Cycle and reaction times
5.2 Cycle time
CPU 31xC and CPU 31x, Technical data
5-8 Manual, Edition 08/2004, A5E00105475-05
Extension of the cycle time due to error
Table 5-8 Cycle time extension as a result of errors
Type of error Programming errors I/O access errors
312C 600 μs 600 μs
313C 400 μs 400 μs
313C2 400 μs 400 μs
314C-2 400 μs 400 μs
312 600 μs 600 μs
314 400 μs 400 μs
315 400 μs 400 μs
317 100 μs 100 μs
The interrupt OB processing time must be added to this extended time. The times required
for multiple nested interrupt/error OBs are added accordingly.
5.2.3 Different cycle times
Overview
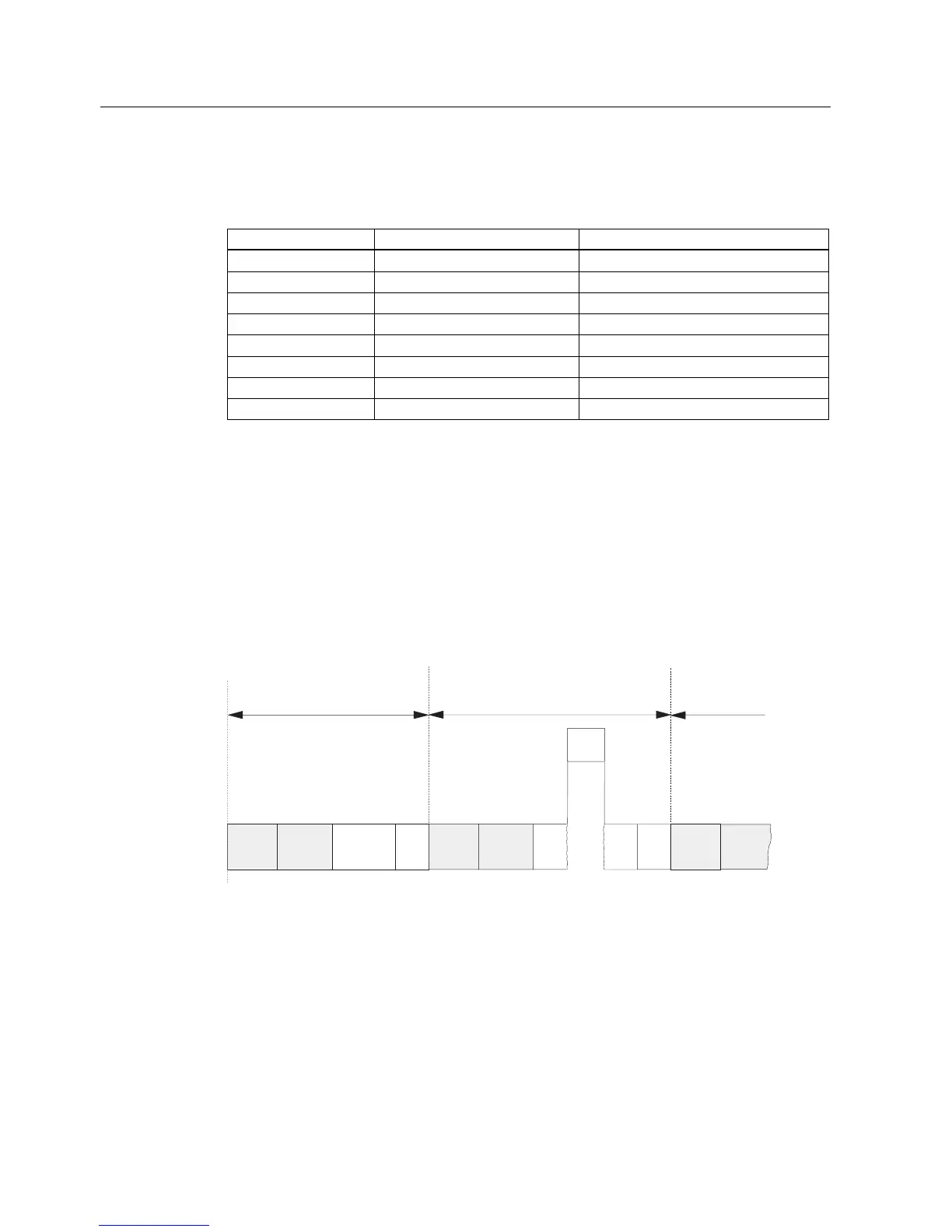
The cycle time (T
cyc
) length is not the same in every cycle. The figure below shows different
cycle times T
cyc1
and T
cyc2
. T
cyc2
is longer than T
cyc1
, because the cyclically executed OB1 is
interrupted by a time-of-day interrupt OB (here: OB 10).
Current cycle
Next cycle
OB10
T
cyc 1
cyc 2
T
Cycle after next
Updating
PIO
Updating
PII
Updating
PIO
Updating
PII
Updating
PIO
Updating
PII
OB1
OB1 OB1
CCP CCP
Block processing times may fluctuate
Fluctuation of the block processing time (e.g. OB 1) may also be a factor causing cycle time
fluctuation, due to:
• conditional instructions,
• conditional block calls,
• different program paths,
• loops etc.

 Loading...
Loading...