
Method Timing
Number
of
Counters
Measurement
Duration
Sample Clock (with Averaging) Sample
Clock
1 Time between
two sample clock pulses
Sample Clock (without Averaging) 1 1 period of input signal
Low Frequency with 1 Counter Sample
Clock or
Implicit
1 1 period of input signal
Large Range with 2 Counters Implicit 2 P periods of input signal
High Frequency with 2 Counters 2 T time
Count
Signal to Measure
Counter Timebase
(100 MHz)
measurement duration = 100 µs
1
0
2
50

 Loading...
Loading...











