9
OPERATION
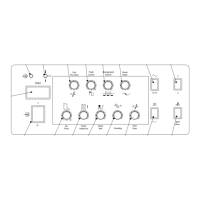
1
2
3
1
4
5
6
7
8
9 10
lead to the + terminal for direct current straight
polarity. Direct current straight polarity is the most
widely used polarity for DC TIG welding. It allows
limited wear of the electrode since 70% of the heat is
concentrated at the work piece. Connect the gas hose
on the TIG torch to the gas outlet on the gas regulator.
Move the selector switch on the front panel of the
machine to the LIFT-TIG posion.
Torch starng in Li TIG mode
Ensure the gas supply is switched on to the machine.
Briey contact the p of the tungsten electrode down
onto the work piece with the torch at around 70
0
from
vercal. Depress the trigger to start the gas ow and
switch on the power, li the torch up from the work
piece to draw out an arc. To prevent melng of the
end of the tungsten the machine will increase the
output current when it detects the rise in arc voltage
as the tungsten is lied from the work piece. At the
end of the weld release the torch trigger and the
power will slope down and switch o.
Torch starng in HF mode
Ensure the gas supply is switched on to the machine.
Hold the torch with the p of the tungsten approx 2-3
mm from the job. Depress the trigger to start the gas
ow and switch on the power. At the end of the weld
release the torch trigger and the power will slope
down and switch o.
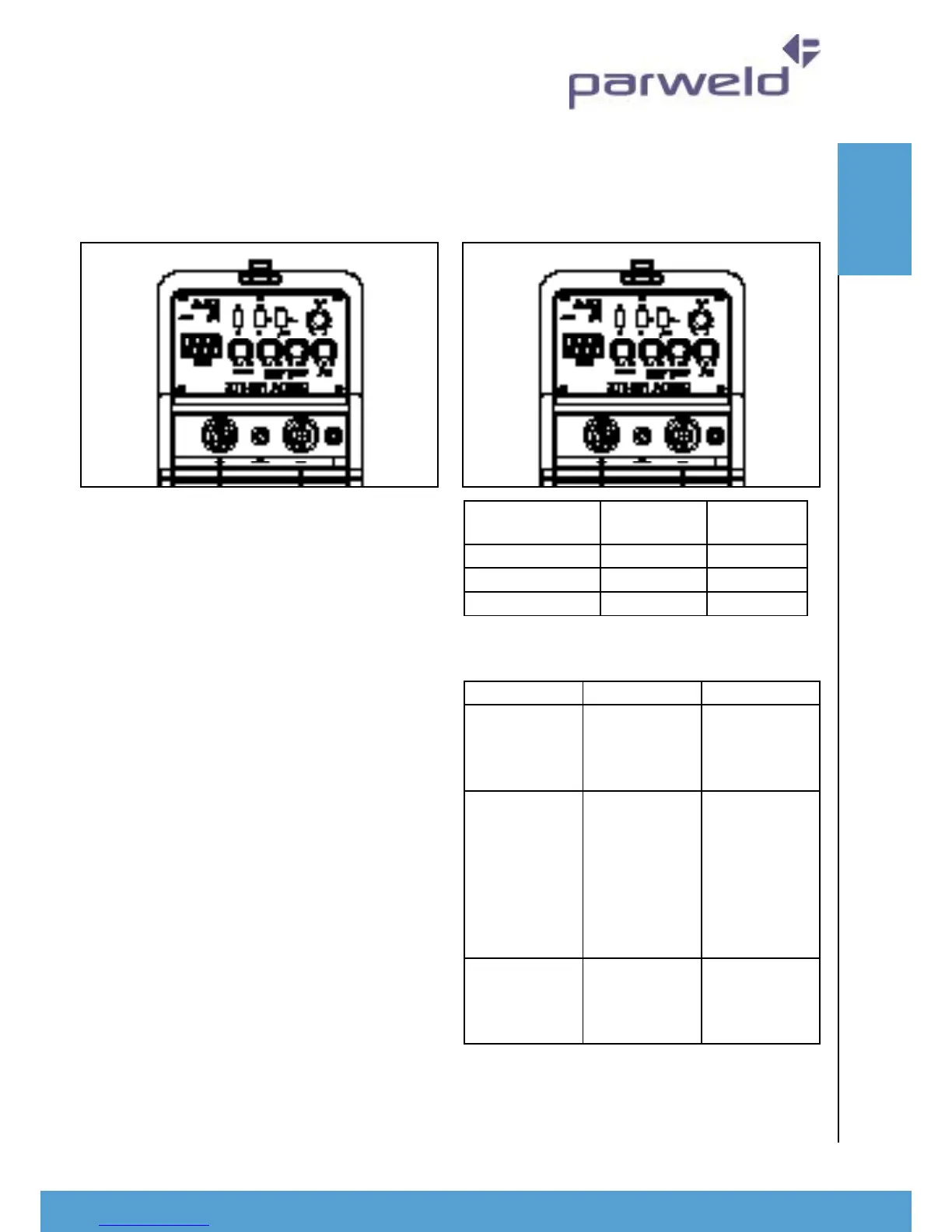
1
2
3
1
4
5
6
7
8
9 10
TIG welding guide ranges
Electrode
diameter
AC current
(amps)
DC current
(amps)
0.040” (1.0mm) 15-30 20-60
1/16” (1.6mm) 60-120 75-150
3/32” (2.4mm) 100-180 150-250
Tungsten electrode types
Type Application Colour
Thoriated 2% DC welding of
mild steel,
Stainless steel
and Copper
Red
Ceriated 2% DC welding
of mild steel,
Stainless steel,
Copper
AC welding of
aluminium,
magnesium and
their alloys
Grey
Zirconiated AC welding of
aluminium,
magnesium and
their alloys
White
Guide for selecng ller wire diameter
11
 Loading...
Loading...