6.27 Convolution
Convolution algorithms in the LBA-PC may take on a number of forms, some of which might not fit the
exact description that is to follow. In the broadest sense, convolution refers to a general-purpose
algorithm that can be used in performing a variety of area process transformations. One such general-
purpose algorithm will be described here.
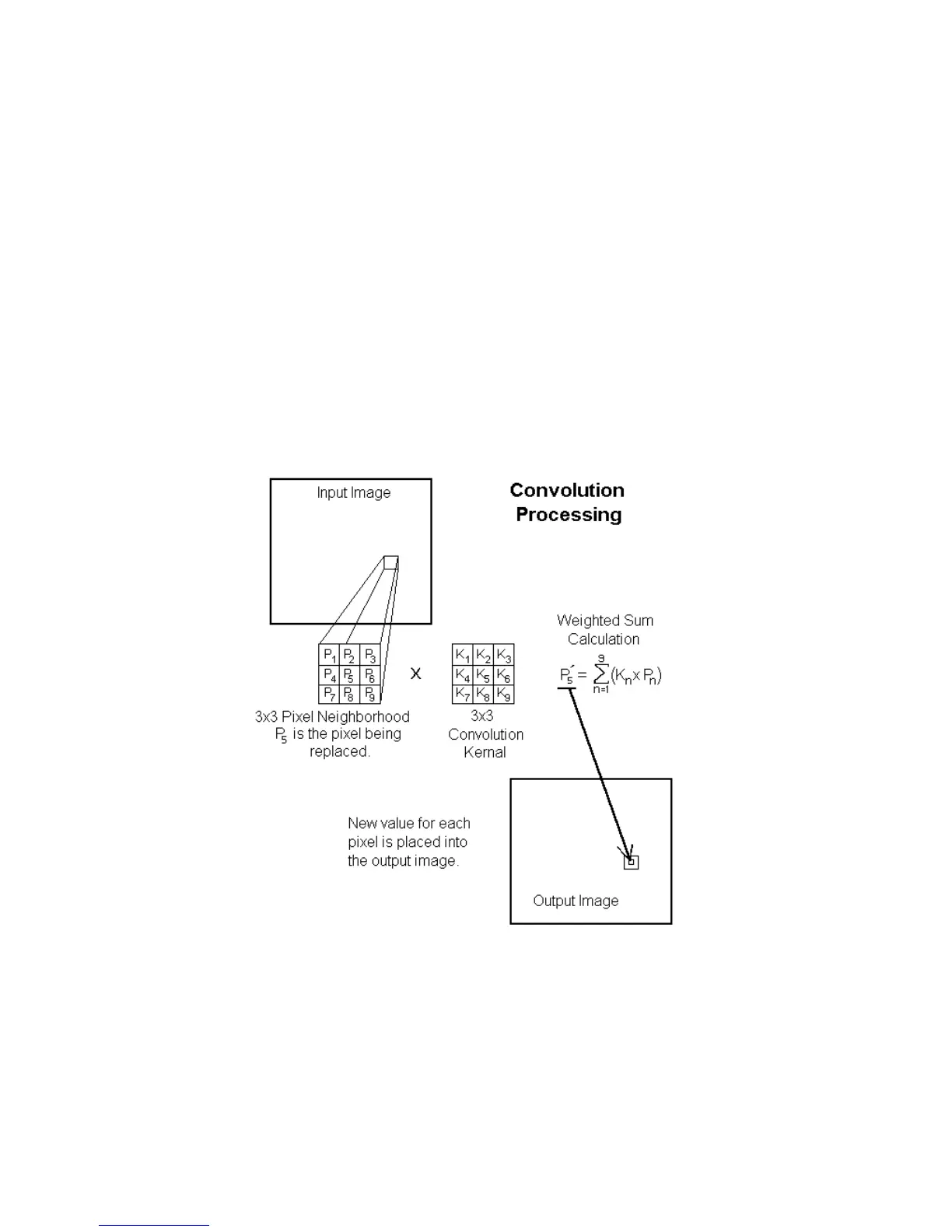
For the purpose of this description, the best way to understand a convolution is to think of it is a
weighted summation process. Each pixel in an image becomes the center element in a neighborhood of
pixels. A similarly dimensioned convolution kernel multiplies each pixel in the neighborhood. The
sum of these products is then used to replace the center pixel.
Each element of the convolution kernel is a weighting factor called a convolution coefficient. The
size and arrangement of the convolution coefficients in a convolution kernel determine the type of area
transform that will be applied to the image data.
The figure below shows a 3x3 neighborhood and convolution kernel.
Figure 58
The tables below give the convolution coefficients (K values) for some of the included low-pass spatial
filters.
Operator’s Manual LBA-PC
146
 Loading...
Loading...