F3SJ-E/F3SJ-B/F3SJ-A
41
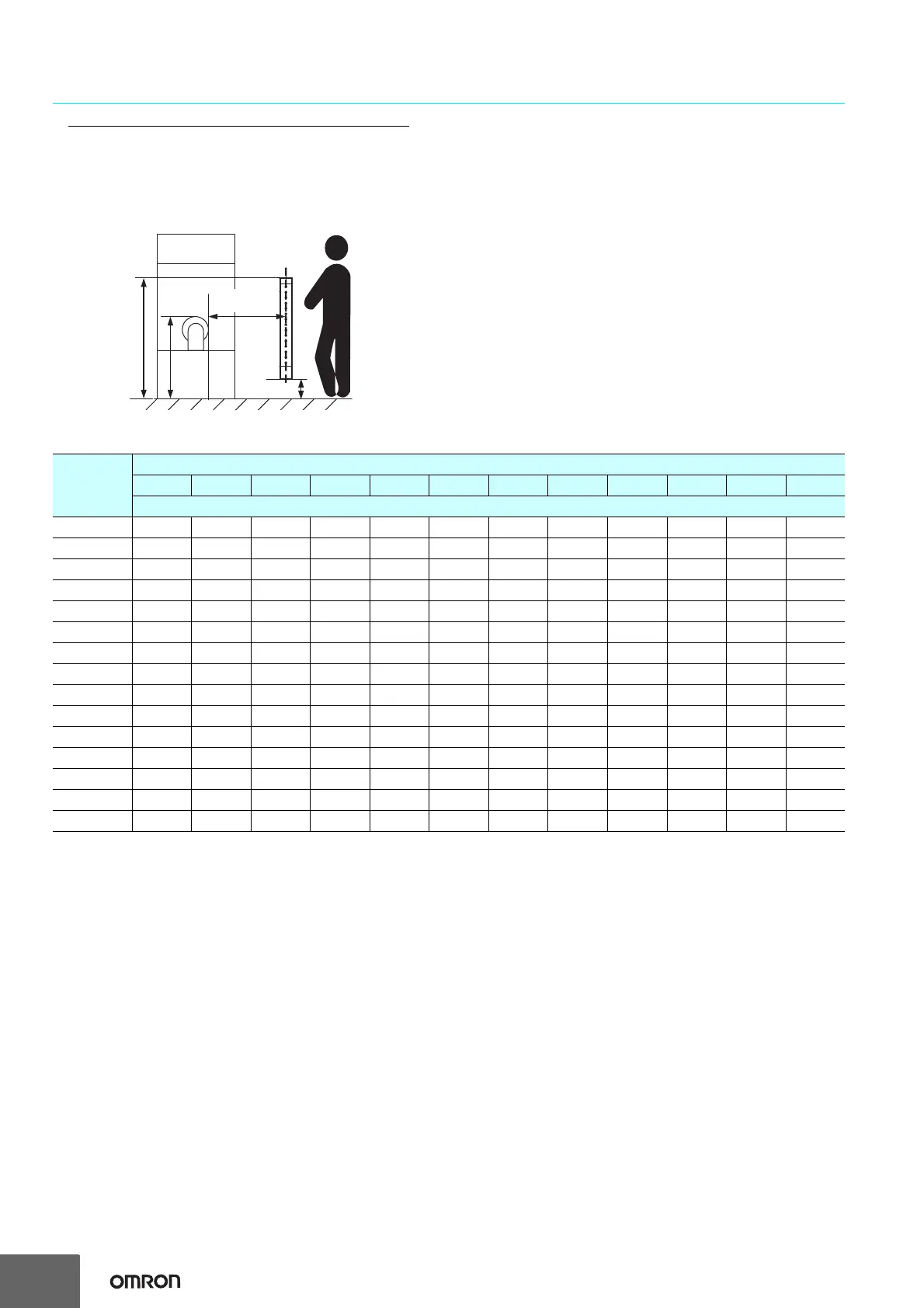
Possible Circumventing by Reaching Over the Detection Zone
If access to the hazardous zone by reaching over the detection
zone of vertically mounted F3SJ cannot be excluded, the height
and the safety distance, S, of the F3SJ shall be determined. S shall
be determined by comparison of the calculated values in Detection
Zone Orthogonal to Direction of Approach. The greater value
resulting from this comparison shall be applied.
S=(K × T) + Cro . . . Formula (5)
• S: Safety distance
• K: Approach speed to the detection zone
• T: Total response time of the machine and F3SJ
• Cro: Approach distance based on the distance which personnel
can move towards the hazardous zone of a machine by reaching
over the detection zone. The distance is determined in the table
below based on the height of the hazardous zone, a, and the
height of the upper edge of the detection zone, b.
Note: Lower edge of the detection zone above 300 mm in relation to
the reference plane does not offer sufficient protection against
crawling below.
First, use K = 2,000 mm/s in formula (5) for the calculation. If the
result of this calculation is less than 100 mm, use S = 100 mm.
If the result exceeds 500 mm, use K = 1,600 mm/s to recalculate it.
If the result of the recalculation is less than 500 mm, use S = 500
mm.
Note: 1. Upper edge of the detection zone below 900 mm is not included since they do not offer sufficient protection against circumventing or
stepping over.
2. When determining the values of this table, it shall not be interpolated. If the known values a, b or Cro are between two values of this table,
the greater safety distance shall be used.
[Calculation example]
•
T:
Tm + Ts (s)
•
T
m: Machine's response time (s)
•
T
s: Response time of the F3SJ from ON to OFF (s)
• a: Height of machine hazardous zone (mm)
•
b
: Height of upper edge of detection zone (mm)
When Tm = 0.05 s, Ts = 0.01 s, a = 1,400 mm, b = 1,500 m:
From the table above, Cro = 850 mm. Since b is between 1,400
mm and 1,600 mm, b = 1,400 mm which has the greater Cro value,
shall be used.
S = 2,000 mm/s × (0.05 s + 0.01 s) + 850 mm
= 970 mm
Since 970 mm is greater than 500 mm, use K = 1,600 mm/s and
recalculate it.
S = 1,600 m/s × (0.05 s + 0.01 s) + 850 mm
= 946 mm
Compare S = 946 mm with the calculation in Detection Zone
Orthogonal to Direction of Approach, and choose the larger value
as the safety distance.
For the system with a detection capability of 40 mm max., the
safety distance S is 946 mm since this is larger than S = 120 mm
calculated in the calculation example of Detection Zone
Orthogonal to Direction of Approach.
For the system with a detection capability larger than 40 mm, the
safety distance S is 946 mm since this is the same value as S =
946 mm calculated in the calculation example of Detection Zone
Orthogonal to Direction of Approach.
Hazard
Safety
distance (S)
Reference plane
a
b
300 mm max.
Height of
hazardous
zone, a
Height of upper edge of detection zone, b
900 1000 1100 1200 1300 1400 1600 1800 2000 2200 2400 2600
Additional distance to hazardous zone, Cro
2600 000000000000
2500 400 400 350 300 300 300 300 300 250 150 100 0
2400 550 550 550 500 450 450 400 400 300 250 100 0
2200 800 750 750 700 650 650 600 550 400 250 0 0
2000 950 950 850 850 800 750 700 550 400 0 0 0
1800 1100 1100 950 950 850 800 750 550 0 0 0 0
1600 1150 1150 1100 1000 900 850 750 450 0 0 0 0
1400 1200 1200 1100 1000 900 850 650 00000
1200 1200 1200 1100 1000 850 800 000000
1000 1200 1150 1050 950 750 700 000000
800 1150 1050 950 800 500 450 000000
600 1050 950 750 550 0 0 000000
4009007000000000000
20060000000000000
0 000000000000

 Loading...
Loading...