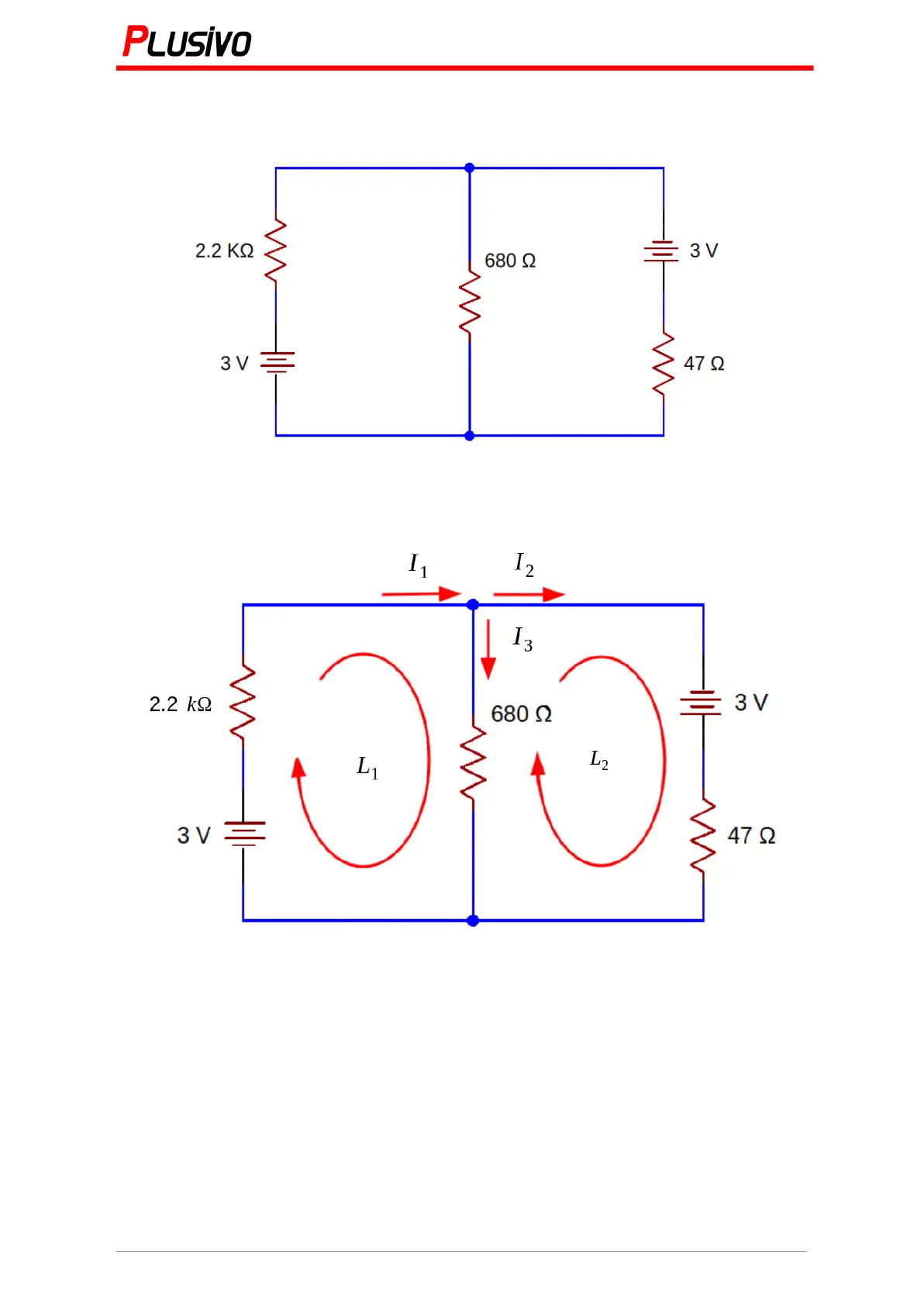
6.3.3 Example
Calculate the voltage around the resistors.
In this case, we are going to use Kirchhoff's law, we need to suppose the paths for
the current to use Kirchhoff's current law, and we need to suppose two loops to use
Kirchhoff's voltage law.
To use Kirchhoff's voltage law, we need to know some rules, for example, in if the
𝐿
1
loop passes the battery from - to + we write it in the equation (+3 V), but if the loop passes
the battery from + to - we write it in the equation (-3 V). Let us take 2.2 resistor as an
𝑘Ω
example, if the loop passes the resistor in the same direction with the current we write it
, but if the loop passes the resistor in the opposite direction with the current
− 2. 2 𝑘Ω · 𝐼
1
( )
we write it ( ).
+ 2. 2 𝑘Ω · 𝐼
1
We get this equation from .
𝐿
1
Equation 1:
3 𝑉 − (𝐼
1
· 2. 2 𝑘Ω) − (𝐼
3
· 680 Ω) = 0 𝑉
 Loading...
Loading...