22 Rockwell Automation Publication PFLEX-AP005A-EN-P - October 2010
Chapter 1 Drive Selection Considerations
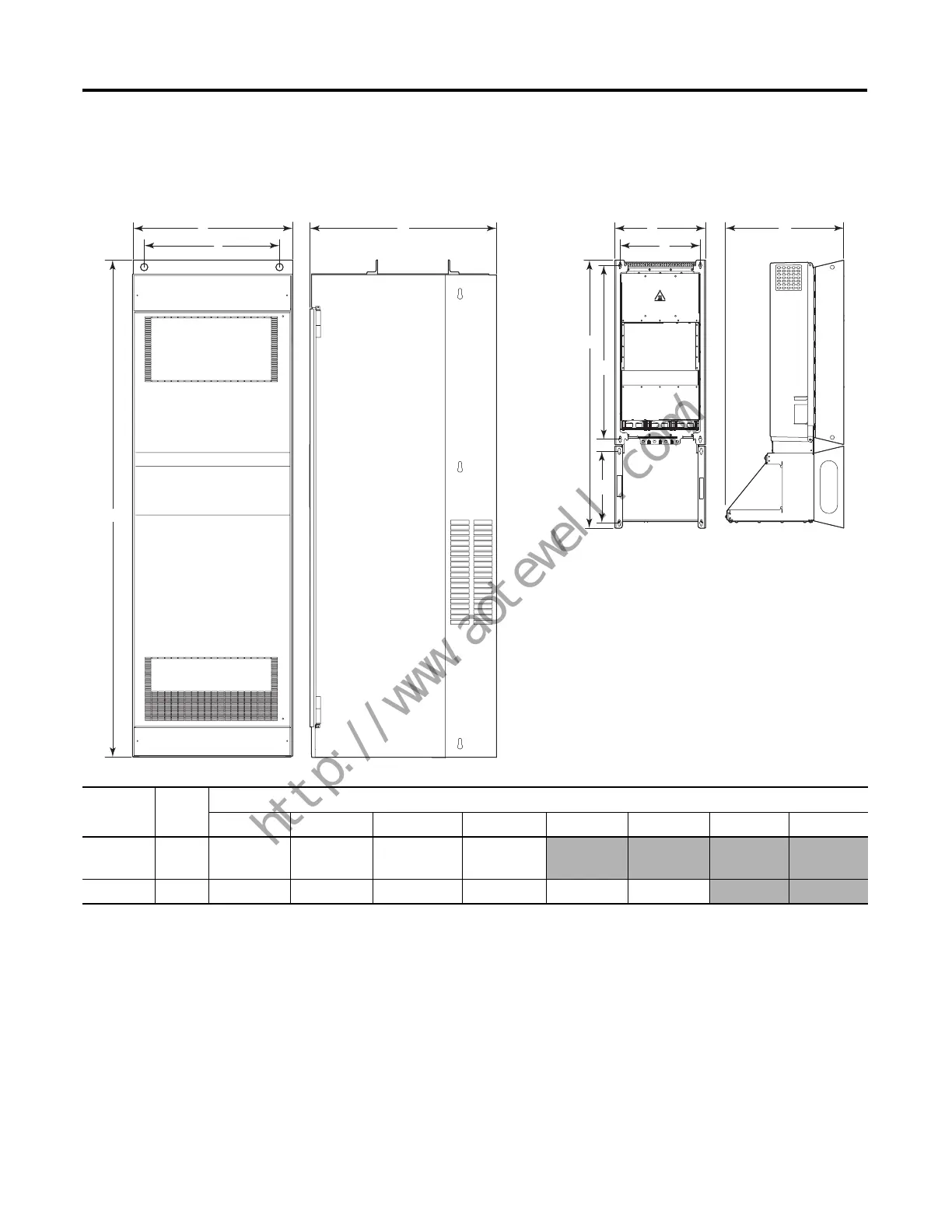
Figure 10 - PowerFlex 700 Frames 8 & 9 (IP20) to PowerFlex 750-Series Frame 7 (IP20)
Dimensions mm (in.)
Drive Frame A B C D E F G H
700 8 & 9 757.7 (29.83) —
889.0 (35.0)
(1)
1016.0 (40.0)
(2)
2373.9 (93.46)
750-Series 7 430.0 (16.93) 380.0 (14.96) 561.0 (22.08)
1271.0 (50.04)
825.0 (32.48) 339.2 (13.35)
(1) For PowerFlex 700 drive catalog numbers 20Bx365…20Bx481.
(2) For PowerFlex 700 drive catalog numbers 20Bx535…20Bx730.
C
A
B
E
D
F
C
A
B
D
PowerFlex 700 Frames 8 & 9
(IP20, NEMA/UL Type 1)
PowerFlex 750-Series Frame 7
(IP20, NEMA/UL Type 1)

 Loading...
Loading...











